settlingtime
Settling time for bilevel waveform
Syntax
Description
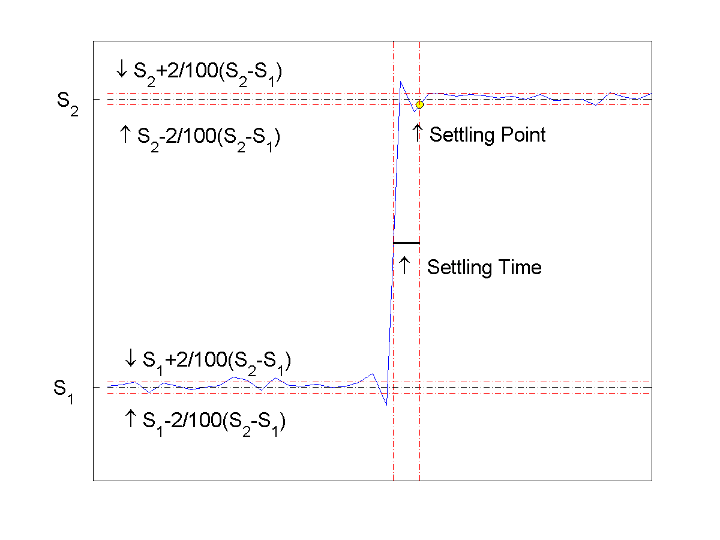
s = settlingtime(x,d)d. To determine the transitions, the
settlingtime function estimates the state levels of the
input waveform by a histogram method and identifies all regions that cross the
upper-state boundary of the low state and the lower-state boundary of the high state.
Note
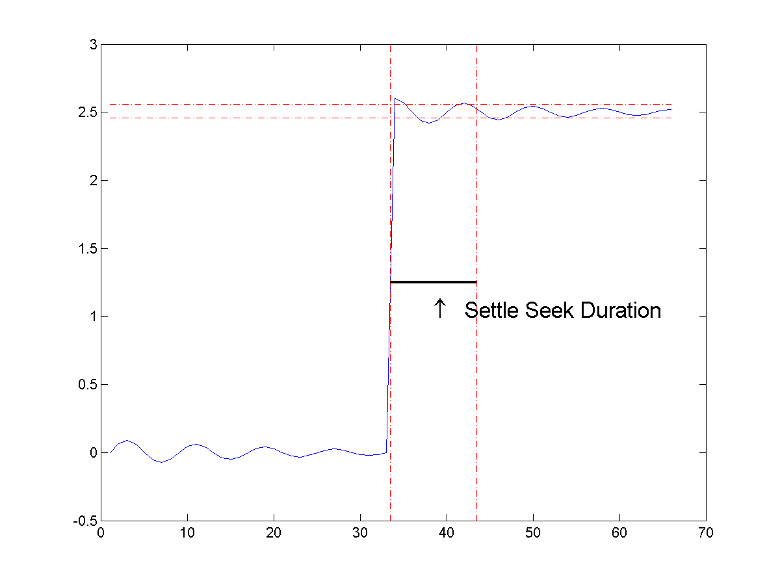
If for any transition, the level of the waveform does not remain within
the lower and upper tolerance boundaries, the requested duration is not
present, or an intervening transition is detected,
settlingtime marks the corresponding element in
s as NaN. For cases in which
settlingtime returns a NaN, see
Settle Seek Duration.
[
returns the settling times, levels, and corresponding sample instants with
additional options specified by one or more name-value arguments. You can specify an
input combination from any of the previous syntaxes.s,slev,sinst]
= settlingtime(___,Name,Value)
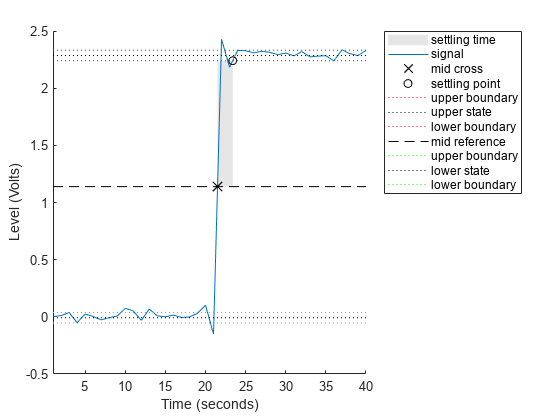
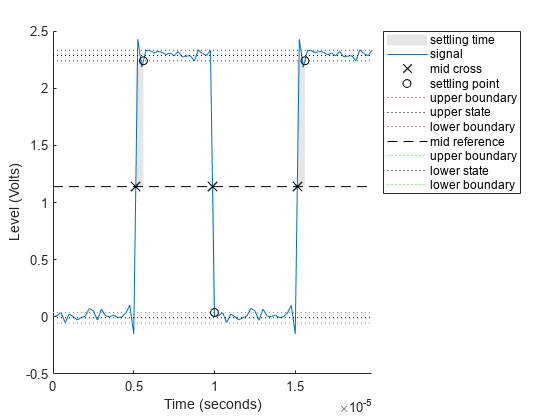
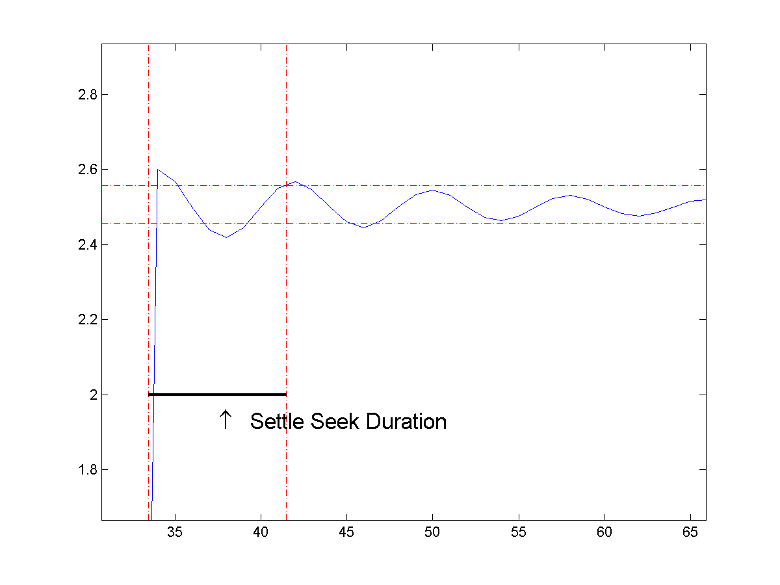
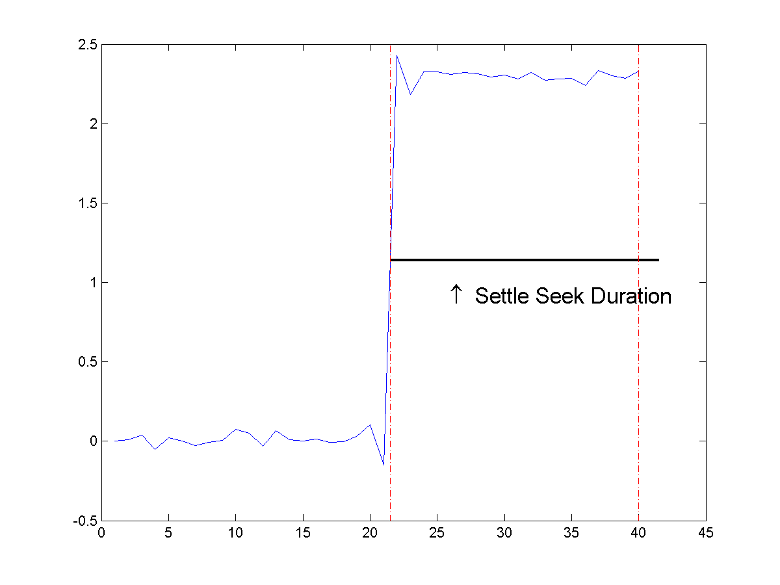
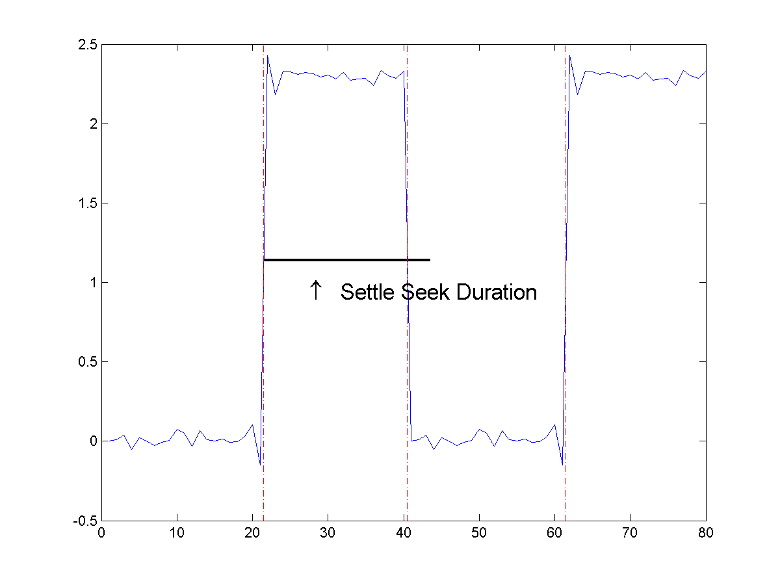
settlingtime(___) plots the signal and darkens
the regions of each transition where settling time is computed. The plot marks the
location of the settling time of each transition, the mid-crossings, and the
associated reference levels. The plot also displays the state levels with the
corresponding lower and upper tolerance boundaries.
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
More About
References
[1] IEEE® Standard on Transitions, Pulses, and Related Waveforms, IEEE Standard 181, 2003, pp. 23–24.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2012a
See Also
falltime | midcross | pulsewidth | risetime | statelevels