boustrophedonOptions
Description
The boustrophedonOptions object defines the behavior of polygon
decomposition using the boustrophedon algorithm and enables you to generate a connectivity
graph of polygon cells post-decomposition. Specify this object to the polygonDecomposition
function to perform decomposition using the boustrophedon decomposition algorithm with the
specified options [1].
Creation
Description
options = boustrophedonOptions generates a polygon decomposition
options object with default properties. Specify this object to the polygonDecomposition function to perform decomposition using the
boustrophedon decomposition algorithm with the specified options.
options = boustrophedonOptions(
sets one or more properties for PropertyName=Value)options using name-value
arguments.
Properties
Decomposition generates and returns a connectivity graph, specified as a logical
true (1) or false
(0):
false— Do not generate a connectivity graph.Note
When
ReturnConnectivityisfalse, theReconnectionMethod,ConnectedCostFcn,DisconnectedCostFcn, andUserDataproperties have no effect.true— Generate anavGraphobject representing the connectivity between cells in the polygon decomposition output, and return thenavGraphin thesolnInfoargument of thepolygonDecompositionfunction.
Method to connect groups of polygon clusters, specified as one of these options:
"none"— Do not connect unconnected polygon clusters."nearest"— Connect polygon clusters by the minimum distance edge between the polygon clusters."all"— Connect every cell within a connected polygon cluster to every cell outside that cluster.Note
The
"nearest"and"all"options use theDisconnectedCostFcnproperty to determine the distance and the resulting edge costs between polygon clusters.
For more information about how ReconnectionMethod
works, see Specify Options for Polygon Decomposition.
Function for computing distance and edge costs between sets of neighboring polygons, specified as a function name. Neighboring polygons are polygons that share edges with each other.
Using the default "boustrophedonOptions.defaultConnectedCostFcn"
function, the cost of connecting adjacent polygons is 0.
Cost functions must be of the form:
function cost = costFcn(polySet,i,J,userData) arguments (Inputs) polySet {mustBeA(polySet,{'polyshape','nav.decomp.internal.polyshapeMgr'})} i (1,1) {mustBeInteger,mustBePositive} J (:,1) {mustBeInteger,mustBePositive} userData (1,1) struct %#ok<INUSA> end arguments (Outputs) cost (:,1) end ... end
For an example of how to specify ConnectedCostFcn, see Define Custom Connected Cost Function and User Data.
Data Types: char | string
Function for computing distance cost between sets of nonneighboring polygons, specified as a function name. Nonneighboring polygons are polygons that do not share an edge with each other.
Using the default
"boustrophedonOptions.defaultDisconnectedCostFcn" function, the
cost of connecting nonneighboring polygons is the distance between polygon
centroids.
Cost functions must be of the form:
function cost = costFcn(polySet,i,J,userData) arguments (Inputs) polySet {mustBeA(polySet,{'polyshape','nav.decomp.internal.polyshapeMgr'})} i (1,1) {mustBeInteger,mustBePositive} J (:,1) {mustBeInteger,mustBePositive} userData (1,1) struct %#ok<INUSA> end arguments (Outputs) cost (:,1) end ... end
For an example of how to specify DisconnectedCostFcn, see Define Disconnected Cost Function.
Data for cost functions, specified as a structure. Store any data that you need for the cost functions as fields of this structure.
For an example of how to specify UserData, see Define Custom Connected Cost Function and User Data.
Examples
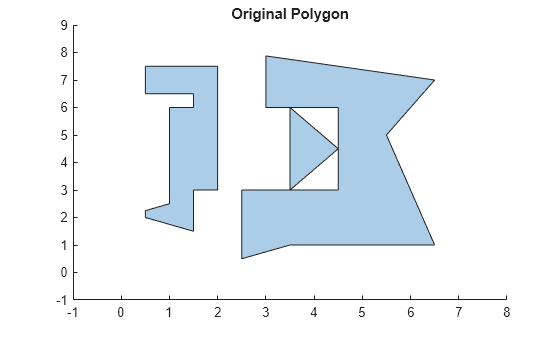
Load a polyshape and plot it.
load("exampleComplexPolyshape.mat","p") plot(p) title("Original Polygon")
Decompose the polygon using each reconnection method.
bOpts1 = boustrophedonOptions(ReconnectionMethod="nearest"); [polySet1,info1] = polygonDecomposition(p,bOpts1); bOpts2 = boustrophedonOptions(ReconnectionMethod="none"); [polySet2,info2] = polygonDecomposition(p,bOpts2); bOpts3 = boustrophedonOptions(ReconnectionMethod="all"); [polySet3,info3] = polygonDecomposition(p,bOpts3);
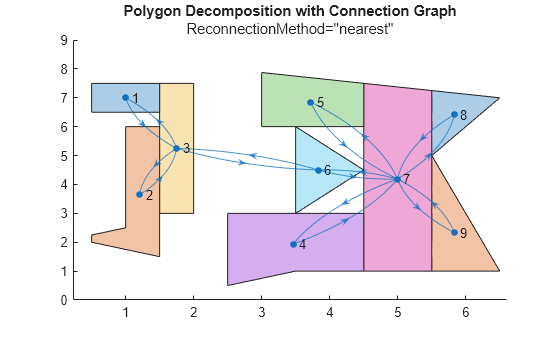
Show the polygon decomposition with a connectivity graph overlay for each reconnection method.
plot(polySet1) hold on exampleHelperShowGraphConnectionsOnPolyset(polySet1,info1.Connectivity,0.5); title("Polygon Decomposition with Connection Graph"); subtitle("ReconnectionMethod=''nearest''") hold off
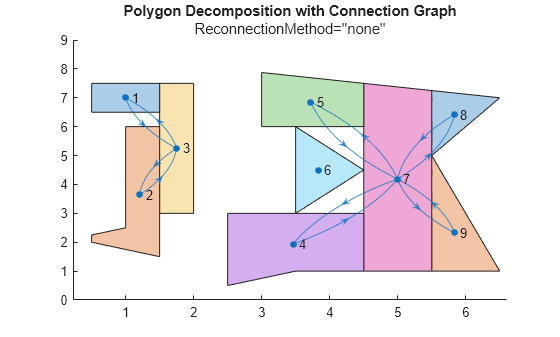
plot(polySet2) hold on exampleHelperShowGraphConnectionsOnPolyset(polySet2,info2.Connectivity,0.5); title("Polygon Decomposition with Connection Graph"); subtitle("ReconnectionMethod=''none''"); hold off
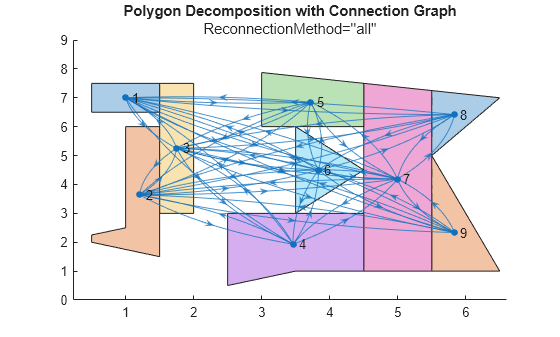
plot(polySet3) hold on exampleHelperShowGraphConnectionsOnPolyset(polySet3,info3.Connectivity,0.5); title("Polygon Decomposition with Connection Graph"); subtitle("ReconnectionMethod=''all''"); hold off
This is the helper function for plotting the polygon decomposition and overlaying the connectivity graph.
function gHandle = exampleHelperShowGraphConnectionsOnPolyset(polySet,connectionGraph,lineWidth) % Get the current axes ax = gca; ax.ColorOrderIndex = 1; % Reset the color order index % Overlay the connectivity graph gHandle = show(connectionGraph); gHandle.EdgeAlpha = 0.75; gHandle.LineWidth = lineWidth; % Set the line width for the graph edges % Calculate and plot the centroids [cx,cy] = centroid(polySet); % Set the xy-positions of the connectivity graph to the centroids of % the polygons gHandle.XData = cx'; gHandle.YData = cy'; end
Load a rectangular polygon with multiple holes as a polyshape object.
load("exampleRectangleWithHolesPolyshape.mat","p")
Define a connected cost function that uses terrain data and assigns costs to edges based on the magnitude of the slope change.
function cost = terrainConnectedCostFcn(polySet,i,J,userData) arguments polySet {mustBeA(polySet,{'polyshape','nav.decomp.internal.polyshapeMgr'})} i (1,1) {mustBeInteger,mustBePositive} J (:,1) {mustBeInteger,mustBePositive} userData (1,1) struct end % Extract dx, dy, and the coordinate bounds from userData dx = userData.XSlope; dy = userData.YSlope; xBounds = userData.XBounds; yBounds = userData.YBounds; % Calculate the slope magnitude slope_magnitude = sqrt(dx.^2 + dy.^2); % Define the coordinates for the slope map based on the provided bounds x = linspace(xBounds(1),xBounds(2),size(slope_magnitude,1)); y = linspace(yBounds(1),yBounds(2),size(slope_magnitude,2)); % Initialize the cost array cost = zeros(size(J)); % Calculate the average slope for the starting polyshape avgSlope_i = calculateAverageSlope(polySet(i),slope_magnitude,x,y); for idx = 1:numel(J) % Calculate the average slope for each target polyshape avgSlope_j = calculateAverageSlope(polySet(J(idx)),slope_magnitude,x,y); % Define a cost function that includes the average slope difference % For example, prioritize smaller slope differences cost(idx) = abs(avgSlope_i-avgSlope_j); end end function avgSlope = calculateAverageSlope(poly,slope_magnitude,x,y) % Find the bounding box of the polyshape [x_lim,y_lim] = boundingbox(poly); % Determine the indices in the slope map that correspond to this % polyshape x_indices = find(x >= x_lim(1) & x <= x_lim(2)); y_indices = find(y >= y_lim(1) & y <= y_lim(2)); % Extract the relevant portion of the slope map slopesInPoly = slope_magnitude(y_indices,x_indices); % Compute the average slope for the polyshape avgSlope = mean(slopesInPoly(:)); end
Define custom data for the cost functions to use. Create an L-membrane to represent terrain, and calculate the slope at each point.
Z = membrane(1,3); [dx,dy] = gradient(Z);
Store the slope and bounds data in a structure.
terrainData.XSlope = dx; terrainData.YSlope = dy; terrainData.XBounds = [1 8]; terrainData.YBounds = [1 8];
Create a boustrophedon options object, and specify the custom connected cost function and terrain data.
bOpts = boustrophedonOptions(ConnectedCostFcn="terrainConnectedCostFcn",UserData=terrainData);Decompose the polygon and plot the set of resulting polygons.
[polySet,info] = polygonDecomposition(p,bOpts); plot(polySet) axis equal hold on
Overlay the connectivity graph, and highlight the edges to show the edge costs between the decomposed polygons. Note that the peak of the L-membrane is around polygons 8, 11, and 13, so edges connecting these polygons to polygons in the top-left have a higher edge cost.
gHandle = exampleHelperShowGraphConnectionsOnPolyset(polySet,info.Connectivity,2);
exampleHelperVisualizeConnectionGraphWeights(info.Connectivity,gHandle);
title("Connection Graph with Cost Visualized")
customLinkInfo = info.Connectivity.LinkscustomLinkInfo=44×2 table
EndStates Weight
_________ ________
1 2 0.090406
1 3 0.026001
1 4 0.27418
2 1 0.090406
2 5 0
3 1 0.026001
3 5 0.11641
3 6 0.29335
4 1 0.27418
4 6 0.04517
5 2 0
5 3 0.11641
5 7 0.062287
5 8 0.4142
6 3 0.29335
6 4 0.04517
⋮
hold off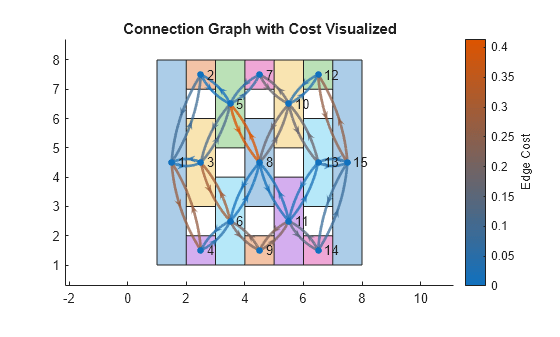
Load a complex polyshape.
load exampleComplexPolyshape.matDefine a custom disconnected cost function that prioritizes reconnecting the disconnected polygons using the longest edge possible.
function cost = longEdgeDisconnectedCostFcn(polySet,i,J,userData) arguments polySet {mustBeA(polySet,{'polyshape','nav.decomp.internal.polyshapeMgr'})} i (1,1) {mustBeInteger,mustBePositive} J (:,1) {mustBeInteger,mustBePositive} userData (1,1) struct %#ok<INUSA> end c1 = [0 0]; c2 = zeros(numel(J),2); % Calculate the centroid of the current polygon [c1(1),c1(2)] = polySet(i).centroid; % Get the centroids of possible polygons connections for i = 1:numel(J) [c2(i,1),c2(i,2)] = polySet(J(i)).centroid; end % Calculate the centroid distances between the current polygon and % other polygons distances = vecnorm(c2-c1,2,2); % Calculate the inverse distance cost. Add a small number to avoid % division by zero cost = 1./(distances + 1e-6); end
Create a boustrophedon polygon decomposition options object, and specify the disconnected cost function.
bOpts = boustrophedonOptions(DisconnectedCostFcn="longEdgeDisconnectedCostFcn", ... ReconnectionMethod="nearest");
Decompose the polygon and visualize the graph connection.
[polySet,info] = polygonDecomposition(p,bOpts);
plot(polySet)
hold on
gHandle = exampleHelperShowGraphConnectionsOnPolyset(polySet,info.Connectivity,0.5);
info.Connectivity.Linksans=16×2 table
EndStates Weight
_________ _______
1 3 0
1 6 0.26465
1 9 0.14884
2 3 0
3 1 0
3 2 0
4 7 0
5 7 0
6 1 0.26465
7 4 0
7 5 0
7 8 0
7 9 0
8 7 0
9 1 0.14884
9 7 0
c = colororder;
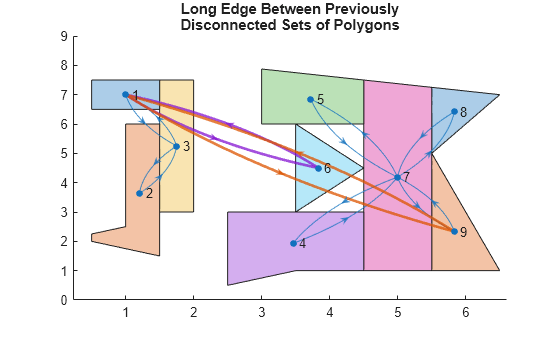
Highlight the edges between the previously disconnected sets of polygons. Note that polygon 6 is also disconnected, because it does not share any edges even though its vertices are in contact with other edges.
highlight(gHandle,Edges=[3 15],EdgeColor=c(2,:),LineWidth=2) % Edge from Polygon 1 to Polygon 9 highlight(gHandle,Edges=[2 9],EdgeColor=c(4,:),LineWidth=2) % Edge from Polygon 1 to Polygon 6 title(["Long Edge Between Previously","Disconnected Sets of Polygons"]) hold off
References
[1] Choset, Howie. "Coverage of Known Spaces: The Boustrophedon Cellular Decomposition." Autonomous Robots 9 no. 3, (2000): 247–53. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008958800904.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2025a
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)