Overview of Signal Loading Techniques
Simulink® provides several techniques for importing signal data into a model. Each of the signal data loading techniques uses blocks to represent signal data sources visually.
For additional details about which technique to use to meet specific modeling requirements, see Comparison of Techniques.
Source Blocks
You can add a source block, such as a Sine Wave block, to generate
signals to input to another block. To specify how to generate the signal, use the Block
Parameters dialog box. For example, in the Sine Wave Block Parameters dialog
box, you can specify the sim function to use and time-based or
sample-based data.

The output data types of source blocks vary. For example, a Sine Wave block outputs a vector of real doubles.
For an example of using a source block, see Open Models.
Recommended Uses
Do initial prototyping in a model, when the generated signal data serves your modeling requirements
Avoid creating the data manually.
Reduce memory consumption. Source blocks do not store signal data.
Make the kind of signal data visually clear in the model.
Limitations
Source blocks generate signals based on a predefined algorithm. To use actual data from an external source or to test a model without having to modify the model, use a different signal loading technique.
Root-Level Input Ports
You can import signal data from a workspace and apply it to a root-level input port using one of these blocks:
The root-level input ports load external inputs from the MATLAB® (base), model, or mask workspace. These blocks import data from the workspace
based on the value of the Configuration Parameters > Data Import/Export > Input parameter or a sim command argument. For an example, see
Load Data to Represent Variable-Step Input from Model Hierarchy.
To import many signals to root-level input ports, consider using the Root Inport Mapper tool. This tool updates the Input configuration parameter based on the signal data that you import and map to root-level input ports. For an example, see Map Data Using Root Inport Mapper Tool.

Recommended Uses
Use root input ports to:
Import many signals to many blocks
Test your model as a referenced model in a wider context with signals from the workspace, without modifying your model
For importing signal data to meet most modeling requirements and to maintain model flexibility, root-level inport mapping is a convenient technique. Root-level inport mapping:
Displays signal data for you to inspect without loading all the signal data into MATLAB memory
Provides memory-efficient signal viewing
Requirements
To ensure that the Simulink variable solver executes at the times that you specify in the imported data,
set the Configuration Parameters >
Data Import/Export > Additional parameters >
Output options parameter to Produce additional output.
Limitations
You cannot use input ports to import buses in external modes. To import bus data in rapid accelerator mode, use
Datasetformat.The Root Inport Mapper tool supported map modes depend on the data type of a signal. For details, see Choose a Base Workspace and MAT-File Format.
From File Block
A From File block reads data from a MAT file and outputs the data as a signal.

For more information, see Load Data Using the From File Block.
Recommended Uses
Consider using a From File block for loading:
Large amounts of data. For a Version 7.3 MAT file, the From File block loads data incrementally from the MAT file during simulation.
Tip
To convert a Version 7.0 file to Version 7.3 (for example,
my_data_file.matthat contains the variablevar), at the MATLAB command line, enter:load('my_data_file.mat') save('my_data_file.mat', 'var', '-v7.3')Data that was exported to a To File block. The From File block reads data written by a To File block without any you modifying the data or making other special provisions.
Data stored in a MAT file that is separate from the model file.
Limitations
For Version 7.0 or earlier MAT file, the From File block reads only array-format data.
Version 7.3 and Version 7.0 or earlier MAT files handle multiple variables differently.
The From File block supports loading input data for a nonvirtual bus stored as a structure of
timeseriesobjects.For array data, the From File block reads only double signal data.
Code generation that involves building ERT or GRT targets, or using SIL or PIL simulation modes, has some special considerations. See Code Generation.
From Spreadsheet Block
The From Spreadsheet block reads data from Microsoft® Excel® spreadsheets (all platforms) or CSV spreadsheets (Microsoft Windows® platform with Microsoft Office only) and outputs the data as one or more signals.
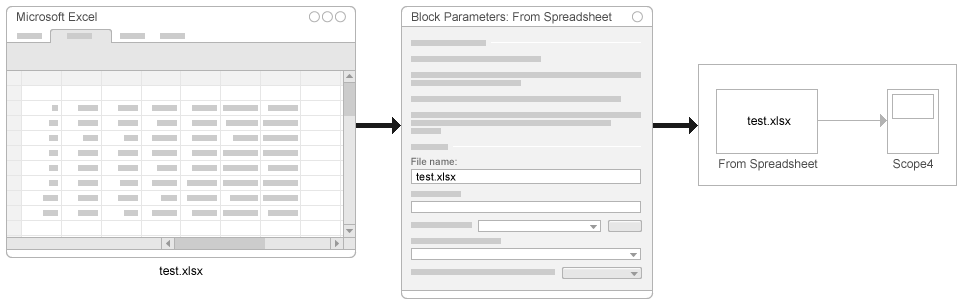
Recommended Uses
Use the From Spreadsheet block for loading:
Large Microsoft Excel or CSV spreadsheets. The From Spreadsheet block incrementally reads data from the spreadsheet during simulation, rather than loading the data into Simulink memory.
Spreadsheets that you expect to modify. The From Spreadsheet block handles changes to worksheet values automatically, because it loads data directly from the spreadsheet.
Limitations
You cannot import bus data.
The From Spreadsheet file has requirements for the spreadsheet data. Organize Excel spreadsheet data using the format described in Supported Microsoft Excel File Formats.
Linux® and Mac platforms do not support using a From Spreadsheet block to import data from a CSV spreadsheet.
From Workspace Block
The From Workspace block reads signal data from a workspace and outputs the data as a signal. In the Block Parameters dialog box, in the Data parameter, enter a MATLAB expression that specifies the workspace data.
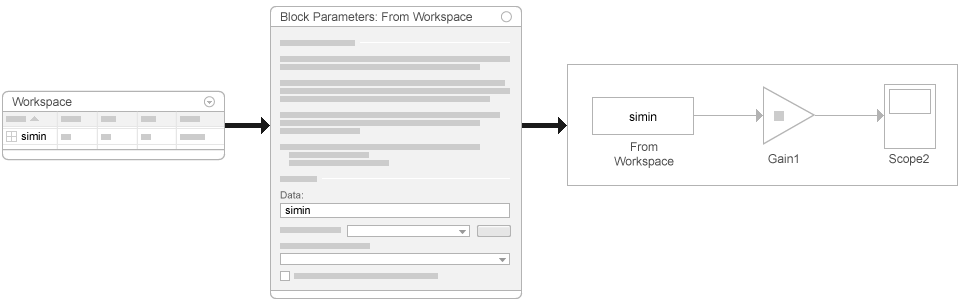
For an example of how to use a From Workspace block, see Load Data Using the From Workspace Block.
Recommended Uses
Use the From Workspace block for loading:
A small set of signal data to perform local, temporary testing
Data from the MATLAB (base), model, mask, or function workspace
Variable-size signals
Data that you saved using a To Workspace block in MATLAB
timeseriesformat, without manual changes to the dataData saved in a previous simulation by a To Workspace block in either
TimeseriesorStructure with Timeformat for use in a later simulation
Limitations
The data expressions that you specify must evaluate to one of these types of data:
A
timeseriesortimetableobjectA structure of
timeseriesortimetableobjectsA structure, with or without time
A two-dimensional matrix
Signal Editor Block
Using a Signal Editor block, you can create interchangeable scenarios to use in a model.
For examples of how to use a Signal Editor block, see:
Recommended Uses
Use the Signal Editor block to create and load scenarios to use in testing.
These products integrate the Signal Editor block into their workflows:
Simulink Test™
Simulink Coverage™
Simulink Design Verifier™
Limitations
Function-calls
Array of buses
Buses while using rapid accelerator mode
timetableobjectsGround signals
The Signal Editor block supports dynamic strings. It does not support strings with maximum length. In addition, strings in the Signal Editor block cannot output:
Non-scalar MATLAB strings.
String data that contains missing values.
String data that contains non-ASCII characters.