genqammod
General quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)
Description
Examples
Transmit and receive data using a nonrectangular 16-ary constellation in the presence of Gaussian noise. Show the scatter plot of the noisy constellation and estimate the symbol error rate (SER) for two different SNRs.
Create a 16-QAM constellation based on the V.29 standard for telephone-line modems.
c = [-5 -5i 5 5i -3 -3-3i -3i 3-3i 3 3+3i 3i -3+3i -1 -1i 1 1i]; sigpower = pow2db(mean(abs(c).^2)); M = length(c);
Generate random symbols.
data = randi([0 M-1],2000,1);
Modulate the data by using the genqammod function. General QAM modulation is necessary because the custom constellation is not rectangular.
modData = genqammod(data,c);
Pass the signal through an AWGN channel with a 20 dB SNR.
rxSig = awgn(modData,20,sigpower);
Display a scatter plot of the received signal and the reference constellation c.
h = scatterplot(rxSig); hold on scatterplot(c,[],[],'r*',h) grid hold off

Demodulate the received signal by using the genqamdemod function. Determine the number of symbol errors and the SER.
demodData = genqamdemod(rxSig,c); [numErrors,ser] = symerr(data,demodData)
numErrors = 4
ser = 0.0020
Repeat the transmission and demodulation process with an AWGN channel with a 10 dB SNR. Determine the SER for the reduced SNR. As expected, the performance degrades when the SNR is decreased.
rxSig = awgn(modData,10,sigpower); demodData = genqamdemod(rxSig,c); [numErrors,ser] = symerr(data,demodData)
numErrors = 457
ser = 0.2285
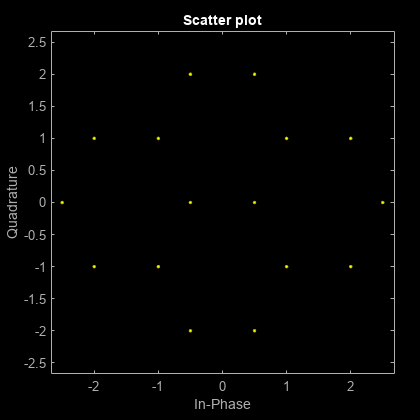
Create the points that describe a hexagonal constellation.
inphase = [1/2 1 1 1/2 1/2 2 2 5/2]; quadr = [0 1 -1 2 -2 1 -1 0]; inphase = [inphase;-inphase]; inphase = inphase(:); quadr = [quadr;quadr]; quadr = quadr(:); const = inphase + 1i*quadr;
Plot the constellation.
h = scatterplot(const);
Generate input data symbols. Modulate the symbols using this constellation.
x = [3 8 5 10 7]; y = genqammod(x,const);
Demodulate the modulated signal, y.
z = genqamdemod(y,const);
Plot the modulated signal in same figure.
hold on; scatterplot(y,1,0,'ro',h); legend('Constellation','Modulated signal'); hold off;
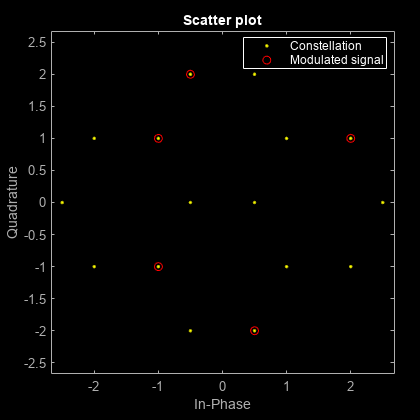
Determine the number of symbol errors between the demodulated data to the original sequence.
numErrs = symerr(x,z)
numErrs = 0
Input Arguments
Message signal, specified as a scalar, vector, matrix, 3-D array, 4-D array,
dlarray (Deep Learning Toolbox)
object, or gpuArray object. For more information, see Array Support. The message signal
must be binary values or consist of integers in the range
[0,length(const) – 1]. If X
is a matrix with multiple rows, the function processes the columns independently.
Data Types: double | single | fi | int8 | int16 | uint8 | uint16
Signal mapping, specified as a complex vector, dlarray (Deep Learning Toolbox)
object, or gpuArray object .
Data Types: double | single | fi | int8 | int16 | uint8 | uint16
Complex Number Support: Yes
Input type, specified as one of these options.
"integer"— The message signal is an integer in the range [0, M-1], where M is the length of the constellation."bit"— The message signal is binary, containing values of0and1. In this case, the number of rows must be an integer multiple of log2(M). The function maps a group of log2(M) bits onto a symbol, with the first bit representing the most significant bit (MSB) and the last bit representing the lowest significant bit (LSB).
Output Arguments
Complex envelope, returned as a scalar, vector, matrix, 3-D array, 4-D array,
dlarray object, or gpuArray object.
y is a gpuArray object if either
x or const is a gpuArray
object. y is a dlarray object if either
x or const is a dlarray
object.
For integer inputs, output Y has the same dimensions as input
signal X. For bit inputs, the number of rows in
Y is the number of rows in X divided by
log2(M).
Data Types: double | single | fi | int8 | int16 | uint8 | uint16
Complex Number Support: Yes
More About
The genqammod function supports input signals represented in a
numeric array, dlarray (Deep Learning Toolbox), or
gpuArray (Parallel Computing Toolbox). If inputs are specified as a
combination of dlarray and gpuArray, the returned
matrix is a dlarray object on the GPU.
The number of batch observations (NB) is an optional dimension that can be added to the input for all supported data types.
X— The input data can be a 3-D array, specified as NSym-by-NChan-by-NB array.
NSym is the number of symbols. NChan is the number of channels.
For a list of Communications Toolbox™ features that support dlarray objects, see AI for Wireless.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
This function supports GPU array inputs. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced before R2006aThe genqammod function adds support for C code generation with
input signals stored as dlarray (Deep Learning Toolbox)
objects.
The genqammod function adds support for dlarray (Deep Learning Toolbox) object
processing for deep learning applications.
The genqammod function adds support for gpuArray (Parallel Computing Toolbox) object processing to run code on a graphics processing unit (GPU).
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)