groundTrack
Description
groundTrack( adds ground track
visualization for each satellite in sat)sat based on their current
positions. The ground track begins at the scenario StartTime, and ends at
the StopTime. The spacing
between samples that make up the ground track visualization is determined by the scenario
SampleTime. If no viewer is
open, a new viewer is launched, and the ground track is displayed. If a viewer is already
open, the ground track is added to that viewer. By default, ground tracks will be displayed
in 2-D.
groundTrack( adds ground track
visualization for each platform in pltf)pltf based on their current
positions. The ground track begins at the scenario StartTime, and ends at
the StopTime. The spacing
between samples that make up the ground track visualization is determined by the scenario
SampleTime. If no viewer is
open, a new viewer is launched, and the ground track is displayed. If a viewer is already
open, the ground track is added to that viewer. By default, ground tracks will be displayed
in 2-D.
groundTrack(___, adds a
Name=Value)groundTrack object by using one or more name-value pairs. Enclose each
property name in quotes.
Examples
Create a satellite scenario object.
startTime = datetime(2020,5,10);
stopTime = startTime + days(5);
sampleTime = 60; % seconds
sc = satelliteScenario(startTime,stopTime,sampleTime);Calculate the semimajor axis of the geosynchronous satellite.
earthAngularVelocity = 0.0000729211585530; % rad/s orbitalPeriod = 2*pi/earthAngularVelocity; % seconds earthStandardGravitationalParameter = 398600.4418e9; % m^3/s^2 semiMajorAxis = (earthStandardGravitationalParameter*((orbitalPeriod/(2*pi))^2))^(1/3);
Define the remaining orbital elements of the geosynchronous satellite.
eccentricity = 0; inclination = 60; % degrees rightAscensionOfAscendingNode = 0; % degrees argumentOfPeriapsis = 0; % degrees trueAnomaly = 0; % degrees
Add the geosynchronous satellite to the scenario.
sat = satellite(sc,semiMajorAxis,eccentricity,inclination,rightAscensionOfAscendingNode,... argumentOfPeriapsis,trueAnomaly,"OrbitPropagator","two-body-keplerian","Name","GEO Sat");
Visualize the scenario using the Satellite Scenario Viewer.
v = satelliteScenarioViewer(sc);
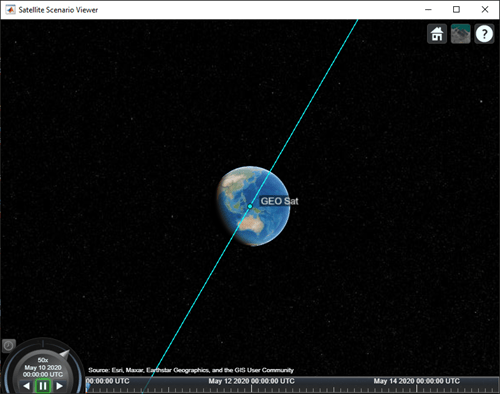
Add a ground track of the satellite to the visualization and adjust how much of the future and history of the ground track to display.
leadTime = 2*24*3600; % seconds trailTime = leadTime; gt = groundTrack(sat,"LeadTime",leadTime,"TrailTime",trailTime)
gt =
GroundTrack with properties:
LeadTime: 172800
TrailTime: 172800
LineWidth: 1
LeadLineColor: [1 1 0.0670]
TrailLineColor: [1 1 0.0670]
VisibilityMode: 'inherit'
Visualize the satellite movement and its trace on the ground. The satellite covers the area around Japan during one half of the day and Australia during the other half.
play(sc);

Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: LeadTime=3600 sets the lead time of the ground track to 3600
seconds upon creation.
Satellite scenario viewer, specified as a scalar, vector, or array of satelliteScenarioViewer objects. If the AutoSimulate property of the scenario is false,
adding a satellite to the scenario disables any previously available timeline and
playback widgets.
Period of the ground track to be visualized in the satellite scenario viewer, specified as
'LeadTime' and a positive
scalar in seconds.
The default value is:
Satellite scenario
StartTimetoStopTimewhenOrbitPropagatoris set to'ephemeris'Satellite scenario
StartTimetoStopTimewhen the orbit is parabolic or hyperbolic andOrbitPropagatoris set to'numerical'One orbital period, in all other cases.
Period of the ground track history to be visualized in Viewer, specified
as 'TrailTime' and a positive scalar in
seconds.
The default value is:
Satellite scenario
StartTimetoStopTimewhenOrbitPropagatoris set to'ephemeris'Satellite scenario
StartTimetoStopTimewhen the orbit is parabolic or hyperbolic andOrbitPropagatoris set to'numerical'One orbital period, in all other cases.
Visual width of the ground track in pixels, specified as 'LineWidth' and
a scalar in the range (0 10].
The line width cannot be thinner than the width of a pixel. If you set the line width to a value that is less than the width of a pixel on your system, the line displays as one pixel wide.
Color of the future ground track line, specified as 'LeadLineColor' and
an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red"
|
"r"
|
[1 0 0]
|
"#FF0000"
|
|
"green"
|
"g"
|
[0 1 0]
|
"#00FF00"
|
|
"blue"
|
"b"
|
[0 0 1]
|
"#0000FF"
|
|
"cyan"
|
"c"
|
[0 1 1]
|
"#00FFFF"
|
|
"magenta"
|
"m"
|
[1 0 1]
|
"#FF00FF"
|
|
"yellow"
|
"y"
|
[1 1 0]
|
"#FFFF00"
|
|
"black"
|
"k"
|
[0 0 0]
|
"#000000"
|
|
"white"
|
"w"
|
[1 1 1]
|
"#FFFFFF"
|
|
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB® uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410]
|
"#0072BD"
|
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980]
|
"#D95319"
|
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250]
|
"#EDB120"
|
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560]
|
"#7E2F8E"
|
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880]
|
"#77AC30"
|
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330]
|
"#4DBEEE"
|
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840]
|
"#A2142F"
|
|
Example: 'blue'
Example: [0 0 1]
Example: '#0000FF'
Color of the ground track line history, specified as 'TrailLineColor' and
an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red"
|
"r"
|
[1 0 0]
|
"#FF0000"
|
|
"green"
|
"g"
|
[0 1 0]
|
"#00FF00"
|
|
"blue"
|
"b"
|
[0 0 1]
|
"#0000FF"
|
|
"cyan"
|
"c"
|
[0 1 1]
|
"#00FFFF"
|
|
"magenta"
|
"m"
|
[1 0 1]
|
"#FF00FF"
|
|
"yellow"
|
"y"
|
[1 1 0]
|
"#FFFF00"
|
|
"black"
|
"k"
|
[0 0 0]
|
"#000000"
|
|
"white"
|
"w"
|
[1 1 1]
|
"#FFFFFF"
|
|
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410]
|
"#0072BD"
|
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980]
|
"#D95319"
|
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250]
|
"#EDB120"
|
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560]
|
"#7E2F8E"
|
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880]
|
"#77AC30"
|
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330]
|
"#4DBEEE"
|
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840]
|
"#A2142F"
|
|
Example: 'blue'
Example: [0 0 1]
Example: '#0000FF'
Version History
Introduced in R2021a
See Also
Objects
Functions
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)