MODBUS RS485 Communication Between Client and Server Devices Using STMicroelectronics Discovery Board
This example shows how to use the Embedded Coder® Support Package for STMicroelectronics® STM32 Processors to implement a MODBUS® RS485 asynchronous, serial communication between MODBUS client and server devices. The example also shows the four modes of operation: Client Read, Client Write, Server Read, and Server Write.
Supported STMicroelectronics® Discovery Boards:
STM32L475VG-Discovery (B-L475E-IOT01A)
STM32F746G-Discovery
STM32F746I-Discovery
Introduction
Simplicity, efficient communication, and streamlined and fast data communication make MODBUS RTU RS485 one of the most widely used serial communication protocols in electronics and instrumentation industries. In this client/server architecture, the client device acts as a client and the server device acts as a server. Each device on the RS485 network is referenced by a unique 8-bit address or identifier.
This example shows the capabilities of the MODBUS RS485 protocol using two STM32L475VG Discovery (B-L475E-IOT01A) boards acting as client and server, with the MODBUS Client model deployed on the former and the MODBUS Server model deployed on the latter.
The example also deals with utilizing different modes of operation for the client and server device.
Client Read: client device reads data from server device register(s) over RS485 network
Client Write: client device writes data to server device register(s) over RS485 network
Server Read: server device reads data from the server device registers over RS485 network
Server Write: server device writes data to the server device registers over RS485 network
This table categories the different server device registers referenced by the MODBUS client and server devices.
Register Type | Register Size | Allowed client Operation on Register ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Coil | 1-bit | Read and Write Discrete Input | 1-bit | Read Holding Register | 16-bit | Read and Write Input Register | 16-bit | Read
Prerequisites
We recommend that you complete the Getting Started with Embedded Coder Support Package for STMicroelectronics Discovery Boards example.
Required Hardware
STM32L475VG Discovery (B-L475E-IOT01A) boards
This example uses one STM32L475VG Discovery (B-L475E-IOT01A) board as a client and another STM32L475VG Discovery (B-L475E-IOT01A) board as a server. You can use any of the STMicroelectronics Discovery boards from the list of suggested boards.
Two micro USB cables
Two RS485 shields
Dependencies
Implementing this example requires you to successfully deploy these Simulink® models on each of the supported STMicroelectronics Discovery boards:
Simulink Model Name | Deployed Hardware | Purpose ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 1. stm32l475vg_modbus_server | First of the two STMicroelectronics Discovery board | Behaves as a server device 2. stm32l475vg_modbus_client | Second of the two STMicroelectronics Discovery board | Behaves as a client device
Task 1: Connection Setup
The MODBUS client and server devices must be connected on the same RS485 network for successful communication.
Task 2: Configure Client Model and Calibrate Parameters
This support package provides a preconfigured model for the MODBUS Client.
To open this model, run this command at the MATLAB® Command Window:
open_system('stm32l475vg_modbus_client');
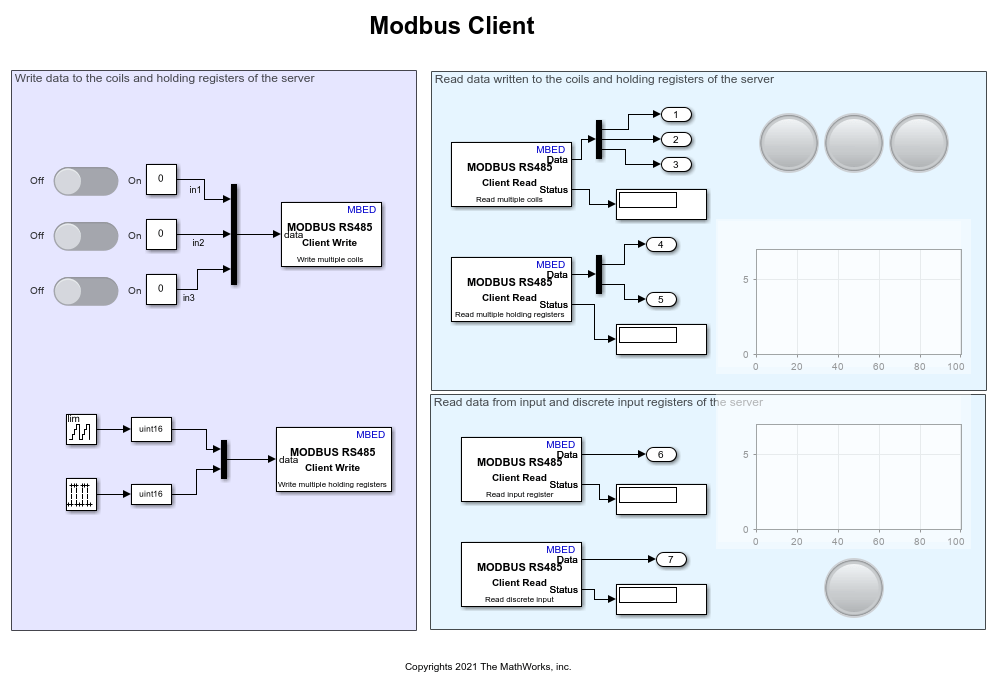
The Simulink model for the client can be divided into two parts, Write to Server and Read from Server, based on the type of operation the client can perform on the server device registers. The default values for the Simulink client model are preconfigured in this example depending on the server register size and the allowed client operations.
MODBUS Client Configuration for Write to Server Mode of Operation
The client write operation is valid on coil and holding registers. This example uses two MODBUS RS485 Client Write blocks to implement the write operation on the coil registers and the holding registers, respectively.
To perform the 1-bit write operation on the coil registers, change the position of the slider switches. The On position depicts that data 1 is written on these registers, whereas the Off position depicts that data 0 is written on these registers. Three slider switches are used in this model, whose output is multiplexed and fed as an input to one of the MODBUS RS485 Client Write blocks.
You can configure the following parameters to write data from the slider switches to the coil registers:
Enter the unique 8-bit server address of the identifier in the server address parameter. In this model, it is configured as
1.Select the Write Multiple Coils option in the Function parameter.
To notify the client to write data to three coil registers, specify the address of the first coil register in the Coil Address parameter. The default value is
0.Enter
3in the Number of Coils parameter.
Similarly, to perform the 16-bit client write operation on the holding registers, this example uses a counter that counts values from 0 to 255. The output from the free-running counter is fed as an input to the second MODBUS RS485 Client Write block.
You can configure the following parameters to write data from the free-running counter to the holding registers:
Enter the unique 8-bit server address of the identifier in the server address parameter. In this model, it is configured as
1.Select the Write Multiple Holding registers option in the Function parameter.
To notify the client to write data to the holding registers, specify the address of the first coil register in the Holding Register Address parameter. The default value is
0.Enter
2in the Number of Holding registers parameter.
MODBUS Client Configuration for Read from Server Mode of Operation
The client read operation is valid on all the server device registers (coil, holding, discrete input, and input). Four MODBUS RS485 Client Read blocks are used to implement the read operation on input and discrete input registers, respectively.
A 1-bit pulse generator is used to write data to the discrete input registers. The data read from the discrete input registers is available on the data port of the MODBUS Client Read block for the discrete input register. This data is valid only if the status port value is 0, indicating a successful read operation and the presence of valid data on its data port. A lamp indicator is used to signify the 1-bit read from the discrete input register.
You can configure the following parameters to read 1-bit pulse generator data from the discrete input register:
Enter the unique 8-bit server address of the identifier in the server address parameter. In this model, it is configured as
1. Ensure to configure the same server address as used in the MODBUS RS485 Server Write block for the discrete input register.Select the Read Discrete input option in the Function parameter.
To notify the client to read data from one discrete input register, specify its address in the Discrete Input Address parameter. Ensure to configure the same discrete input register address as used in the MODBUS RS485 Server Write block for the discrete input register. The default value is
0.Set the Sample Time parameter.
Similarly, this example uses a free-running counter to write data to the input register. The data read from the input register is available on the data port of the MODBUS RS485 Client Read block for the input register. This data is valid only if the status port value is 0, indicating a successful read operation and the presence of valid data on its data port. A Display block is used to show the 16-bit data read from the input register.
You can configure the following parameters to read the counter data from the input register:
Enter the unique 8-bit server address of the identifier in the server address parameter. In this model, it is configured as
1. Ensure to configure the same server address as used in the MODBUS RS485 Server Write block for the input register.Select the Read Input register option in the Function parameter.
To notify the client to read data from one input register, specify its address in the Input Register Address parameter. Ensure to configure the same input register address as used in the MODBUS RS485 server Write block for the input register. The default value is
0.Set the Sample Time parameter.
You can configure the following parameters to read the data from the server coil registers:
Enter the unique 8-bit server address of the identifier in the server address parameter. In this model, it is configured as
1. Ensure to configure the same server address as used in the MODBUS RS485 client Write block for the coil register.Select the Read multiple Coils option in the Function parameter.
To notify the client to read data from three coil register, specify its address in the Coil Register Address parameter. Ensure to configure the same coil register address as used in the MODBUS RS485 client Write block for the coil register. The default value is
0.Set the Sample Time parameter.
You can configure the following parameters to read the data from the holding registers:
Enter the unique 8-bit server address of the identifier in the server address parameter. In this model, it is configured as
1. Ensure to configure the same server address as used in the MODBUS RS485 client Write block for the coil register.Select the Read multiple holding registers option in the Function parameter.
To notify the client to read data from two holding register, specify its address in the Holding Register Address parameter. Ensure to configure the same coil register address as used in the MODBUS RS485 client Write block for the holding register. The default value is
0.Set the Sample Time parameter.
Task 3: Configure Server Model and Calibrate Parameters
This support package provides a preconfigured model for the MODBUS Server.
To open this model, run this command at the MATLAB® Command Window:
open_system('stm32l475vg_modbus_server');
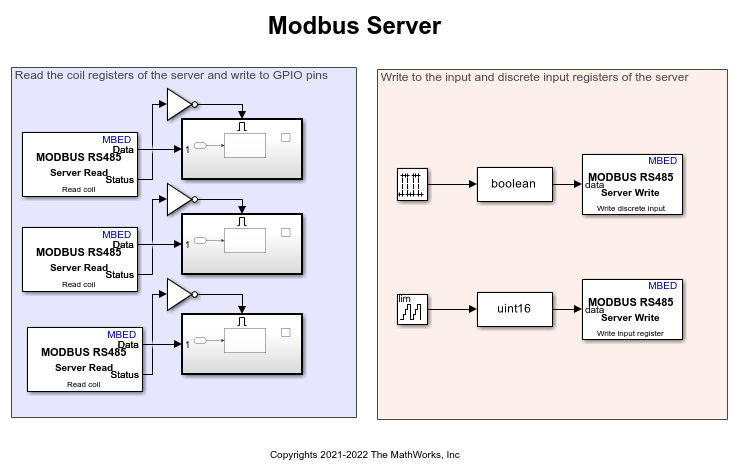
The Simulink model for the server can be divided into two parts, Write to Client and Read from Client, based on the type of operation the server device can perform on its registers. The default values for the Simulink server model are preconfigured in this example.
MODBUS Server Configuration for Write to Client Mode of Operation
This example uses two MODBUS RS485 Server Write blocks to implement the write operation on the input register and the discrete input register, respectively.
To perform the 16-bit server write operation on the input registers, this example uses a counter that counts values from 0 to 255. The output from the free-running counter is fed as an input to the MODBUS RS485 Server Write block for the input register.
You can configure the following parameters to write data from the free-running counter to the input registers:
Select the Write Input register option in the Function parameter.
To notify the client to read data from one input register, specify its address in the Input Register Address parameter. Ensure to configure the same input register address as used in the MDOBUS RS485 Client Read block for the input register. The default value is
0.
Similarly, this example uses a 1-bit pulse generator to write data to the discrete input register.
You can configure the following parameters to write 1-bit data from the pulse generator to the discrete input register:
Select the Write Discrete Input option in the Function parameter.
To notify the client to read data from one input register, specify its address in the Discrete Input Address parameter. Ensure to configure the same discrete input register address as used in the MDOBUS RS485 Client Read block for the input register. The default value is
0.
MODBUS Server Configuration for Read from Client Mode of Operation
This example uses two MODBUS RS485 Server Read blocks to implement the read operation on the coil and holding registers, respectively.
The server device reads the data written by the client device using three slider switches. This 1-bit data read from the coil registers is available on the data port of the MODBUS RS485 Server Read block for the coil registers. This data is valid only if the status port value is 0, indicating a successful read operation and the presence of valid data on its data port. 1-bit data read from the coil registers is written into GPIO PB_7, GPIO pin D8 and GPIO pin D11.
You can configure the following parameters to read 1-bit slider switch data from the coil registers:
Select the Read Coil option in the Function parameter.
To notify the server to read data from the coil registers, specify its address in the Coil Address parameter. Ensure to configure the same coil register address as used in the MDOBUS RS485 Client Write block for the coil register. The default value is
0.Set the Sample Time parameter.
Task 4: Run Model on Client and Server Devices
1. Connect the STMicroelectronics Discovery boards acting as the server device and the client device to the host computer.
2. On the Hardware tab of the stm32l475vg_modbus_client Simulink model, click Monitor & Tune.
3. On the Hardware tab of the stm32l475vg_modbus_server Simulink model, click Monitor & Tune or Build, Deploy & Start.
4. Coil register:
MODBUS RS485 Client Write block: Change the position of the slider switches to write data to the coil registers.
MODBUS RS485 Client Read block: Verify the status of the read operation on the coil registers. Observe the lamp displaying the corresponding data obtained from the coil registers. Verify that the lamp status exhibits the correct data written on the coil registers.
MODBUS RS485 Server Read block: Writing data to GPIO pins. Verify that the data written to the GPIO pins of the server exhibits the correct data written on the coil registers.
5. Holding register:
MODBUS RS485 Client Write block: The Counter and Pulse starts writing data to the holding register.
MODBUS RS485 Client Read block: Check the status of the read operation on the holding register. Observe the counter and the pulse generator values corresponding to the data obtained from the holding register and verify that the same value is displayed on the Display block.
6. Input register:
MODBUS RS485 Server Write block: The counter starts counting from the value that ranges from 0 to 255.
MODBUS RS485 Client Read block: Check the status of the read operation on the input register. Observe the counter value corresponding to the data obtained from the input register and verify that the same value is displayed on the Display block.
7. Discrete Input register:
MODBUS RS485 Server Write block: The 1-bit pulse generator starts toggling between 0 and 1.
MODBUS RS485 Client Read block: Check the status of the read operation on the discrete input register. Observe the lamp displaying the corresponding data obtained from the discrete input register. Verify that the lamp status exhibits the correct data written on the discrete input register.
Other Things to Try
Implement the MODBUS Client and Server models to read and write from and to multiple server device registers for all the register types.
Use MODBUS Server devices such as temperature sensors, humidity sensors, and so on and communicate real-time data to the STMicroelectronics Discovery board acting as the client device.
Implement a monitoring system using PID controller as the server device and the STMicroelectronics Discovery board as the client device.
Migrate to STM32CubeMX Workflow
To migrate to the STM32CubeMX workflow for STM32 processor based boards, use the MODBUS Communication Between Client and Server Devices Using STMicroelectronics Nucleo Boards example to implement the equivalent STM32CubeMX workflow.