Create Encrypted Connection to Remote Applications and Containers
If you want to create an encrypted connection between your local client machine and an application running on a remote machine, you can use SSH tunneling. Some applications transmit information without adding encryption. To access this type of applications over the internet using encryption, use SSH tunneling, also called SSH port forwarding. Doing so provides an encrypted connection between the local client machine and the remote application such as a container session. If the remote host or the local machine is protected by a firewall, you must use SSH tunnelling.
SSH Tunneling
These instructions show you how to forward a port on the client machine to a port on the
remote machine. For example, if you create a port forwarding mechanism between port
5903 on your local client machine and port 5902 on
the remote machine, all connections to localhost:5903 are automatically
forwarded to remotehost:5902, where localhost and
remotehost are the names or IP addresses of your local and remote
machines, respectively. Therefore, if you set up port 5902 on the remote
machine to allow you to access a container session, then you can access the container
session directly from localhost:5903. After you set up an SSH tunnel, all
communication between the client port and the container session is encrypted.
Using PuTTY on a Windows Client
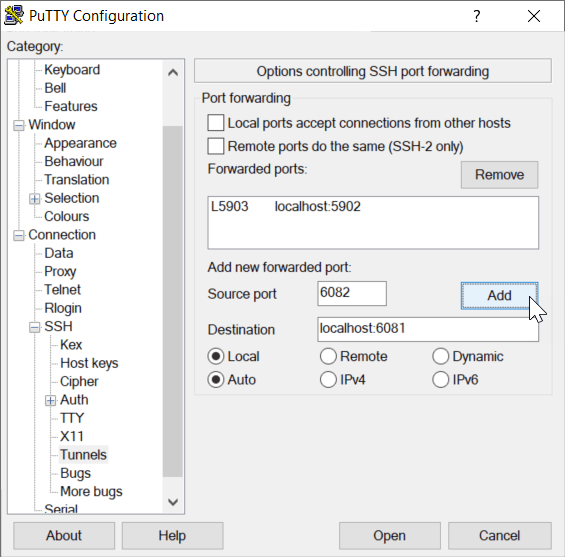
If you are using PuTTY to connect to your remote machine, add a new forwarded port
using the PuTTY Configuration dialog box. Under Category, choose
Connection > SSH >
Tunnels.
To connect via VNC, set up a tunnel from the port on your local machine to the port
on your remote instance that is connected to the container port 5901
(default VNC port).
In the Source port field, enter a free port on the local client machine starting at
5900, for example5903.In the Destination field, enter the relevant host port that you connected to container port
5901when you executed thedocker runcommand, for example,localhost:5902, and clickAdd. Note that you must uselocalhostand not the name of the host machine. This is because the Destination field interpretslocalhostas the name of the destination machine.
To connect via a web browser, set up a tunnel from the port on your local machine to
the port on your remote instance that is connected to the container port
6080 (default noVNC port).
In the Source port field, enter a free port on the client machine, for example
6082.In the Destination field, enter the relevant host port that you connected to container port
6080when you executed thedocker runcommand, for example,localhost:6081, and clickAdd. Note that you must uselocalhostand not the name of the host instance. This is because the Destination field interpretslocalhostas the name of the destination machine.
If you are using multiple containers or running a VNC server on the client machine,
you must increment the source ports on the client machine until you find a free port, for
example, 5905 or 6085.
Using a Command-Line Interface
If you are using a command-line interface to SSH tunnel from your host machine port to the remote instance that is connected to a container port, use a command of this form in your local terminal:
ssh -L clientport:localhost:hostport ubuntu@MyRemoteMachine
clientport is a free port on the client machine, for example
5903 or 6082. hostport is the
host port on the remote instance that you connected to the container port when you
executed the docker run command, for example 5902 or
6081. Note that you must use localhost and not the
name of the host instance. This is because the command interprets
localhost as the name of the host machine.
For example, use the following command:
ssh -L 5903:localhost:5902 ubuntu@MyCompanyDGX1
If you are running a VNC server on the client machine, you must increment the client
ports until you find a free port on your local machine, for example
5905 or 6085.
Connect to Container Desktop
To connect to the container desktop from your local machine, you must ensure that you
started a VNC server and mapped a container port to a port on the remote Docker® host instance when you executed the docker run, for
example:
docker run -it --rm -p 5902:5901 -p 6081:6080 --shm-size=512M mathworks/matlab:r2021a -vnc
-vnc starts the VNC server and the flag -p
maps the Docker host ports 5902 and 6081 on the remote
instance to the container ports 5901 and 6080,
respectively. For more information about running the MATLAB® container and using these flags, see MATLAB Container on Docker Hub.After you set up SSH tunneling from your local client machine to the remote Docker host instance, to connect using a web browser on your local machine, use the URL:
http://localhost:6082
Note that you must use localhost and not the name of the host
instance.
If you incremented the client port when making the tunnel, use the appropriate client
port number, for example 6085.
After you set up SSH tunneling from your local client machine to the remote Docker host instance, to connect with VNC on your local machine, use your VNC client to connect to the appropriate display port on the client, for example:
localhost:1
Note that you must use localhost and not the name of the host
instance.
If you incremented the client port when making the tunnel, use the appropriate client
display port number, for example, 5 for port
5905.