Maintain Compatibility of Library Blocks Using Forwarding Tables
Forwarding Table allow you to check that the changes to blocks in a library do not break the model if you have saved the model with an older version of the library block. Forwarding tables help you to maintain compatibility of library blocks when you change the path or name of the library, or add, remove, or rename the parameters in the library block. For more information see, Create Custom Library.
Create a forwarding table entry for mapping old library blocks to new library blocks.
When you open the model, the links to the old library block are updated automatically
without losing data or functionality. Forwarding tables are executed when you open a
model, close a model, or when you execute the add_block or
replace_block command.
Create a forwarding table entry when you:
Rename a block.
Move a block from one library to another library.
Add or remove parameters from the block.
Split the functionality of a block.
Forwarding Table Entry for a Renamed Block
Consider an example where the block name in a library testlib
is renamed from ss1 to ss2.
Open the locked library
Lib1.In the Library window, on the Library tab, click Locked Library. The library is now unlocked for editing.
On the Modeling tab, click Library Properties. The Library Properties dialog box opens.
Click the Forwarding Table tab.
Click Add New entry. A new row is added in the forwarding table.
Specify the name of the old block in Old Block Path and the corresponding new block path in the New Block Path. If you do not know the path, select the block in the model and click Get gcb button. The path of the block is automatically populated in the respective columns.

The mapping of the old path to new path is created in the forwarding table. Now, open a model that contains links to the library. The links to the old library blocks in the model are updated automatically. You can use the search bar above the table to filter the table contents. You can sort the columns in ascending or descending order. You can also group columns by their values.
Assign Version Numbers to Library Blocks
In the Version column, you can specify a version number for the library block.
If the old block name is the same as new block name, the forwarding table
populates the version number automatically. The initial value of the library version
LibraryVersion is derived from the
ModelVersion property of the library at the time the library
link is created. Any subsequent updates to the library block will update the library
version to match the model version of the library.
The version number:
Must be a numeric value.
Must be of the format
<major_version>.<minor_version>when the old and the new block paths are the same.Must not have more than one dot notation. For example, a version number of 1.3 is acceptable. A version number 1.3.1 is not acceptable.
Format is not critical when you use a forwarding table to move a library block from one library to another.
Move Block from One Library to Another
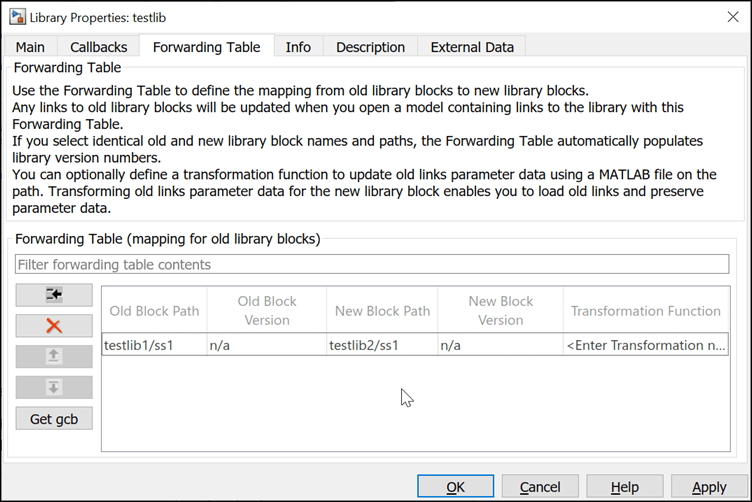
Consider an example where a block ss1 is moved from
testlib1 to testlib2`. The forwarding
table entry in this case is shown here:
Add or Remove Parameters from the Block
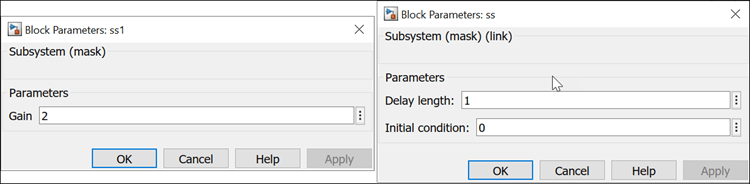
Consider an example where the Gain parameter of
ss1 in library testlibis removed, and two
other parameters Initial condition and Delay
length are added to it.
To handle this change we use a transformation function. A transformation function
corrects the mismatch of parameters between the new and old library links, which
ensures that the library links continue to work. You can define a transformation
function using a .m function file on MATLAB® path, then call the function in the Transformation Function column of the Forwarding Table.
A linked block contains an instance of the block parameters in the form of
name-value arguments to instantiate the block. This instance data is passed to
transformation function as InstanceData along with forwarding
entry. This data is stored as struct fields.
When you create versions of a library block, parameters are added or removed from
the InstanceData. In this example, the
InstanceData before removal of the Gain parameter and after the addition of initial condition and delay
length looks like this
Before:
'RTWMemSecFuncInitTerm' 'Inherit from model' 'RTWMemSecFuncExecute' 'Inherit from model' 'RTWMemSecDataConstants' 'Inherit from model' 'RTWMemSecDataInternal' 'Inherit from model' 'RTWMemSecDataParameters' 'Inherit from model' 'ContentPreviewEnabled' 'on' 'Gain' '0'
After:
'RTWMemSecFuncInitTerm' 'Inherit from model' 'RTWMemSecFuncExecute' 'Inherit from model' 'RTWMemSecDataConstants' 'Inherit from model' 'RTWMemSecDataInternal' 'Inherit from model' 'RTWMemSecDataParameters' 'Inherit from model' 'ContentPreviewEnabled' 'on' 'DelayLength' '1' 'InitialCondition' '0'
This is the syntax for transformation function.
function outData = TransformationFcn(inData)In this function syntax:
inDatais a structure with fieldsForwardingTableEntryandInstanceData.ForwardingTableEntryis also a structure.The
ForwardingTableEntryhas the old name, new name, old path, and new path of a block. Refer to the code to access the members of theForwardingTableEntry.
outDatais a structure with fieldsNewInstanceDataandNewBlockPath.
To add or remove parameters from a block:
Obtain the instance data and the forwarding table entry.
Extract the list of name-value pair and block names.
Get the old and new block names.
Check if the old and new block names are same. If so, then extract the versions of the block.
Check if the old version is 1.1 and the new version is 1.2. Then, remove the
Gainparameter and add the parametersDelay lengthandInitial condition.
Note
You can have multiple transformation function files for your library. However, for effective maintenance it is recommended that you have one transformation function file per library.
To add or remove parameters, use this transformation function.
function [outData] = txFcnTestlib(inData) outData.NewBlockPath = ''; outData.NewInstanceData = []; % Get linked block instance data and forwarding entry for which % function is called instanceData = inData.InstanceData; forwardingTableEntry = inData.ForwardingTableEntry; % Get list of name value pair and block names [ParamNames{1:length(instanceData)}] = instanceData.Name; % Get old and new block paths or simply names oldName = forwardingTableEntry.('__slOldName__'); newName = forwardingTableEntry.('__slNewName__'); % If block names are same and its subsys block in the lib if strcmp(oldName, newName) % Get old and new block versions from forwarding table oldVer = forwardingTableEntry.('__slOldVersion__'); newVer = forwardingTableEntry.('__slNewVersion__'); % Each forwarding entry with different version can have separate % entry. Here, for one single entry in forwarding table i.e. % 1.2->1.3 or 1.3->2.0, we have separate transformation making one % TX Fcn for one library or block. if strcmp(oldName, 'testlib/ss1') % Forwarding with same block name ss1 if oldVer == '1.1' && newVer == '1.2' % Remove gain param if (ismember('Gain',ParamNames)) for (i = 1:length(instanceData)) if (strcmp(instanceData(i).Name,'Gain') == true) instanceData(i) = []; break; end end end % Add delay length param if (ismember('DelayLength',ParamNames)) for (i = 1:length(instanceData)) if (strcmp(instanceData(i).Name,'Value') == true) instanceData(i).Value = '5'; break; end end else instanceData(end+1).Name = 'DelayLength'; instanceData(end).Value = '1'; end % Add initial condition param if (ismember('InitialCondition',ParamNames)) for (i = 1:length(instanceData)) if (strcmp(instanceData(i).Name,'InitialCondition') == true) instanceData(i).Value = '0'; break; end end else instanceData(end+1).Name = 'InitialCondition'; instanceData(end).Value = '0'; end elseif (oldVer == '1.2' && newVer == '1.3') % Do version 1.2 to 1.3 specific changes elseif (oldVer == '1.3' && newVer == '2.0') % Do version 1.3 to 2.0 specific changes else % Do default changes not applicable to any version if % required end elseif strcmp(oldName, 'testlib/ss2') % Forwarding for block ss2 with version upgrade end elseif strcmp(oldName, 'testlib/oldblk') && strcmp(newName, 'testlib2/newblk') % Block moved to new library or just block is renamed within same % library, no version is checked here. Do transformation is % required i.e. is block has been modified while renaming or moving % to new lib. elseif strcmp(oldName, 'testlib/blkX') && isempty(newName) % We are splitting the block into 2 different blocks. Hence, kept % newName empty in fwd table. Using one of the block param from its % instance data (which is name-value pair of all block params) to % decide how and what to divide. % Get the index of param we are interested in i.e. param X i = find(contains({instanceData.Name},'X'), true); % Based on its value, do block splitting switch (instanceData(i).Value) case 'op1' newName = 'newlibX/blkX'; % Remove existing param or add new param or modify existing % params etc. case 'op2' newName = 'newlibY/blkX'; otherwise newName = oldName; end end % Return new instance data and new block path outData.NewInstanceData = instanceData; outData.NewBlockPath = newName; end
Split Block Functionality
Splitting the functionality of a block involves adding, removing, or modifying the existing parameter of the block and adding it to the new block. To split the functionality of a block:
Leave the
newNameargument empty.Get the index and value of the parameter.
Split the block based on its value.
Return the
NewBlockPathwith the updatedInstanceDataif required.
Create Mask Parameter Aliases
If you rename a mask parameter, you must ensure that the existing MATLAB scripts that use the old parameter names, continues to work. To check compatibility, you can create an alias for a mask parameter name. An alias allows you to change the name of a mask parameter in a library block without having to recreate links to the block in existing models.
Consider a masked block that contains an Edit parameter. The
mask parameter name for this Edit parameter is
p1.
MaskObj = Simulink.Mask.get(gcb)); hEdit = MaskObj.getParameter('p1'); hEdit= % MaskParameter with properties: Type: 'edit' TypeOptions: {0×1 cell} Name: 'p1' Prompt: 'p1' Value: '0' Evaluate: 'on' Tunable: 'on' NeverSave: 'off' Hidden: 'off' Enabled: 'on' Visible: 'on' ToolTip: 'on' Callback: '' Alias: ''
Notice that the Edit mask parameter does not have an alias.
To add an alias for the mask parameter, set a value for the Alias
mask parameter property.
MaskObj.Alias = 'pa'You can either use the mask parameter name or the alias to do a function call on
the mask parameter. For example, you can either use set_param(gcb, 'p1,
'10) (mask parameter name) or set_param(gcb, 'pa,
'10) (mask parameter alias) to set a value for the
Edit mask parameter.