treeplot
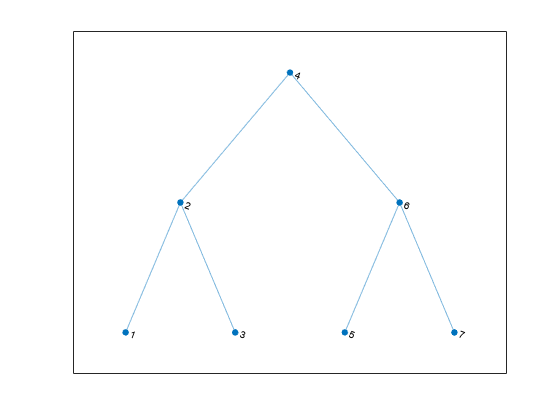
Plot picture of tree
Description
treeplot( plots one or more trees specified
as a row vector of parent indices. p)p(i) = j indicates that node
j is a parent of node i, and p(i) =
0 indicates that node i is a root node.
Examples
Input Arguments
Tips
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
See Also
etree | etreeplot | treelayout | graph | digraph