Global Variables Usage in Polyspace Platform User Interface
This topic focuses on the Polyspace® Platform user interface. To learn about the equivalent pane in the Polyspace Access™ desktop interface, see Variable Access in Polyspace Desktop User Interface.
The Global Variables Usage pane displays global variables and local static variables. For each global variable, the pane lists all functions and tasks performing read/write access on the variables, along with their attributes, such as values, read/write accesses and shared usage.
Open the Global Variables Usage pane by using the ![]() icon in your Results Details pane,
or by going to Window > Global Variables Usage. Additionally, you can open the Global Variables Usage
pane by selecting a global variable in the Source Code pane,
right-clicking, and selecting Show Global Variable usage.
icon in your Results Details pane,
or by going to Window > Global Variables Usage. Additionally, you can open the Global Variables Usage
pane by selecting a global variable in the Source Code pane,
right-clicking, and selecting Show Global Variable usage.
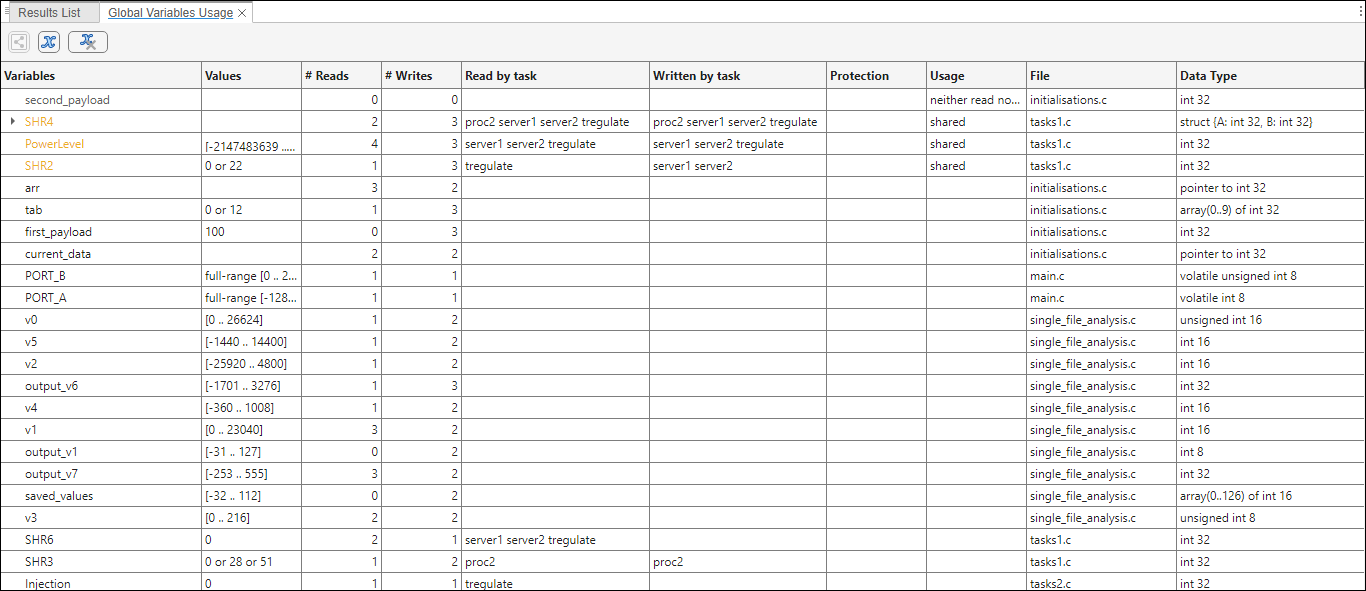
For each variable and each read/write access, the Global Variables Usage pane contains the relevant attributes. For the variables, the various attributes are listed in this table.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Variables | Name of Variable |
| Values | Value (or range of values) of variable This column is empty for pointer variables. |
| # Reads | Number of times the variable is read |
| # Writes | Number of times the variable is written |
| Read by task | Name of tasks reading variable |
| Written by task | Name of tasks writing on variable |
| Protection | Whether shared variable is protected from concurrent access (Filled only when Usage column has entry, Shared) The possible entries in this column are:
For more details on these entries, see the documentation for Polyspace Code Prover™ or Polyspace Code Prover Server™. |
| Usage | Shared, if variable is shared between tasks; otherwise,
blank |
| File | Source file containing variable declaration |
| Data Type | Data type of variable (C/C++ data types or structures/classes) |
Click a variable name to view read/write access operations on the variable in the
Global Variable Accesses pane. The arrowhead symbols ![]() (read) and
(read) and ![]() in the Global Variable Accesses pane
indicate functions performing read and write access respectively on the global variable.
For further information on tasks, see analysis option
in the Global Variable Accesses pane
indicate functions performing read and write access respectively on the global variable.
For further information on tasks, see analysis option Tasks (-entry-points).
For access operations on the variables, the various attributes described in the Global Variables Usage pane are listed in this table.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Values | Value or range of values of variable in the function or task performing read/write access This column is empty for pointer variables. |
| Written by task | Only for tasks: Name of task performing write access on variable |
| Read by task | Only for tasks: Name of task performing read access on variable |
| File | Source file containing access operation on variable |
The Global Variables Accesses pane also lists the Scope of the access operation on the variable.
For example, consider the global variable, SHR2:
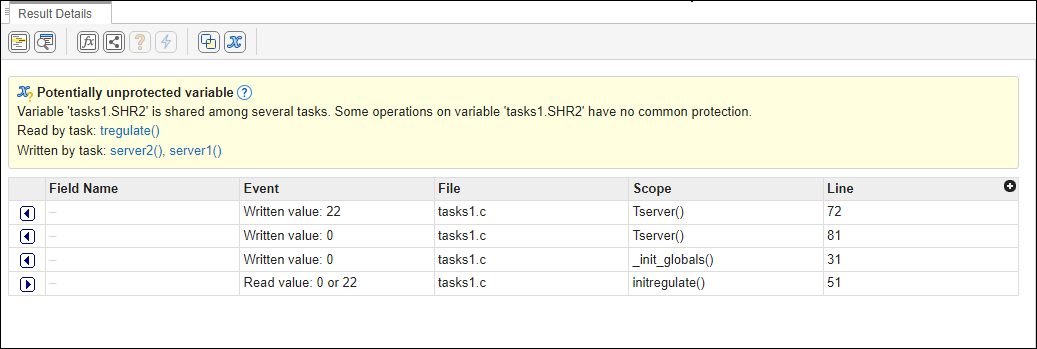
The function, Tserver(), in the file, tasks1.c,
performs two write operations on SHR2. This is indicated in the
Global Variables Accesses pane by the two instances of
Tserver() in the table, marked by ![]() . Likewise, the read access by task
. Likewise, the read access by task
initregulate() is also listed in the table and marked by ![]() .
.
The color scheme for variables in the Global Variables Usage pane is:
Black: global variable.
Orange: global variable, shared between tasks with no protection against concurrent access.
Green: global variable, shared between tasks and protected against concurrent access.
Gray: global variable, declared but not used in reachable code.
If a task performs certain operations on a global variable, but the operations are in unreachable code, the tasks are colored gray.
The information about global variables and read/write access operations obtained from the Global Variables Usage pane is called the data dictionary.
You can also perform the following actions from the Global Variables Usage pane.
View Structured Variables
For structured variables, double click the variable in the Global Variables Usage pane to view the individual fields. For example, for the structure,
SHR4, the pane displays the fields,SHR4.AandSHR4.B, and the functions performing read/write access on them.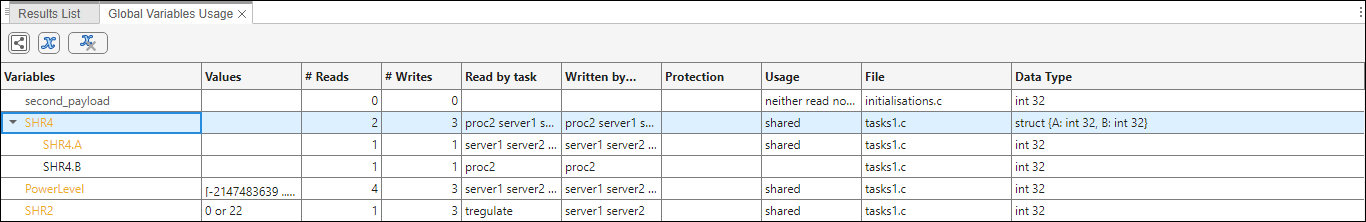
View Access Through Global Pointers
If a read/write access on a variable is performed indirectly through global pointers, then the access is marked by
 (read) or
(read) or  (write).
(write).For instance, in the file,
initialisations.c, the variable,arr, is declared as a pointer to the array,tab.In the file
main.c,tabis read in the function,interpolation(), through the pointer variable,arr. This operation is shown in the Global Variable Accesses pane by the icon. Click the row in the table in the
Global Variables Accesses pane to show the relevant line of
code in the Source Code pane.
icon. Click the row in the table in the
Global Variables Accesses pane to show the relevant line of
code in the Source Code pane.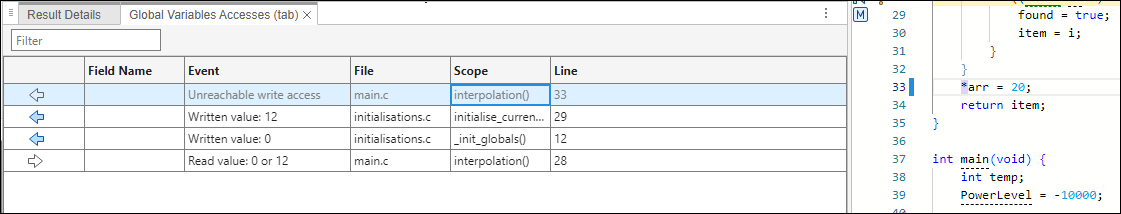
During dynamic memory allocation, memory is allocated directly to a pointer. Because the Values column is populated only for non-pointer variables, you cannot use this column to find the values stored in dynamically allocated memory. Use the Global Variables pane to navigate to dereferences of the pointer on the Source pane. Use the tooltips on this pane to find the values following each pointer dereference.
Show/Hide Callers and Callees
Customize the Global Variables Usage pane to show only the shared variables. On the Global Variables Usage pane toolbar, click the Non-Shared Variables button
 to show or hide non-shared variables.
to show or hide non-shared variables.Hide Access in Unreachable Code
Hide read/write access occurring in unreachable code by clicking the
 icon.
icon.
Limitations
You cannot see an addressing operation on a global variable or object (in C++) as a read/write operation in the Global Variables Usage pane. For example, consider the following C++ code:
class C0
{
public:
C0() {}
int get_flag()
{
volatile int rd;
return rd;
}
~C0() {}
private:
int a; /* Never read/written */
};
C0 c0; /* c0 is unreachable */
int main()
{
if (c0.get_flag()) /* Uses address of the method */
{
int *ptr = take_addr_of_x();
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}You do not see the method call c0.get_flag() in the
Global Variables Usage pane because the call is an addressing
operation on the method belonging to the object c0.