Model a Spring in Chamber with Composite Components in the Position-Based Translational Domain
This example shows how to model a spring in a chamber by using a composite component or by modeling the chamber using Simscape™ blocks. To learn about how to model other kinds of valves, see Model a Pressure Relief Valve in the Position-Based Translational Domain and Create Equivalent Systems for Conical Poppet Valves.
Open the Model
The PositionBasedSpringChamber model compares the pressure relief valve implemented with the Spring in Chamber block to an equivalent system. Open the model.
close_system('PositionBasedSpringChamber',0); open_system('PositionBasedSpringChamber');

The Spring in Chamber block represents a fluid chamber that contains a spring between two pistons. The spring assembly can move in the casing, but remains inside the casing. The chamber contains fluid and is connected to an orifice that allows fluid to transfer in or out.
Build a Spring in a Chamber Using a Composite Component
You can construct the Spring in Chamber composite component by adding a Spring block and a Translational Mechanical Converter block connected in parallel. Connect the isothermal liquid port of the converter to the isothermal liquid port int the system with an Orifice (IL) block.
% Specify model and block paths. SubSystem = 'PositionBasedSpringChamber/Spring in Chamber1'; Spring = [SubSystem '/Spring']; Orifice = [SubSystem '/Orifice (IL)']; HsLeft = [SubSystem '/Hard Stop Left']; HsRight = [SubSystem '/Hard Stop Right']; Spacer = [SubSystem '/Maximum Distance Between B and F']; % Uncomment composite system blocks set_param(SubSystem, 'Commented', 'off'); set_param('PositionBasedSpringChamber/Translational World (PB)1', 'Commented', 'off') set_param('PositionBasedSpringChamber/Solver Configuration1', 'Commented', 'off') set_param('PositionBasedSpringChamber/Knob1', 'Commented', 'off') set_param('PositionBasedSpringChamber/Conical Poppet Valve1', 'Commented', 'off') set_param('PositionBasedSpringChamber/Reservoir (IL)1', 'Commented', 'off') set_param('PositionBasedSpringChamber/Pressure Source (IL)1', 'Commented', 'off') set_param('PositionBasedSpringChamber/PS Ramp1', 'Commented', 'off') % Open the model open_system(SubSystem) % Add Spring PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Spring','Add'); % Add Translational Mechanical Converter PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Converter','Add'); % Add Orifice PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Orifice','Add'); % Connect Spring PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Spring','Connect'); % Connect Orifice PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Orifice','Connect'); % Connect Converter PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Converter','Connect');
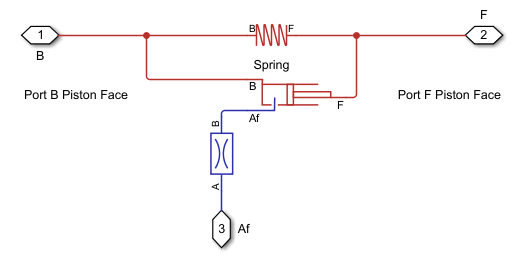
The image above shows a Simscape model that is equivalent to the Spring in Chamber composite component. This model does not restrict motion, and the composite component has both lower and upper length restrictions on the spring. At the low end, the spring in the Simscape model cannot be compressed below a length of zero, because the piston heads would collide. At the upper end, the spring cannot exceed the length of the casing containing the spring, piston, and fluid chamber system.
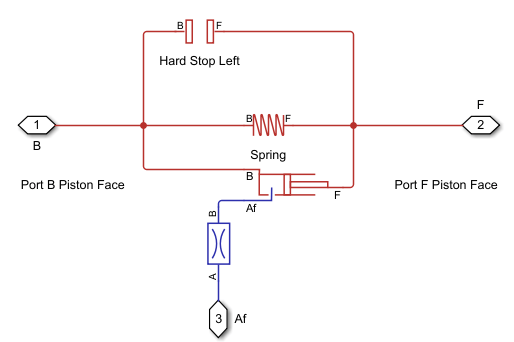
In the PositionBasedSpringChamber model, open the Spring In Chamber 1 subsystem. Add a Hard Stop Left block and connect its B and F ports to the B and F Inport and Outport blocks, respectively. This configuration prevents the spring from being compressed to a length less than zero.
PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Hardstop Left','Add');
To model both contraction and expansion hard stops, delete the connections to the Inport and Outport blocks and add a Spacer block and another Hard Stop block and connect them as shown below. The Length initial target of the Spacer block corresponds to the maximum size allowed by the component casing. The hard stop prevents the Spring block from extending beyond the specified maximum length.
% Delete Hard Stop F Connection HsPortHandles = get_param(HsLeft, 'PortHandles'); line_handle = get_param(HsPortHandles.RConn, 'Line'); delete_line(line_handle); % Add Spacer PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Spacer','Add'); % Add Hard Stop for Extension PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Hardstop Right','Add'); % Connect Hard Stops PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Hard stops','Connect'); % Connect Spacer PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Spacer','Connect'); % Connect Hard Stop Assembly to Spring and Chamber PositionBasedSpringChamberBuildSystem('Assembly','Connect');
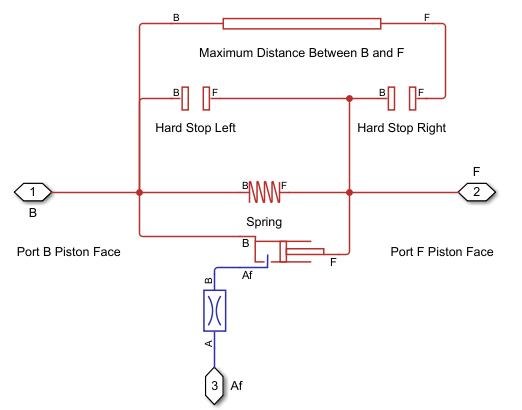
This model is equivalent to the composite component.
open_system('PositionBasedSpringChamber');Set Parameter Values
Set these parameters on the blocks in the Spring in Chamber1 subsystem.
Parameterization in Spring in Chamber Composite Component Block Parameter | Equivalent System Block | Equivalent System Parameter |
Spring stiffness parameter set to | Spring block | Spring stiffness to |
Cross-sectional area at ports Af and Bf parameter set to | Orifice block | Cross-sectional area at ports Af and Bf to |
Upper bound distance between F and B parameter set to | Space block, named | Length to |
Set the parameter values manually or by entering this code at the Command Window.
set_param(Spacer, 'length', '80', 'length_unit', 'mm', 'length_specify', 'on', 'length_priority', 'High'); %mm set_param(Spring, 'stiffness', '20000', 'stiffness_unit', 'N/m'); % N/m set_param(Orifice, 'area', '0.01', 'area_unit', 'm^2'); % m^2
Initialize the Model
To run the model, you must set initial targets for the blocks, because there is not enough information for the simulation to solve. Open the Hard Stop Left block and set the Gap length initial target to 45 mm. Set the Hard Stop Right block Gap length initial target to 35 mm. Open the Spring block and set the Length initial target to 45 mm and the Force initial target to 100 N. This value is the spring preload that balances the initial force value of the Conical Poppet Valve block.
To set these parameters programmatically, enter this code at the Command Window.
% Initialize Left Hard Stop set_param(HsLeft, 'gap_length_specify', 'on'); set_param(HsLeft, 'gap_length_priority', 'high'); set_param(HsLeft, 'gap_length', '45'); set_param(HsLeft, 'gap_length_unit', 'mm'); % Initialize Right Hard Stop set_param(HsRight, 'gap_length_specify', 'on'); set_param(HsRight, 'gap_length_priority', 'high'); set_param(HsRight, 'gap_length', '35'); % 80 mm - 45 mm set_param(HsRight, 'gap_length_unit', 'mm'); % Initialize Spring set_param(Spring, 'f_specify', 'on'); set_param(Spring, 'f_priority', 'high'); set_param(Spring, 'f', '100'); set_param(Spring, 'f_unit', 'N'); set_param(Spring, 'length_specify', 'on'); set_param(Spring, 'length_priority', 'high'); set_param(Spring, 'length', '45'); set_param(Spring, 'length_unit', 'mm');
The Spring in Chamber block automatically handles some of the variable initialization based upon its block parameters. Review spring_chamber.ssc in the +PositionBasedValve library for more details.
Compare the Models
Plots and compare the behavior of the Spring in Chamber composite block and the equivalent model.
PositionBasedSpringChamberPlot
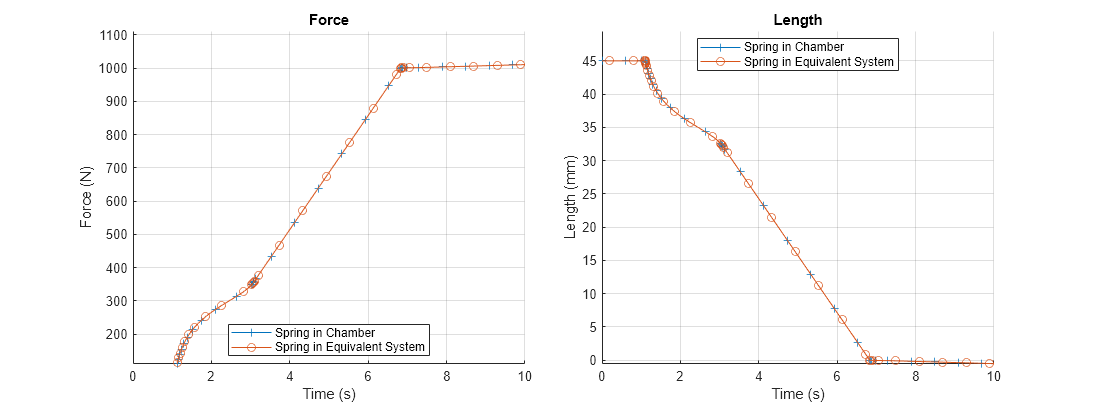
The behavior matches.
Summary
Complicated blocks can be modeled as composite components.
The initialization specification process may differ depending on the composite component architecture, but the systems will perform similarly if you initialize them correctly.