assema
(Not recommended) Assemble area integral contributions
assema is not recommended. Use assembleFEMatrices instead.
Description
Examples
Assemble finite element matrices for an elliptic problem on complicated geometry.
The PDE is Poisson's equation,
Partial Differential Equation Toolbox™ solves equations of the form
So, represent Poisson's equation in toolbox syntax by setting c = 1, a = 0, and f = 1.
c = 1; a = 0; f = 1;
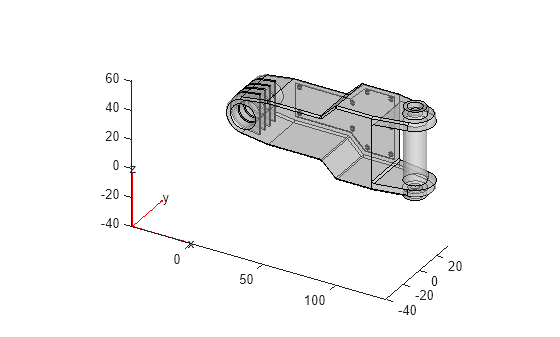
Create a PDE model container. Import the ForearmLink.stl file into the model and examine the geometry.
model = createpde; importGeometry(model,'ForearmLink.stl'); pdegplot(model,'FaceAlpha',0.5)
Create a mesh for the model.
generateMesh(model);
Create the finite element matrices from the mesh and the coefficients.
[K,M,F] = assema(model,c,a,f);
The returned matrix K is quite sparse. M has no nonzero entries.
disp(['Fraction of nonzero entries in K is ',num2str(nnz(K)/numel(K))])Fraction of nonzero entries in K is 0.00046964
disp(['Number of nonzero entries in M is ',num2str(nnz(M))])Number of nonzero entries in M is 0
Assemble finite element matrices for the 2-D L-shaped region, using the [p,e,t] mesh representation.
Define the geometry using the lshapeg function included your software.
g = @lshapeg;
Use coefficients c = 1, a = 0, and f = 1.
c = 1; a = 0; f = 1;
Create a mesh and assemble the finite element matrices.
[p,e,t] = initmesh(g); [K,M,F] = assema(p,t,c,a,f);
The returned matrix M has all zeros. The K matrix is quite sparse.
disp(['Fraction of nonzero entries in K is ',num2str(nnz(K)/numel(K))])Fraction of nonzero entries in K is 0.042844
disp(['Number of nonzero entries in M is ',num2str(nnz(M))])Number of nonzero entries in M is 0
Input Arguments
PDE model, specified as a PDEModel object.
Example: model = createpde
PDE coefficient, specified as a scalar, matrix, character vector, character array, string
scalar, string vector, or coefficient function. c
represents the c coefficient in the scalar PDE
or in the system of PDEs
Example: 'cosh(x+y.^2)'
Data Types: double | char | string | function_handle
Complex Number Support: Yes
PDE coefficient, specified as a scalar, matrix, character vector, character array, string
scalar, string vector, or coefficient function. a represents the
a coefficient in the scalar PDE
or in the system of PDEs
Example: 2*eye(3)
Data Types: double | char | string | function_handle
Complex Number Support: Yes
PDE coefficient, specified as a scalar, matrix, character vector, character array, string
scalar, string vector, or coefficient function. f
represents the f coefficient in the scalar PDE
or in the system of PDEs
Example: char('sin(x)';'cos(y)';'tan(z)')
Data Types: double | char | string | function_handle
Complex Number Support: Yes
Mesh points, specified as a 2-by-Np matrix of points, where
Np is the number of points in the mesh. For a description of the
(p,e,t) matrices, see Mesh Data as [p,e,t] Triples.
Typically, you use the p, e, and t
data exported from the PDE Modeler app, or generated by initmesh or refinemesh.
Example: [p,e,t] = initmesh(gd)
Data Types: double
Mesh triangles, specified as a 4-by-Nt matrix of
triangles, where Nt is the number of triangles in the mesh. For a
description of the (p,e,t)
matrices, see Mesh Data as [p,e,t] Triples.
Typically, you use the p, e, and t
data exported from the PDE Modeler app, or generated by initmesh or refinemesh.
Example: [p,e,t] = initmesh(gd)
Data Types: double
Output Arguments
Stiffness matrix, returned as a sparse matrix. See Elliptic Equations.
Typically, you use K in a subsequent call to
assempde.
Mass matrix. returned as a sparse matrix. See Elliptic Equations.
Typically, you use M in a subsequent call
to a solver such as assempde or hyperbolic.
Load vector, returned as a vector. See Elliptic Equations.
Typically, you use F in a subsequent call to
assempde.
Version History
Introduced before R2006aassema is not recommended. Use assembleFEMatrices instead. There are no plans to remove
assema.
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)