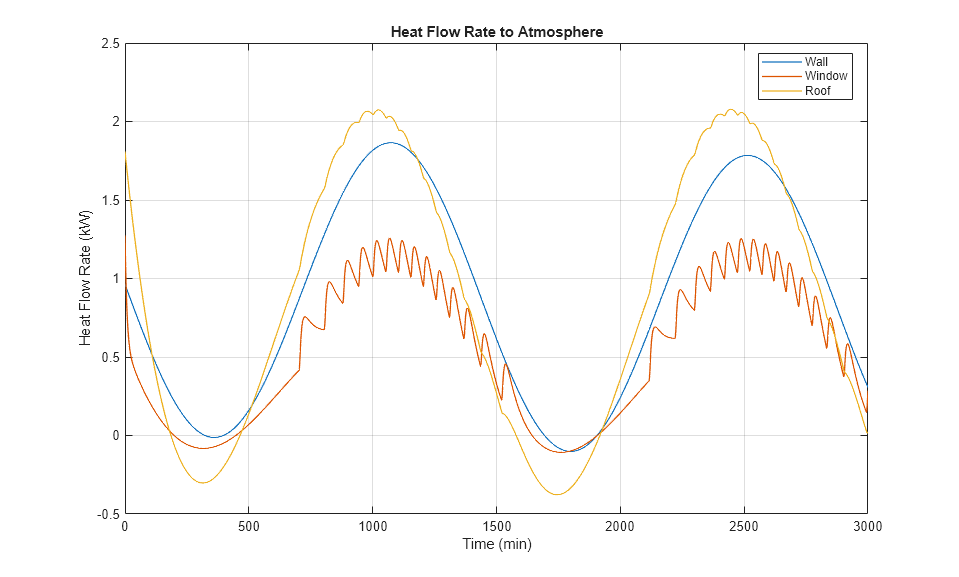
Sistema di riscaldamento domestico
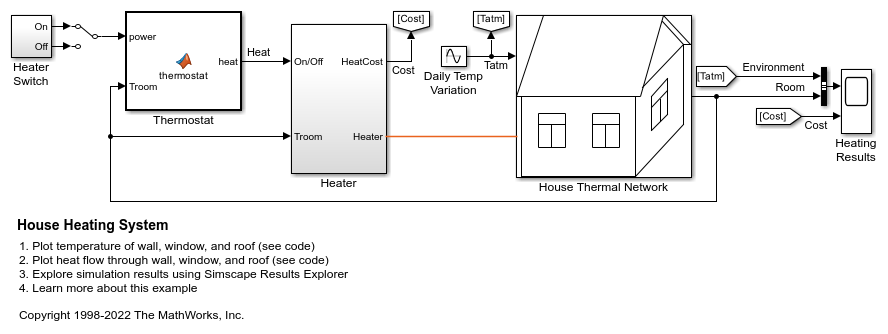
Questo esempio mostra come modellare un semplice sistema di riscaldamento domestico. Il modello contiene un riscaldatore, un termostato e una struttura dell'abitazione con quattro parti: aria interna, pareti dell'abitazione, finestre e tetto.
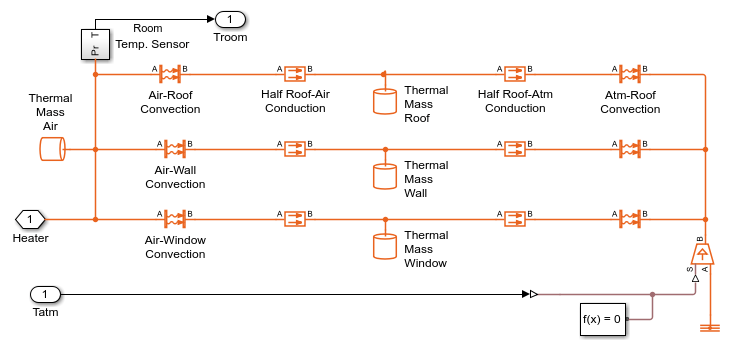
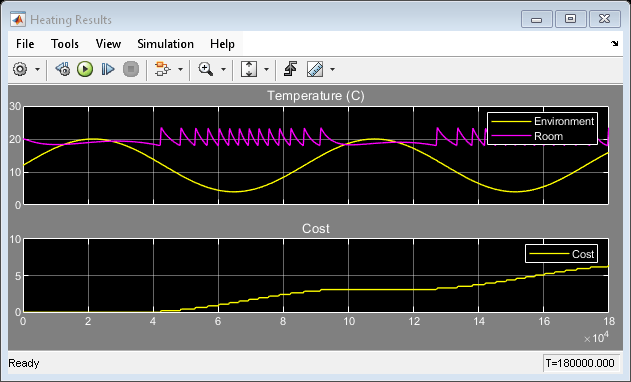
L'abitazione scambia il calore con l'ambiente attraverso le pareti, le finestre e il tetto. Ciascun percorso è simulato come una combinazione di convezione termica, conduzione termica e massa termica. Il riscaldatore inizia a pompare aria calda se la temperatura ambiente scende sotto i 18 gradi C e si spegne se la temperatura supera i 23 gradi C. La simulazione calcola il costo del riscaldamento e le temperature interne.
L'interruttore manuale consente di esaminare il comportamento del sistema con l'impianto di riscaldamento spento.
Modello
Sottosistema di rete termica domestica
Risultati di simulazione dagli Scope
Risultati di simulazione da Simscape Logging