Call C Function Containing C Structure into Simulink
This example shows how to integrate a C function containing C structures into Simulink® using a C Caller block. The C structure (struct) variables are mapped into Simulink® using bus signals and bus data types in a C Caller block.
Generate Simulink Representation of struct Type
This example uses Simulink.importExternalCTypes to parse the header file for struct definition and generate a Simulink representation of this type. The type appears in the MATLAB® workspace.
Simulink.importExternalCTypes('CStructBus.h');Open the model containing the C Caller block.
mdl= "CCallerBusOps.slx";
open_system(mdl)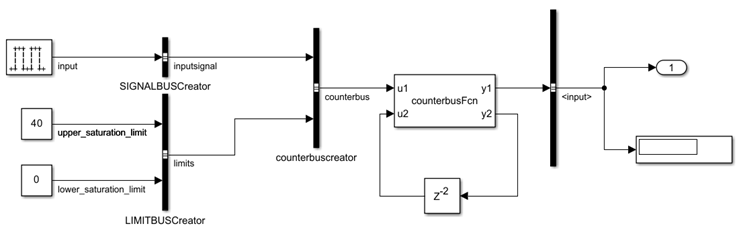
Bus Operations
An input signal and signals representing an upper limit (40) and lower limit (0) are grouped together in the custom C function using C structures (struct).
The C Caller block maps the structure into Simulink® using a bus and a Bus Creator block. The C function counterbusFcn computes a cumulative sum and checks whether the sum value is within the limits. At a given time step, the cumulative sum is calculated by adding the pulse signal value at that time step to the sum value from two time steps prior. A Bus Selector block extracts the output signal element from the output bus signal.
The prototype of the counterbusFcn function is: void counterbusFcn(const counterbus *u1, int32_T u2, counterbus *y1, int32_T *y2)
C Caller Block Configuration
In this example, the C function is declared in CStructBus.h, and the operations are defined in CStructBus.c. To observe the configuration of the C Caller block that calls the function:
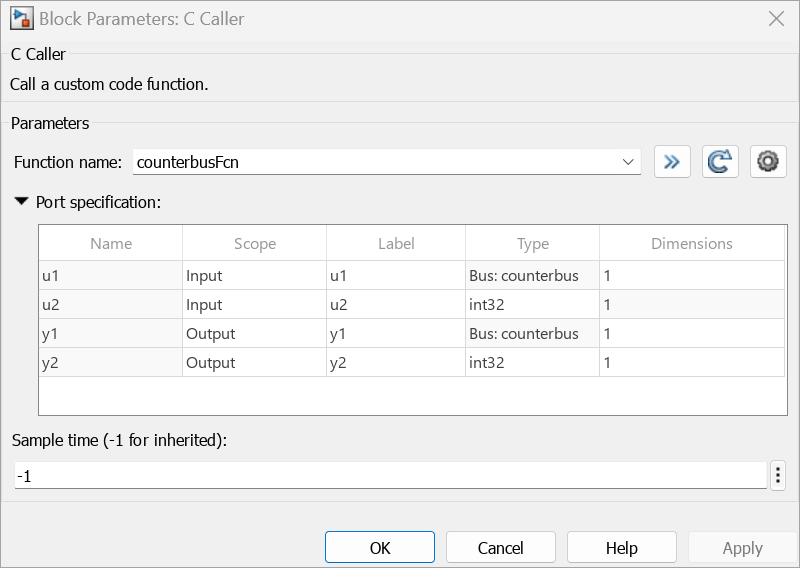
Open the Block Parameters dialog box and observe that Function name specifies
counterbusFcn.In the dialog box, click
 . This action opens the Configuration Parameters dialog box.
. This action opens the Configuration Parameters dialog box.In the Configuration Parameters dialog box, under the Simulation Target pane, select the Code information tab. Observe that Include headers specifies
"CStructBus.h", and the Source files specifiesCStructBus.c.
Observe that the C Caller block populates Scope values for the input arguments u1 and u2 as Input. Similarly, the block populates Scope values for arguments y1 and y2 as InputOutput because the arguments are pass-by-pointer type and not read-only. The output of the function is written to the memory pointed by the pointer. In this example, to use y1 and y2 solely for output, the Scope of y1 and y2 are changed to Output.
Similarly, the C Caller block populates the argument names to the corresponding Label fields. These labels also represent corresponding port names.
In addition to the above port properties, the block populates data types of struct members as Bus. For example, the block populates the Type of members (u1 and y1) of counterbus as Bus:counterbus.
Simulate and Visualize Results
Simulate the model for different time durations and visualize the results using a Display block. Observe these results at different simulation time steps:
For Stop Time of
5s, the Display block displays26.For Stop Time of
5.1s, the Display block displays0.
At both 5 s and 5.1 s, the cumulative sum is within the limits, and the model outputs the sum.
For Stop Time of
10s, the Display block displays40.For Stop Time of
11s, the Display block displays40.
However, at 10 s and 11 s, the cumulative sum is either more than or equal to the upper limit. Consequently, the Display block displays the upper limit of 40.
out = sim(mdl);
See Also
C Caller | Bus Creator | Bus Selector | Delay