Getting Started with URScript Execution Commands and Handback Control for Universal Robots
Overview
This example shows how to use specific functions that help you configure additional program nodes with MathWorks External Control URCap node. These functions associated with URScript commands can be used along with the functionalities provided by the urROSNode object, to connect with simulated or physical cobot using the ROS network. This example shows the functionality of the three functions executePrimaryURScriptCommand, executeSecondaryURScriptCommand, and handBackControl, which are available in the Robotics System Toolbox™ Support Package for Universal Robots UR Series Manipulators. These functions allow you to use the functionality supported by the some of the URScript commands and end-effector external URCap integration.
In this example, you can select the URSim offline simulator or a physical hardware. All the necessary files required to setup URSim are included in the support package. Refer to Install ROS Packages and Dependencies for ROS and Set Up URSim Offline Simulator for more details.
Clear all output in the live script by right-clicking anywhere in the live script and then clicking ‘Clear All Output’ or navigate to VIEW > Clear all Output.
Note: Execute the script section by section as mentioned in this example.
Required Products
Robotics System Toolbox
Robotics System Toolbox Support Package for Universal Robots UR Series Manipulators
ROS Toolbox
Load Rigid Body Tree Model
Load rigid body tree model for Universal Robot UR5e robot manipulator.
ur5e = loadrobot('universalUR5e');Select Interface and Define IP address of ROS Enabled Device and Robot
The below diagram shows the naming convention of the various IP addresses used in this example.
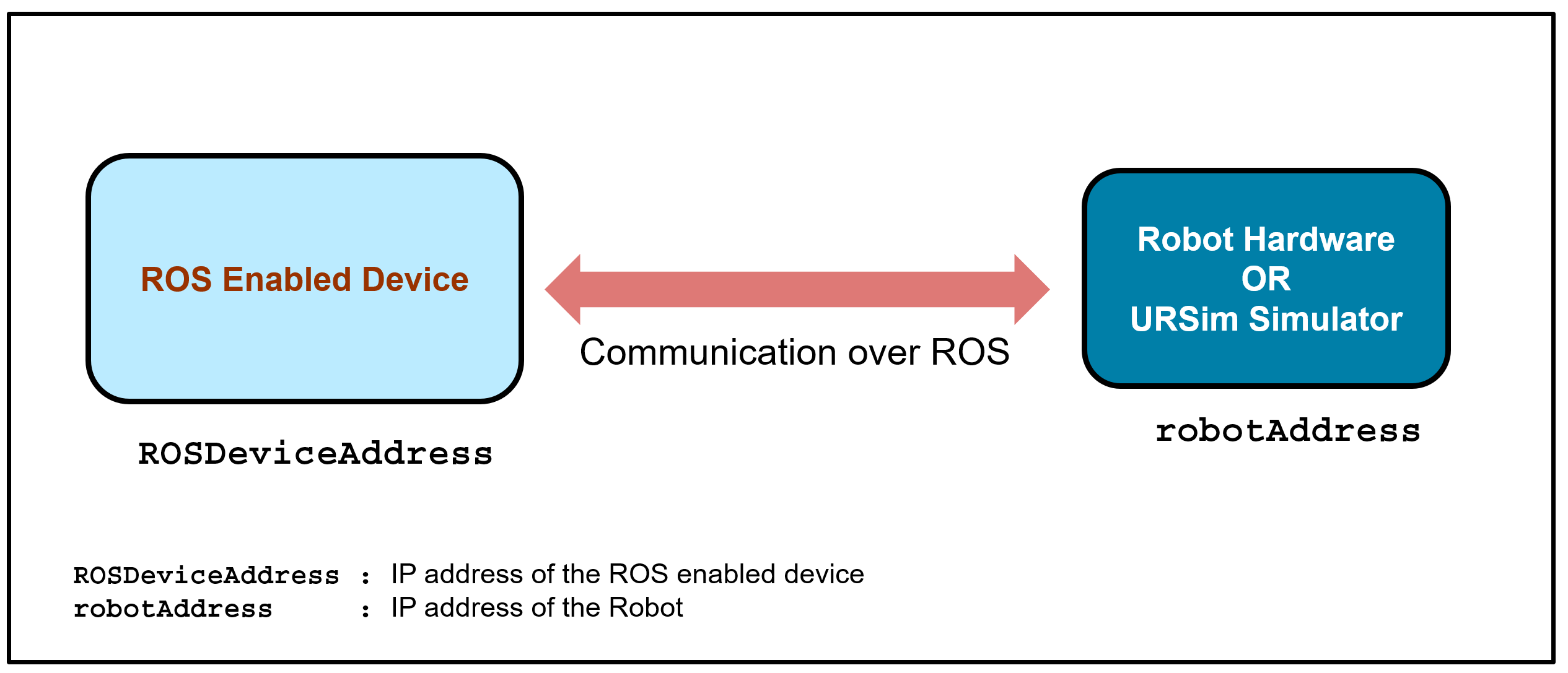
Note: The above diagram is only applicable for the URSim simulator or UR Series hardware. MATLAB® can be present inside the same ROS machine or it can also be on any external machine.
The ROSDeviceAddress is the IP address of your PC/VM where you have installed the ROS and the other required ROS drivers.
The robotAddress is the IP address of your robot hardware or simulated robot(in case of URSim). If you have installed URSim in the same ROS device, then the robot IP will be the same as the local host IP i.e. '127.0.0.1'. Hence robotIPAddress for URSim will be 127.0.0.1.
interface =  "URSim"
"URSim"interface = "URSim"
If you select URSim:
Launch URSim with the desktop shortcut of a desired robot model (by default this example uses UR5e).
Ensure that the external control program is configured and loaded in the program section. Refer to Install MATLAB URCap for External Control for more details. Also, ensure that you have configured the "Host IP" parameter value as the IP address of your ROS machine inside the URCap installation tab of URSim.
Specify the
ROSDeviceAddressandrobotAddressas described in above diagram.
If you select Hardware:
Ensure that the external control program is configured and loaded in the program section. Refer to Install MATLAB URCap for External Control for more details.
Ensure that the polyscope is in remote control mode. You can set this by pressing a teach pendant icon with 'Local' text on the top right corner of the teach pendant.
Specify the
ROSDeviceAddressandrobotAddressas described in above diagram.
Specify the below address parameters based on the above given diagram.
% IP of ROS enabled machine ROSDeviceAddress = '192.168.92.132'; % IP of the robot (in case of URSim, this IP address will be 127.0.0.1) robotAddress = '192.168.1.10';
Generate Automatic Launch Script and Transfer It to ROS Host Computer
Provide parameters of the host machine with ROS.
Note: If you have not yet installed the required ROS drivers in your ROS machine then follow Install ROS Packages and Dependencies for ROS document to setup a catkin workspace.
username = 'user'; password = 'password'; ROSFolder = '/opt/ros/melodic'; WorkSpaceFolder = '~/ur_ws';
Connect to ROS device.
device = rosdevice(ROSDeviceAddress,username,password); device.ROSFolder = ROSFolder;
Generate launch script and transfer it to ROS host computer.
generateAndTransferLaunchScriptForHybridWorkflow(device,WorkSpaceFolder,interface,robotAddress);
Launch the required nodes if the ROS core is not running.
if ~isCoreRunning(device) w = strsplit(system(device,'who')); displayNum = cell2mat(w(2)); system(device,['export SVGA_VGPU10=0; ' ... 'export DISPLAY=' displayNum '.0; ' ... './launchURHybrid.sh &']); end
Optional: Launch Required ROS Driver Manually
Manually launch the required ROS driver in your ROS machine
Follow these instructions to manually launch the required ROS drivers in the ROS enabled machine.
Step 1
Open the terminal in your ROS machine and cd to the catkin workspace you built for the UR ROS drivers (for example, "cd ~/ur_ws").
Step 2
Source the setup file using the command,
source devel/setup.bash
Now, follow the next setup based on your interface selection.
Step 3
Export the ROS_IP and ROS_MASTER_URI by running below command inside the same terminal.
Replace the ROSDeviceAddress in below command by its value. (Use direct value here and not the char array, that is, export ROS_IP=192.168.92.132).
export ROS_IP=<ROSDeviceAddress> export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://$ROS_IP:11311
Step 4
For URSim:
This step assumes that you have opened the URSim and also configured the external control program node.
If you are using URSim then use the below-given command to launch the required ROS drivers. (As you have installed URSim in the same ROS machine then robot_ip will be localhost 127.0.0.1).
roslaunch ur_robot_driver ur5e_bringup.launch robot_ip:=127.0.0.1
For UR hardware:
This step assumes that you have configured the external control program node on the teach pendant and that also robot is in remote control mode.
If you are using UR hardware then use below given command to launch the required ROS drivers. Use the defined robotAddress as a value to robot_ip in the below command.
Note: Directly use the robot address as a numeric value and do not use a char array to assign value to the robot_ip.
roslaunch ur_robot_driver ur5e_bringup.launch robot_ip:=<robotAddress>
Initialize the urROSNode Interface
ur = urROSNode(device.DeviceAddress,'RigidBodyTree',ur5e)
The urROSNode object has several useful properties. The RigidBodyTree property contains the rigid body tree model, which is being used internally for trajectory generation and motion planning. You can use this rigid body tree model to visualize the robot manipulator in MATLAB.
The JointStateTopic and FollowJoinTrajectoryAction properties consist of ROS message and ROS action respectively, which are used to communicate with the cobot via the ROS network.
The EndEffectorName is the name of the frame of rigid body tree model which is considered as the end effector of the cobot.
Run executePrimaryScriptCommand
The executePrimaryURScriptCommand function is used to execute the primary URScript command over ROS interface.
Execute the below command and verify that the robot moves to the desired joint configuration.
ur.executePrimaryURScriptCommand("movej([0, -1.57, 0,-1.57, 0, 0])");
Run executeSecondaryScriptCommand
The executeSecondaryURScriptCommand function is used to execute the command that is wrapped in a secondary URScript command over ROS interface.
Execute the below command and verify that digital input pin 0 is set "TRUE" state. You can verify this in I/O tab of your teach pendent.
commandString = "set_digital_out(0, True)";
ur.executeSecondaryURScriptCommand(commandString);
Run handBackControl
The handBackControl function is used to execute the hand_back_control ROS service, which takes back the program control from the "External Control" program node of the UR-Program to execute the subsequent program nodes.
To understand the functionality of handBackControl function, you need to create another sample program, as shown below, on the Teach Pendant.

After creating this program, restart the program again by using the Play button from the Teach Pendant.
In the above program, the Popup command is added for the demo purpose only. You can also use your external URCaps for performing its operations along with the motion planning using our tools.
Run the below command.
ur.handBackControl();
You can see that node-3 is getting executed and the popup window is shown. You can press Continue and the program execution will then go to node-4.
Kill the rosmaster and Gazebo
clear ur system(device,'killall -9 rosmaster');