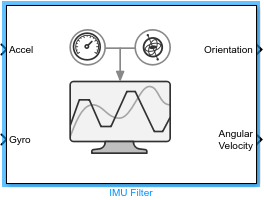
IMU Filter
Libraries:
Navigation Toolbox /
Multisensor Positioning /
Navigation Filters
Sensor Fusion and Tracking Toolbox /
Multisensor Positioning /
Navigation Filters
Description
The IMU Filter Simulink® block fuses accelerometer and gyroscope sensor data to estimate device orientation.
Examples
Compute Orientation from Recorded IMU Data
Load the rpy_9axis file into the workspace. The file contains recorded accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer sensor data from a device oscillating in pitch (around the y-axis), then yaw (around the z-axis), and then roll (around the x-axis). The file also contains the sample rate of the recording.
(Navigation Toolbox)
Ports
Input
Accelerometer readings in the sensor body coordinate system in m/s2, specified as an N-by-3 matrix of real numbers. N is the number of samples, and each row is of the form [x y z].
Data Types: single | double
Gyroscope readings in the sensor body coordinate system in rad/s, specified as an N-by-3 matrix of real numbers. N is the number of samples, and each row is of the form [x y z].
Data Types: single | double
Output
Orientation of the sensor body frame relative to the navigation frame, returned as
an M-by-4 matrix of real numbers or a
3-by-3-by-M array. Each row of the M-by-4
matrix represents the four components of a quaternion. Each
page of the 3-by-3-by-M array represents a 3-by-3 rotation
matrix.
The number of input samples N and the Decimation factor (Navigation Toolbox) parameter determine the output size M.
The output format depends on the value of the Orientation format (Navigation Toolbox) parameter.
Data Types: single | double
Angular velocity, with gyroscope bias removed, in the sensor body coordinate system in rad/s, returned as an M-by-3 matrix of real numbers.
The number of input samples N and the Decimation factor parameter determine the output size M.
Data Types: single | double
Parameters
Specify the navigation reference frame as NED (North-East-Down)
or ENU (East-North-Up).
Specify the format in which to output Orientation as
quaternion or Rotation
matrix.
quaternion— Orientation outputs an M-by-4 matrix of real numbers. Each row of the matrix represents the four components of aquaternion.Rotation matrix— Orientation outputs a 3-by-3-by-M array, in which each page of the array is a 3-by-3 rotation matrix.
The number of input samples N and the Decimation factor parameter determine the output size M.
Specify the initial process noise as a 9-by-9 matrix of real numbers. The
imufilter.defaultProcessNoise variable contains the default
value.
Specify the variance of the accelerometer signal noise in (m/s2)2 as a positive real scalar.
Specify the variance of the gyroscope signal noise in (rad/s)2 as a positive real scalar.
Specify the variance of the gyroscope offset drift in (rad/s)2 as a positive real scalar.
Specify the variance of linear acceleration noise in (m/s2)2 as a positive real scalar. The block models linear acceleration as a lowpass-filtered white noise process.
Specify the decay factor for linear acceleration drift as a scalar in the range [0 1). If linear acceleration changes quickly, set this parameter to a lower value. If linear acceleration changes slowly, set this parameter to a higher value. The block models linear acceleration drift as a lowpass-filtered white noise process.
Select the type of simulation to run from these options:
Interpreted execution— Simulate the model using the MATLAB® interpreter. This option reduces startup time, but has a slower simulation speed thanCode generation. In this mode, you can debug the source code of the block.Code generation— Simulate the model using generated C code. The first time you run a simulation in this mode, Simulink generates C code for the block. Simulink reuses the C code for subsequent simulations, as long as the model does not change. This option requires additional startup time for the initial run, but increases the speed of subsequent simulations relative toInterpreted execution.
Extended Capabilities
Usage notes and limitations:
This block also supports strict single-precision code generation.
Version History
Introduced in R2023b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)