SPST Relay
Single-pole single-throw relay with delays and faults
Libraries:
Simscape /
Electrical /
Switches & Breakers /
Relays
Description
The SPST Relay block models a single-pole single-throw relay. The block has three potential states:
De-energized — The common contact, C, changes from being connected to disconnected from the normally open contact, S.
Energized — The common contact, C, changes from being disconnected to connected to the normally open contact, S.
Open Circuit — The relay is open. The common contact, C, is not connected to the normally open contact, S.
You can:
Control the relay state using a physical signal input port or electrical conserving ports.
Output the relay state.
Delay the breaking and making of the connection.
Introduce a behavioral or temporal fault that results in a stuck connection, an open circuit, or degraded contact resistance.
Relay State Control
The block has two control variants:
Physical signal (PS) control — The state of the relay depends on how the value of the input physical signal compares to the relay threshold. The relay threshold, th, is the value that you by specify for the Threshold parameter.
Electrical control — The state of the relay depends on how the current through the positive and negative electrical conserving ports, which represent the relay winding, compares to the relay upper and lower thresholds. The upper and lower thresholds depend on the values that you specify for the parameters in the Winding settings.
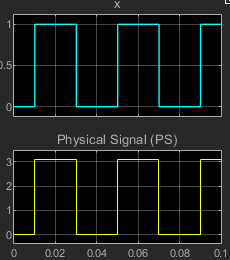
For the PS control variant, at the start of simulation:
If the input signal, PS, is less than or equal to th, the relay is de-energized and the common contact, C, disconnects from the normally open contact, S.
If the input signal, PS, greater than th, the relay is energized and C connects to the normally open contact, S.
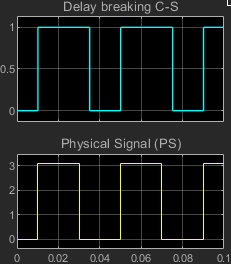
After the simulation starts, if PS rises above th, the block goes from a de-energized state to an energized state and the C–S connection closes after the delay specified in Time-to-make C-S connection.
If the block goes from an energized state to a de-energized state, that is PS falls to or below th, the C–S connection breaks after the delay specified in Time-to-break C-S connection.
For the electrical control variant, the upper and lower thresholds depend on the specified values for the Rated voltage, Percent rated voltage to energize, Percent rated voltage to de-energize, and Winding series resistance parameters. The rated current is:
The equation for the upper current threshold, ienergized, is:
The equation for the lower current threshold, ide-energized, is:
At the start of simulation, if the control current is greater than ienergized, the relay is energized and C connects to the normally open contact, S.
After the start of simulation, if the current rises above ienergized, the block goes from a de-energized state to an energized state. The C–S connection closes after the delay specified in Time-to-make C-S connection.
If the current falls below ide-energized, the block goes from an energized state to a de-energized state. The C–S connection breaks after the delay specified in Time-to-break C-S connection.
Output the Relay State
To view the relay state, expose port x, a physical signal
port that outputs the state of each connection. To expose the x
port, in the Main settings, set State port
to Visible.
The table shows how the state of the relay relates to the state of the connection. A closed connection has a state of 1. An open connection has a state of 0.
Relay and Connection States
| C–S Connection State | Relay State |
|---|---|
| 0 | De-energized or open circuit |
| 1 | Energized |
Connection Delays
You can specify delays for making and breaking connections in the Mechanical settings. The table shows how the make and break time delays affect the connections between contacts S1 and S2 and the common contact, C.
| Mechanical Settings | Relay State | C–S Connection State | Results, with C–S in Blue and PS in Yellow | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| De-energized | 0 |
| ||||||
| Energized | 1 | ||||||||
| De-energized | 1, 0 |
| ||||||
| Energized | 1 | ||||||||
| De-energized | 0 |
| ||||||
| Energized | 0, 1 |
Faults
To model a fault in the SPST Relay block, in the Faults section, click Add fault next to the fault that you want to model. For more information about fault modeling, see Fault Behavior Modeling and Fault Triggering.
You can add a switch fault or an open-circuit fault to the winding. If you add a switch fault, you can set the Switch fault parameter to:
C-S stuck closedC open circuit (no path to S)Degraded contact resistance
You can specify how and when faults occur by using the Trigger type parameter.
For more information about adding faults to blocks and specifying fault triggers, see Introduction to Simscape Faults.
The C–S stuck closed fault occurs if the common contact, C, becomes mechanically, electrically, or chemically stuck to the normally closed contact, S. Causes of this type of fault include:
Contact welding, possibly due to an inrush current or breaking current that exceeds the rating or load short circuit.
Mechanical damage.
Insulation deterioration.
Inductive voltage.
The connection state for a C–S
stuck closed fault is equal to 1.
A C–S stuck closed behavioral fault can occur only if the load current exceeds the current threshold for a period of time that exceeds the behavioral trigger time threshold. That is, the behavioral fault can occur only if:
and
where:
iload is the load current.
ith is the specified value for the Maximum permissible load current parameter.
ti>i_th is the time that the current threshold is exceeded.
tth_b is the specified value for the Time to fail when exceeding current parameter.
When a fault triggers, if C–S is:
Closed — C–S remains closed for the rest of the simulation.
Open — The fault does not take effect unless the relay becomes energized and the C–S connection closes. Once closed, the C–S connection remains closed for the rest of the simulation.
The C open circuit (no path to S) fault occurs if the common contact, C, becomes mechanically stuck in an open position. This type of fault can happen if:
There is contact damage or deterioration.
The switch connector becomes mechanically stuck in the middle of the relay.
The faulted state for a C open circuit (no path
to S) fault is equal to
0.
A C open circuit behavioral fault can occur only if the load current exceeds the current threshold for a period of time that exceeds the behavioral trigger time threshold. That is, the behavioral fault can occur only if:
and then
where:
iload is the load current.
ith is the specified value for the Maximum permissible load current parameter.
ti>i_th is the time that the current threshold is exceeded.
tth_b is the specified value for the Time to fail when exceeding current parameter.
When the temporal fault threshold is exceeded, if:
The relay is in the open-circuit state, that is, the connection has been broken and not yet been made, the relay remains open for the rest of the simulation.
The C–S connection is closed, the fault does not take effect unless the relay is de-energized and the closed connection is broken. If the connection is broken, the relay becomes an open-circuit, and remains open for the rest of the simulation.
When the behavioral fault thresholds are exceeded, if:
The relay is in the open-circuit state, that is, the connection has been broken and not yet been made, the relay remains open for the rest of the simulation.
The C–S connection is closed, the relay state immediately becomes an open circuit and remains an open circuit for the rest of the simulation.
Causes of the degraded contact resistance fault include:
Overuse-induced overload conditions. High inrush currents and voltages can cause overload conditions, as can excessive switching of the relay. Overload conditions ultimately trigger electrical arching, which generates heat that degrades the contact material.
Chemical contamination that interferes with the operation of the relay contacts. Contaminants, which can include oxidation films or foreign particles, tend to produce high or unstable contact resistance readings.
End of relay life.
The faulted state for a degraded contact resistance fault for the C–S connection is equal to either 0 or 1.
When a temporal fault first occurs, the contact resistance of S is:
where:
rcontact_fault_s is the final value of the faulted S contact resistance.
rcontact is the unfaulted S contact resistance.
tth_t is the value of the Trigger fault at time parameter.
A degraded contact resistance behavioral fault can occur only if the load current exceeds the current threshold for a period of time that exceeds the behavioral trigger time threshold. That is, the behavioral fault can occur only if:
and then
where:
iload is the load current.
ith is the specified value for the Maximum permissible load current parameter.
ti>i_th is the time that the current threshold is exceeded.
tth_b is the specified value for the Time to fail when exceeding current parameter.
For a behavioral fault, if continuously over the time interval tth_b,
where:
iS-C is the common contact to normally closed contact, C–S, current.
ith is the specified value for the Maximum permissible load current parameter.
tth_b is the specified value for the Time to fail when exceeding current parameter.
rcontact_fault_s is the final value of the faulted S contact resistance.
rcontact is the unfaulted S contact resistance.
τ is the value of the Time constant for degraded contact resistance parameter.
When the temporal fault threshold is exceeded for the C–S connection, the contact resistance is immediately degraded and remains degraded for the rest of the simulation.
When the behavioral fault thresholds are exceeded for C–S, in terms of iS-C, the resistance for the C–S connection is immediately degraded and remains degraded for the rest of the simulation.
The open-circuit winding fault is available only for the electrical control variant. An open circuit in the winding coil can cause this type of fault.
For timed faults, the block approximates the winding current as:
where:
L is the winding inductance.
R is the winding resistance.
i is the winding current.
vwinding is the voltage across the winding.
tth_t is the value of the Trigger fault at time parameter.
τ is the value of the Time constant for winding open circuit transition parameter.
A behavioral fault in the winding can occur only if one of these conditions is met:
The winding current exceeds the current threshold for a period of time that exceeds the behavioral trigger time threshold.
The winding voltage exceeds the voltage threshold for a number of times that exceeds the threshold for the number of voltage overloads.
That is, the behavioral fault can occur only if:
and then
where:
iwinding is the winding current.
ith is the specified value for the Maximum permissible winding current parameter.
ti>i_th is the time that the current threshold is exceeded.
tth_b is the specified value for the Time to fail when exceeding current parameter.
or if:
and then
where:
vwinding is the winding voltage.
vth is the specified value for the Maximum permissible winding voltage parameter.
Nv>v_th is the number of times that the voltage threshold is exceeded.
Nth is the specified value for the Number of events to fail when exceeding voltage parameter.
Once a fault triggers, C–S remains closed for the rest of the simulation.
Limitations and Assumptions
For behavioral faults, if Time to fail when exceeding current is greater than the time between switches, no fault is triggered because the accumulated heat is too low to melt or break the contacts or windings.
The energize and de-energize delays can differ, but the energize delay must be greater than or equal to the de-energize delay.
Ports
The type, visibility, and location of the block ports depend on how you configure these parameters in the Main settings:
Control port — Choose between a physical signal input port, PS, or electrical conserving ports, + and -, for relay control.
State port — Set the visibility for the relay state physical signal output port, x.
| Control port | State port | Block |
|---|---|---|
PS | Hidden |
|
Visible |
| |
Electrical | Hidden |
|
Visible |
|