Compute Indicated Airspeed for Pitot-Static Airspeed Indicator
This example shows how to compute the indicated airspeed from true airspeed for a pitot-static airspeed indicator using the Aerospace Toolbox correctairspeed function.
Provide a True Airspeed
True airspeed is the airspeed that we would read ideally (and the airspeed value easily calculated using scripts or functions).
trueAirspeedInKTS =  72;
72;Calculate the Calibrated Airspeed
To calculate the calibrated airspeed, you adjust the true airspeed for errors introduced through the pitot-static airspeed indicators used to determine airspeed. These measurement errors are density error, compressibility error, and calibration error. The correctairspeed function can apply the density error and compressibility error computing calibrated airspeed from true airspeed.
Density Error
An airspeed indicator reads lower than true airspeed at higher altitudes. This is due to lower air density at altitude. When the difference or error in air density at altitude from air density on a standard day at sea level is applied to true airspeed, the result is in equivalent airspeed (EAS). Equivalent airspeed is true airspeed modified with the changes in atmospheric density that affect the airspeed indicator.
Compressibility Error
Air has a limited ability to resist compression. This ability is reduced by an increase in altitude, an increase in speed, or a restricted volume. Within the airspeed indicator, there is a certain amount of trapped air. When flying at high altitudes and higher airspeeds, calibrated airspeed (CAS) is always higher than equivalent airspeed. Calibrated airspeed is equivalent airspeed modified with compressibility effects of air, which affect the airspeed indicator.
altitudeInFt =500; altitude = convlength(altitudeInFt,'ft','m'); [~, speedOfSound, pressure0, ~] = atmoscoesa(altitude); calibratedAirspeedInKTS = correctairspeed(trueAirspeedInKTS, speedOfSound, pressure0, 'TAS', 'CAS');
Adjust to Indicated Airspeed for Pitot-Static Airspeed Indicator
Calibration error of the pitot-static airspeed indicator is the last adjustment to the airspeed value. The adjustment results in an indicated airspeed displayed on the airspeed indicator in the cockpit.
Calibration Error
The airspeed indicator has static vent(s) to maintain a pressure equal to atmospheric pressure inside the instrument. Position and placement of the static vent, angle of attack, and velocity of the aircraft determines the pressure inside the airspeed indicator and the amount of calibration error of the airspeed indicator. The calibration error is specific to a given aircraft design. A calibration table is usually given in the pilot operating handbook (POH) or in other aircraft specifications.
Example Calibration Tables
As an example, here is the Cessna 150M airspeed calibration table from "Pilot's Operating Handbook, Cessna 1976 150 Commuter, Cessna Model 150M", Cessna Aircraft Company, Wichita, Kansas, USA, 1976.
Calibration table for 0, 10, and 0 degrees of flap:
flaps0IAS = 40:10:140; flaps0CAS = [43 51 59 68 77 87 98 108 118 129 140]; flaps10IAS = [40:10:80 85]; flaps10CAS = [42 50 60 69 78 82]; flaps40IAS = [40:10:80 85]; flaps40CAS = [40 50 61 72 83 89]; plot(flaps0CAS,flaps0IAS,flaps10CAS,flaps10IAS,flaps40CAS,flaps40IAS) xlabel('Calibrated Airspeed (CAS) (kts)'); ylabel('Indicated Airspeed (IAS) (kts)'); title('Cessna 150M Airspeed Calibration Table'); legend ('0 degrees','10 degrees','40 degrees','Location','southeast');
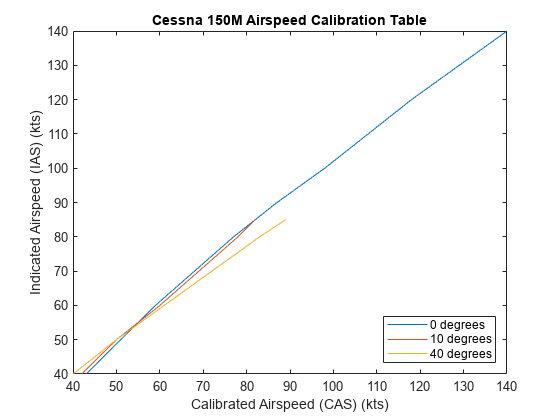
Using this calibration table, the indicated airspeed (IAS) is determined from the calibrated airspeed (CAS).
flapSetting =40; if (flapSetting == 40) tableCAS = flaps40CAS; tableIAS = flaps40IAS; elseif (flapSetting == 0) tableCAS = flaps0CAS; tableIAS = flaps0IAS; else tableCAS = flaps10CAS; tableIAS = flaps10IAS; end indicatedAirspeedInKTS = interp1(tableCAS,tableIAS,calibratedAirspeedInKTS);
Indicated airspeed is displayed on the airspeed indicator in the cockpit instrumentation.
fig = uifigure('Name','Airspeed Indicator',... 'Position',[50,650,220,220],... 'Color',[0.2667 0.2706 0.2784],'Resize','off','Visible','off'); air = uiaeroairspeed('Parent',fig,'Position',[10 10 200 200], ... 'Limits',[25 160],'ScaleColorLimits',[42,85; 47,107; 107,141; 141,145], ... 'Airspeed', indicatedAirspeedInKTS); fig.Visible = "on";
