Non-HT PPDU Structure
IEEE® 802.11™is a packet-based protocol. Each packet, also called a physical layer protocol data unit (PPDU), contains preamble and data fields. The preamble fields contain the transmission vector format information. The data field contains the user payload and higher layer headers, such as medium access control (MAC) fields and cyclic redundancy check (CRC). The transmission vector format and the PPDU structure vary between 802.11 versions. The transmission vector (TXVECTOR) format parameter is classified as:
non-HT to specify a PHY implementation that predates the 802.11n™ standard. Non-HT means non-high-throughput.
Section 17 of [1] defines and describes the OFDM PHY layer and PPDU for non-HT transmission. In addition to supporting non-HT synchronization, the non-HT preamble fields are used in support of HT, VHT, HE, and EHT synchronization.
The table shows 802.11 versions that WLAN Toolbox™ supports, along with the supported TXVECTOR options and associated modulation formats.
802.11 Version | Transmission Vector Format | Modulation Format | Bandwidth/MHz |
|---|---|---|---|
802.11b™ | non-HT | DSSS/CCK | 11 |
| 802.11a™ | non-HT | OFDM only | 5, 10, 20 |
802.11j™ | non-HT | OFDM only | 10 |
802.11p™ | non-HT | OFDM only | 5, 10 |
802.11g™ | non-HT | OFDM | 20 |
non-HT | DSSS/CCK | 11 | |
802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) | HT | OFDM only | 20, 40 |
802.11ac™ (Wi-Fi 5) | VHT | OFDM only | 20, 40, 80, 160 |
802.11ah™ | S1G | OFDM only | 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 |
802.11ad™ | DMG | Single Carrier and OFDM | 2640 |
802.11ax™ (Wi-Fi 6) | HE | OFDMA | 20, 40, 80, 160 |
| 802.11ba™ | WUR | MC-OOK | 20, 40, 80 |
| 802.11be™ (Wi-Fi 7) | EHT | OFDMA | 20, 40, 80, 160, 320 |
To create non-HT PPDUs and waveforms, use the wlanNonHTConfig object.
A non-HT PPDU is made up of preamble and data portions. The legacy preamble fields (L-STF, L-LTF, and L-SIG) are common to non-HT, HT, VHT, HE, and EHT preambles. This diagram1 shows the structure of a non-HT PPDU.
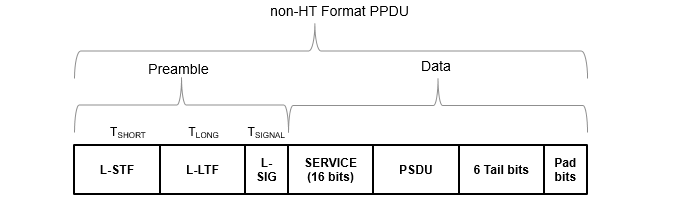
PPDU Field Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|
L-STF | Non-HT Short Training field |
L-LTF | Non-HT Long Training field |
L-SIG | Non-HT SIGNAL field |
Data | The non-HT Data fields includes the service bits, PSDU, tail bits, and pad bits |
Non-HT (Legacy) Preamble Fields
The legacy short training field (L-STF) is the first field of the 802.11 OFDM PLCP legacy preamble. The L-STF is a component of EHT, HE, VHT, HT, and non-HT PPDUs. This diagram2 shows the L-STF in the legacy preamble.
The L-STF duration varies with channel bandwidth.
| Channel Bandwidth (MHz) | Subcarrier Frequency Spacing, ΔF (kHz) | Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Period (TFFT = 1 / ΔF) | L-STF Duration (TSHORT = 10 × TFFT / 4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20, 40, 80, 160, and 320 | 312.5 | 3.2 μs | 8 μs |
| 10 | 156.25 | 6.4 μs | 16 μs |
| 5 | 78.125 | 12.8 μs | 32 μs |
Because the sequence has good correlation properties, receivers use it for start-of-packet detection, coarse frequency correction, and setting the AGC. The sequence uses 12 of the 52 subcarriers that are available per 20 MHz channel bandwidth segment. For 5 MHz, 10 MHz, and 20 MHz bandwidths, the number of channel bandwidth segments is one.
The L-LTF is the second field in the 802.11 OFDM PLCP legacy preamble. The L-LTF is a component of EHT, HE, VHT, HT, and non-HT PPDUs. This diagram3 shows the L-LTF in the legacy preamble.
Channel estimation, fine frequency offset estimation, and fine symbol timing offset estimation rely on the L-LTF.
The L-LTF is composed of a cyclic prefix (CP) followed by two identical long training symbols (C1 and C2). The CP consists of the second half of the long training symbol.
The L-LTF duration varies with channel bandwidth.
| Channel Bandwidth (MHz) | Subcarrier Frequency Spacing ΔF (kHz) | Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Period (TFFT = 1 / ΔF) | Cyclic Prefix or Training Symbol Guard Interval (GI2) Duration (TGI2 = TFFT / 2) | L-LTF Duration (TLONG = TGI2 + 2 × TFFT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20, 40, 80, 160, and 320 | 312.5 | 3.2 μs | 1.6 μs | 8 μs |
| 10 | 156.25 | 6.4 μs | 3.2 μs | 16 μs |
| 5 | 78.125 | 12.8 μs | 6.4 μs | 32 μs |
The L-SIG is the third field of the 802.11 OFDM PLCP legacy preamble. This field is a component of EHT, HE, VHT, HT, and non-HT PPDUs. It consists of 24 bits that contain rate, length, and parity information. The L-SIG field uses BPSK modulation with rate 1/2 binary convolutional coding (BCC). This diagram4 shows the L-SIG field in the legacy preamble.
The L-SIG consists of one OFDM symbol with a duration that varies with channel bandwidth.
| Channel Bandwidth (MHz) | Subcarrier Frequency Spacing ΔF (kHz) | Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Period (TFFT = 1 / ΔF) | Guard Interval (GI) Duration (TGI = TFFT / 4) | L-SIG Duration (TSIGNAL = TGI + TFFT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20, 40, 80, 160, and 320 | 312.5 | 3.2 μs | 0.8 μs | 4 μs |
| 10 | 156.25 | 6.4 μs | 1.6 μs | 8 μs |
| 5 | 78.125 | 12.8 μs | 3.2 μs | 16 μs |
The L-SIG contains packet information for the received configuration. This diagram5 shows the information that the L-SIG bits carry.
Bits 0 through 3 specify the data rate (modulation and coding rate) for the non-HT format. This table6 shows the values.
Rate (Bits 0–3) Modulation Coding Rate (R)
Data Rate (Mb/s) 20 MHz Channel Bandwidth 10 MHz Channel Bandwidth 5 MHz Channel Bandwidth 1101 BPSK 1/2 6 3 1.5 1111 BPSK 3/4 9 4.5 2.25 0101 QPSK 1/2 12 6 3 0111 QPSK 3/4 18 9 4.5 1001 16-QAM 1/2 24 12 6 1011 16-QAM 3/4 36 18 9 0001 64-QAM 2/3 48 24 12 0011 64-QAM 3/4 54 27 13.5 For HT and VHT formats, the L-SIG rate bits are set to
'1 1 0 1'. Data rate information for HT and VHT formats is signaled in format-specific signaling fields.Bit 4 is reserved for future use.
Bits 5 through 16:
For non-HT formats, specify the data length (amount of data transmitted in octets) as described in Table 17-1 and Section 10.27.4 IEEE Std 802.11-2020.
For HT-mixed formats, specify the transmission time as described in Sections 19.3.9.3.5 and 10.27.4 of IEEE Std 802.11-2020.
For VHT formats, specify the transmission time as described in Section 21.3.8.2.4 of IEEE Std 802.11-2020.
Bit 17 has the even parity of bits 0 through 16.
Bits 18 through 23 contain all zeros for the signal tail bits.
Note
Signaling fields added for HT (wlanHTSIG)
and VHT (wlanVHTSIGA, wlanVHTSIGB) formats provide data rate
and configuration information for those formats.
For the HT-mixed format, Section 19.3.9.4.3 of IEEE Std 802.11-2020 describes HT-SIG bit settings.
For the VHT format, Sections 21.3.8.3.3 and 21.3.8.3.6 of IEEE Std 802.11-2020 describe bit settings for the VHT-SIG-A and VHT-SIG-B fields, respectively.
Non-HT Data Field
The non-high throughput Data (non-HT Data) field is used to transmit MAC frames and is composed of a service field, a PSDU, tail bits, and pad bits. This diagram7 shows the non-HT data field.
Service field — Contains 16 zeros to initialize the data scrambler.
PSDU — Variable-length field containing the PLCP service data unit (PSDU).
Tail — Tail bits required to terminate a convolutional code. The field uses six zeros for the single encoding stream.
Pad Bits — Variable-length field required to ensure that the non-HT data field contains an integer number of symbols.
Processing of an 802.11a data field is defined in Section 17.3.5 of [1].
References
[1] IEEE Std 802.11-2020 (Revision of IEEE Std 802.11-2016). “Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications.” IEEE Standard for Information Technology — Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems — Local and Metropolitan Area Networks — Specific Requirements.
1 IEEE Std 802.11-2020 Adapted and reprinted with permission from IEEE. Copyright IEEE 2020. All rights reserved.
2 IEEE Std 802.11-2020 Adapted and reprinted with permission from IEEE. Copyright IEEE 2020. All rights reserved.
3 IEEE Std 802.11-2020 Adapted and reprinted with permission from IEEE. Copyright IEEE 2020. All rights reserved.
4 IEEE Std 802.11-2020 Adapted and reprinted with permission from IEEE. Copyright IEEE 2020. All rights reserved.
5 © IEEE 2021. All rights reserved.
6 © IEEE 2021. All rights reserved.
7 IEEE Std 802.11-2020 Adapted and reprinted with permission from IEEE. Copyright IEEE 2020. All rights reserved.