Create Base Layer from OpenStreetMap Data
When you are in an offline environment, you can create provide geographic context for your data by creating a simple base layer from data stored in an OpenStreetMap® file. This example shows how to create a base layer for several city blocks in Shibuya, Tokyo, Japan by reading building, road, and traffic signal data from the file.
Read Building Data
Read the buildings layer from an OpenStreetMap file [1] by using the readgeotable function. The function derives building information from the file and stores the result in a geospatial table. The table represents the buildings using polygon shapes in geographic coordinates.
filename = "shibuya.osm"; buildingsLayer = readgeotable(filename,Layer="buildings");
Read Road Data
The lines layer of an OpenStreetMap file represents line-like features such as roads, sidewalks, and subway routes. Read the lines layer from the file into a geospatial table. The table represents the lines using polygon shapes in geographic coordinates.
linesLayer = readgeotable(filename,Layer="lines");A table row represents a principal road when the highway table variable has a value of "motorway", "trunk", "primary", "secondary", "tertiary", or "residential". Create a new geospatial table from the table rows that represent principal roads.
roadtypes = ["motorway","trunk","primary","secondary","tertiary","residential"]; roadRows = ismember(linesLayer.highway,roadtypes); roads = linesLayer(roadRows,:);
Read Traffic Signal Data
The points layer of an OpenStreetMap file represents point-like features such as traffic signals, bus stops, and subway entrances. Read the points layer from the file into a geospatial table. The table represents the points using point shapes in geographic coordinates.
pointsLayer = readgeotable(filename,Layer="points");A table row represents a traffic signal when the highway table variable has a value of "traffic_signals". Create a new geospatial table from the table rows that represent traffic signals.
signalRows = ismember(pointsLayer.highway,"traffic_signals");
signals = pointsLayer(signalRows,:); Prepare to display the traffic signals using an icon chart by extracting the latitude and longitude coordinates from the table.
signalLat = signals.Shape.Latitude; signalLon = signals.Shape.Longitude;
Display Base Layer
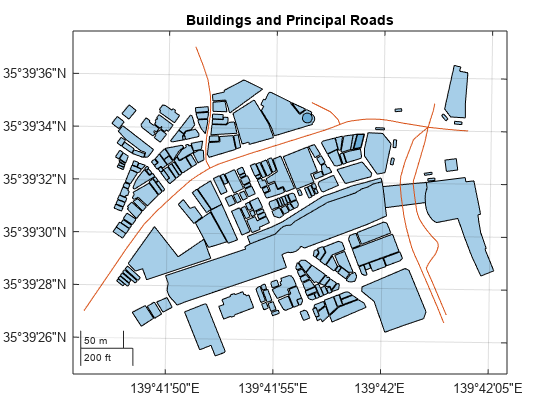
Set up a new map using a projected coordinate reference system (CRS) that is appropriate for Japan. Provide geographic context for the area by displaying the buildings, roads, and traffic signals. Prevent the objects from capturing mouse clicks by setting the PickableParts properties to "none".
figure proj = projcrs(32654); newmap(proj) geoplot(buildingsLayer,PickableParts="none") hold on geoplot(roads,PickableParts="none") geoiconchart(signalLat,signalLon,"traffic-signal.png",SizeData=17,PickableParts="none") title("Buildings, Principal Roads, and Signals")
Load and Plot Data
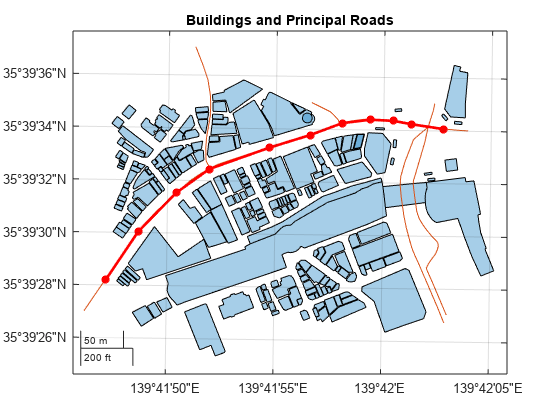
Read a driving track from a GPX file into a geospatial table. Extract the coordinates from the table, Then, display the track on the map using a thick, black line.
trk = readgeotable("shibuya_track.gpx",Layer="track_points"); geoplot(trk.Shape.Latitude,trk.Shape.Longitude,"k",LineWidth=4)
[1] You can download OpenStreetMap files from https://www.openstreetmap.org, which provides access to crowd-sourced map data all over the world. The data is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL), https://opendatacommons.org/licenses/odbl/.