Faulted PMSM
This example shows how to model a faulted permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) using Simscape™ Electrical™. Normally when modeling a PMSM, you can represent each winding as a single entity with associated inductance, induced back electromotive force (EMF), and mutual inductive coupling to adjacent windings. However, when a winding fault occurs, the single entity assumption breaks down. To correctly capture the resulting dynamics, you have to model the motor at a winding slot level. This requires modeling in the magnetic domain.
This example shows how to create a model of a PMSM in the magnetic domain using the Simscape Electrical fundamental blocks for a winding and for a rotor air gap. It also shows how to invoke and assess the impact of winding and rotor permanent magnet faults.
Model Overview
At the top level the model compares the standard library PMSM block with the custom magnetic-domain subsystem that represents a surface-mounted permanent-magnet synchronous machine (SPMSM). You can then use the magnetic-domain model to study different fault behaviors, once validated for the no-fault case.
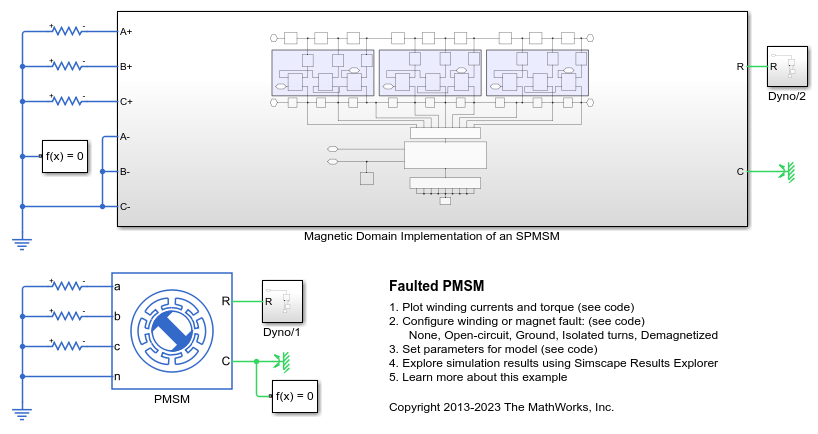
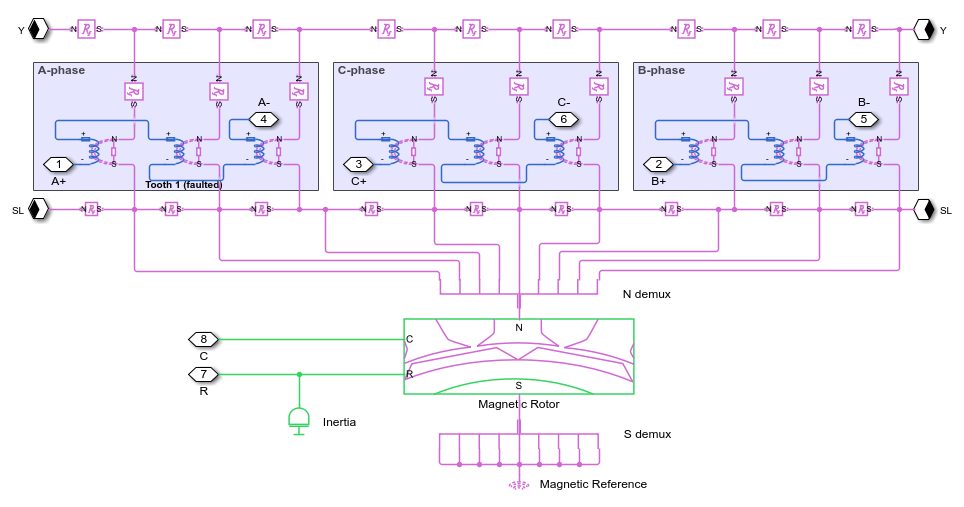
Magnetic Domain SPMSM Subsystem Overview
The figure shows the model architecture of an SPMSM with ten rotor poles and nine stator winding slots. The reference slot, Slot 1, is the middle of the three A-phase slots. Winding faults are introduced in this slot.
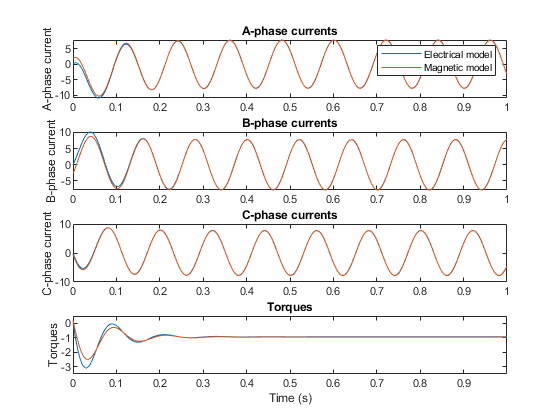
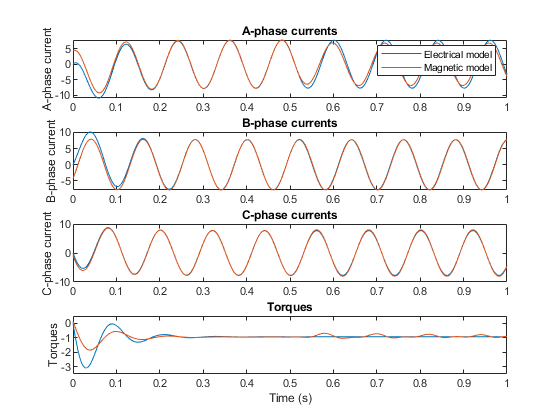
Validation Against Reference Model
The plot below shows simulation results from the custom magnetic domain model against the simulation results from the Simscape Electrical standard PMSM library block.
All faults disabled
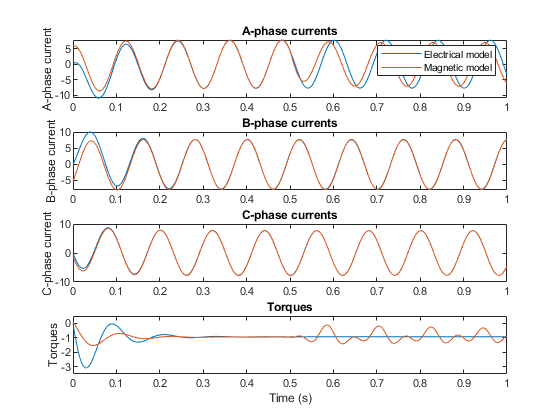
Open-Circuit Fault
The Slot 1 turns are open-circuited halfway through the simulation.
Fault scenario: Open circuit in Tooth 1

Ground Fault
The midpoint of the Slot 1 turns is shorted to ground halfway through the simulation.
Fault scenario: Grounded Tooth 1
Isolated Turns Fault
Half of the Slot 1 turns become isolated halfway through the simulation.
Fault scenario: Isolated turns in Tooth 1
Reduced Magnet Strength Fault
One of the rotor permanent magnets is reduced in strength halfway through the simulation.
Fault scenario: Demagnetized first rotor pole

See Also
PMSM | Rotating Air Gap | Magnetic Rotor | Winding | Fundamental Reluctance