lambertw
Lambert W function
Syntax
Description
Examples
The Lambert W function W(x) is a set of
solutions of the equation x =
W(x)eW(x).
Solve this equation. The solution is the Lambert W function.
syms x W eqn = x == W*exp(W); solve(eqn,W)
ans = lambertw(0, x)
Verify that branches of the Lambert W function are valid solutions of the
equation x = W*eW:
k = -2:2; eqn = subs(eqn,W,lambertw(k,x)); isAlways(eqn)
ans =
1×5 logical array
1 1 1 1 1Depending on its arguments, lambertw can
return floating-point or exact symbolic results.
Compute the Lambert W functions for these numbers. Because the numbers are not symbolic objects, you get floating-point results.
A = [0 -1/exp(1); pi i]; lambertw(A)
ans = 0.0000 + 0.0000i -1.0000 + 0.0000i 1.0737 + 0.0000i 0.3747 + 0.5764i
lambertw(-1,A)
ans =
-Inf + 0.0000i -1.0000 + 0.0000i
-0.3910 - 4.6281i -1.0896 - 2.7664iCompute the Lambert W functions for the numbers converted to symbolic objects.
For most symbolic (exact) numbers, lambertw returns unresolved
symbolic calls.
A = [0 -1/exp(sym(1)); pi i]; W0 = lambertw(A)
W0 = [ 0, -1] [ lambertw(0, pi), lambertw(0, 1i)]
Wmin1 = lambertw(-1,A)
Wmin1 = [ -Inf, -1] [ lambertw(-1, pi), lambertw(-1, 1i)]
Convert symbolic results to double by using double.
double(W0)
ans = 0.0000 + 0.0000i -1.0000 + 0.0000i 1.0737 + 0.0000i 0.3747 + 0.5764i
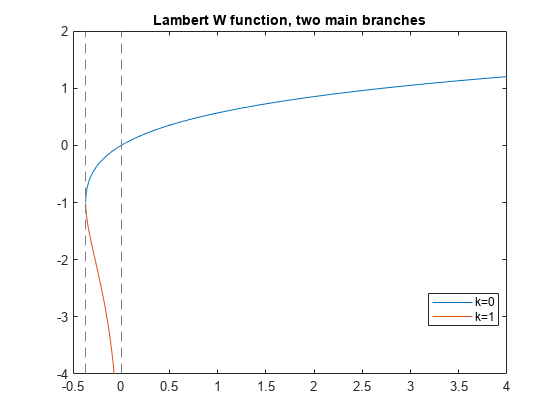
Plot the two main branches, and , of the Lambert W function.
syms x fplot(lambertw(x)) hold on fplot(lambertw(-1,x)) hold off axis([-0.5 4 -4 2]) title('Lambert W function, two main branches') legend('k=0','k=1','Location','best')
Plot the principal branch of the Lambert W function on the complex plane.
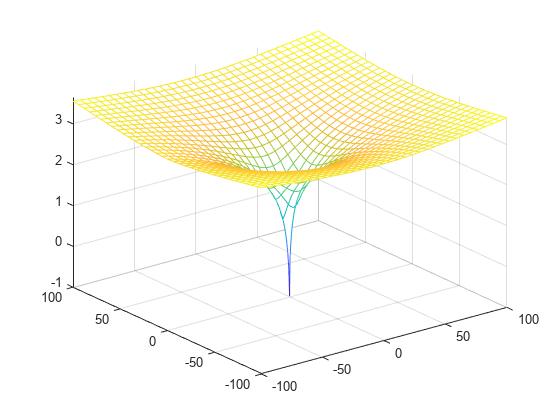
Plot the real value of the Lambert W function by using fmesh. Simultaneously plot the contours by setting 'ShowContours' to 'On'.
syms x y f = lambertw(x + 1i*y); interval = [-100 100 -100 100]; fmesh(real(f),interval,'ShowContours','On')
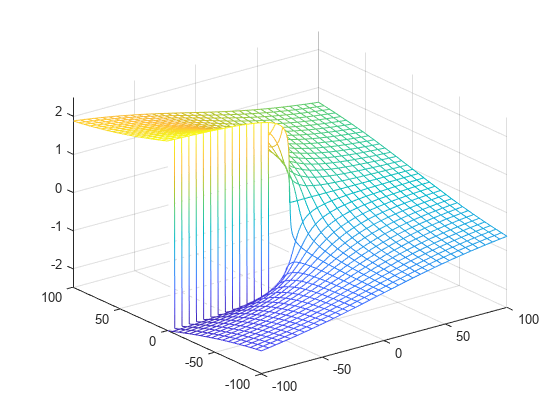
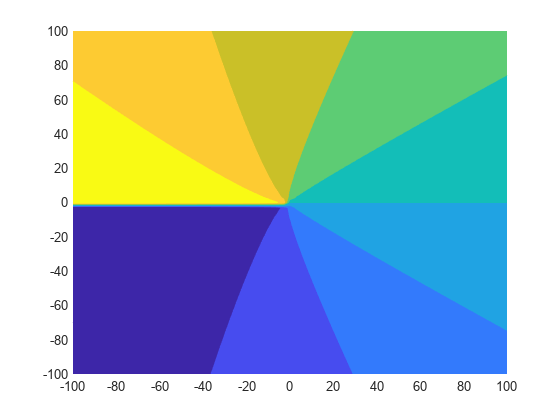
Plot the imaginary value of the Lambert W function. The plot has a branch cut along the negative real axis. Plot the contours separately.
fmesh(imag(f),interval)
fcontour(imag(f),interval,'Fill','on')
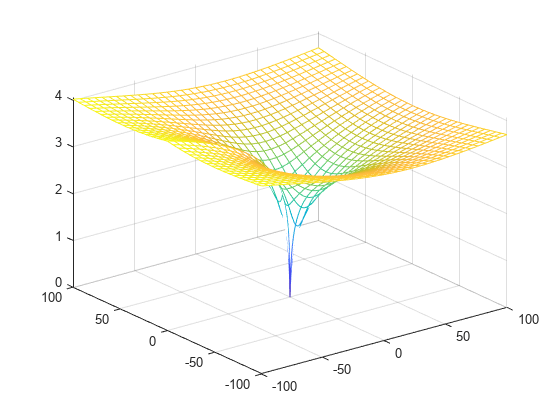
Plot the absolute value of the Lambert W function.
fmesh(abs(f),interval,'ShowContours','On')
Input Arguments
Input, specified as a number, vector, matrix, or array, or a symbolic number, variable, array, function, or expression.
At least one input argument must be a scalar, or both arguments must be vectors
or matrices of the same size. If one input argument is a scalar and the other is a
vector or matrix, lambertw expands the scalar into a vector or
matrix of the same size as the other argument with all elements equal to that
scalar.
Branch of Lambert W function, specified as an integer, a vector or matrix of integers, a symbolic integer, or a symbolic vector or matrix of integers.
At least one input argument must be a scalar, or both arguments must be vectors
or matrices of the same size. If one input argument is a scalar and the other is a
vector or matrix, lambertw expands the scalar into a vector or
matrix of the same size as the other argument with all elements equal to that
scalar.
More About
The Lambert W function W(x) represents the solutions y of the equation for any complex number x.
For complex x, the equation has an infinite number of solutions y = lambertW(k,x) where k ranges over all integers.
For all real x ≥ 0, the equation has exactly one real solution y = lambertW(x) = lambertW(0,x).
For real x where , the equation has exactly two real solutions. The larger solution is represented by y = lambertW(x) and the smaller solution by y = lambertW(–1,x).
For , the equation has exactly one real solution y = –1 = lambertW(0, –exp(–1)) = lambertW(–1, -exp(–1)).
References
[1] Corless, R.M., G.H. Gonnet, D.E.G. Hare, D.J. Jeffrey, and D.E. Knuth. "On the Lambert W Function." Advances in Computational Mathematics, Vol. 5, pp. 329–359, 1996.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)