Collision Box
Libraries:
Robotics System Toolbox /
Collision Detection
Description
The Collision Box block outputs a box collision geometry that is axis-aligned with its body-fixed frame and has the origin of the body-fixed frame at the center of the box.
Examples
Open the Simulink® model. This model contains all five of the collision geometry blocks in the Collision Detection library and checks for collision between any two of the collision geometries. Note that the Collision Mesh block uses vertices from the exampleMeshVertices MAT file. The model loads the exampleMeshVertices MAT file when you open the model by using the PreLoadFcn callback.
model = "CollisionCheckingBetweenGeometries.slx";
open_system(model)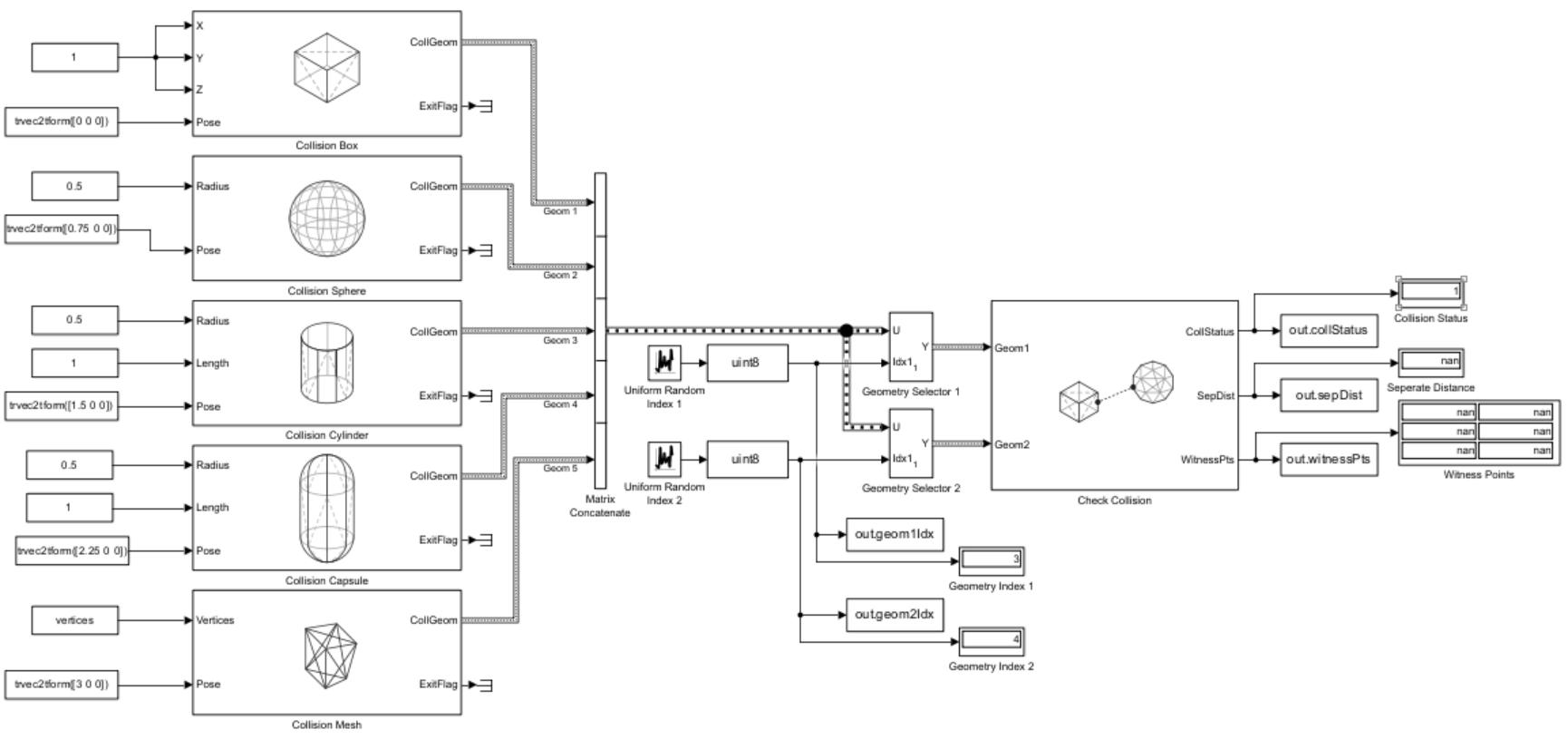
Simulate the model.
out = sim("CollisionCheckingBetweenGeometries.slx")out =
Simulink.SimulationOutput:
collStatus: [1x1 timeseries]
geom1Idx: [1x1 timeseries]
geom2Idx: [1x1 timeseries]
logsout: [1x1 Simulink.SimulationData.Dataset]
sepDist: [1x1 timeseries]
tout: [101x1 double]
witnessPts: [1x1 timeseries]
SimulationMetadata: [1x1 Simulink.SimulationMetadata]
ErrorMessage: [0x0 char]
Get data from the simulation output.
collCheckingPairs = [out.geom1Idx.Data out.geom2Idx.Data]; collStatuses = out.collStatus.Data; sepDistances = out.sepDist.Data; witnessPoints = out.witnessPts.Data;
Ports
Input
Side length of box geometry along the x-axis, specified as a positive scalar. Units are in meters.
Side length of box geometry along the y-axis, specified as a positive scalar. Units are in meters.
Side length of box geometry along the z-axis, specified as a positive scalar. Units are in meters.
Pose of the collision geometry relative to the world frame, specified as a 4-by-4 homogeneous matrix.
Output
Collision geometry, returned as a bus.
To perform collision checking, connect this output to a Check Collision block as input.
Validity collision box dimensions, returned as an integer scalar where each digit represents the validity of a dimension:
First Digit — Validity of the x-axis length at the X port.
Second Digit — Validity of the y-axis length at the Y port.
Third Digit — Validity of the z-axis length at the Z port.
Each of these digits can be one of these values:
4— Specified dimension value is not numeric.3— Specified dimension value is not a real number.2— Specified dimension value is nonfinite.1— Specified dimension value is not positive.0— Specified dimension value is valid.
For example, if the exit flag is 230, then the
x-length of the box is nonfinite, the y-length
is not a real value, and the z-length is valid.
To validate dimensions at runtime instead, select the Enable Runtime Input Dimensions Error parameter.
Data Types: uint16
Parameters
To edit block parameters interactively, use the Property Inspector. From the Simulink® Toolstrip, on the Simulation tab, in the Prepare gallery, select Property Inspector.
Select this parameter to enable runtime validation of the collision box dimensions and return an error if X, Y, or Z is invalid.
If you clear this parameter, the block does not error during simulation, and instead uses the ExitFlag port to identify invalid box dimensions.
Code generation— Simulate model using generated C code. The first time you run a simulation, Simulink generates C code for the block. The block reuses the C code for subsequent simulations, as long as the model does not change.Interpreted execution— Simulate model using the MATLAB® interpreter. For more information, see Interpreted Execution vs. Code Generation (Simulink).
More About
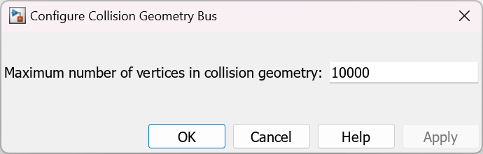
To configure the maximum number of vertices in a collision geometry block, click
Configure Collision Geometry Bus in the block mask to open the
Configure Collision Geometry Bus dialog box, and set the Maximum number of
vertices in collision geometry parameter. The default number of vertices is
10000.
Extended Capabilities
Collision Box block supports code generation with dynamic memory allocation disabled. For more information about disabling dynamic memory allocation, see Dynamic memory allocation in MATLAB functions (Simulink).
Version History
Introduced in R2025a
See Also
Objects
Blocks
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)