mapaxes
Description
Create Map Axes
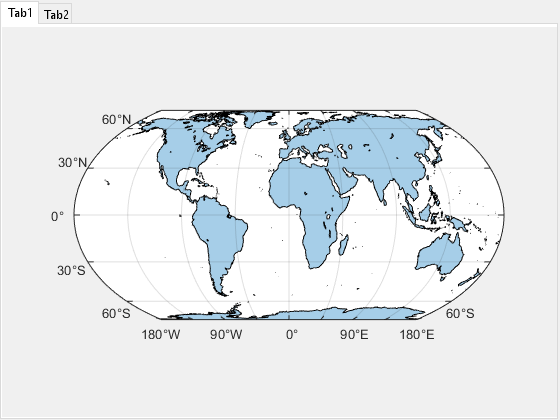
mapaxes creates the default map axes in the current figure. By
default, the function creates a world map that uses an Equal Earth projection.
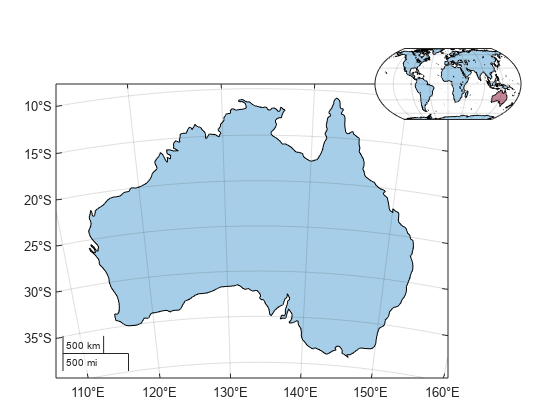
Use the mapaxes function when you want advanced control of the
map axes, or when you want to include the map axes in an app. In other cases, create a map
axes by using the newmap
function.
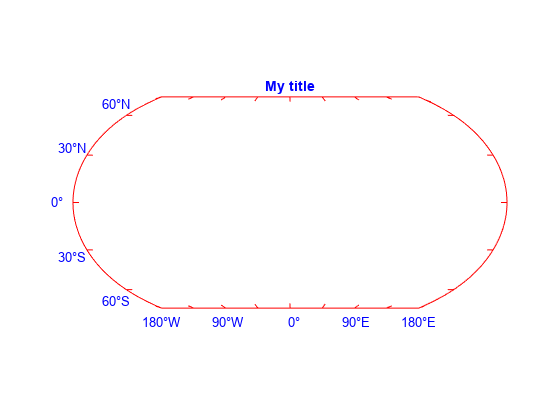
mapaxes( specifies options for
the map axes using one or more name-value arguments. For example,
Name=Value)FontSize=14 sets the font size for the map axes text to 14 points.
For a list of properties, see MapAxes Properties.
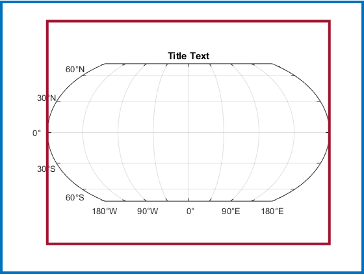
mapaxes( creates the
map axes in the object specified by parent,___)parent, instead of in the current
figure, in addition to any combination of inputs from the previous syntaxes.
mx = mapaxes(___) returns the
MapAxes object. Use mx to query and modify
properties of the MapAxes object after creation. For a list of
properties, see MapAxes Properties.
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Version History
Introduced in R2023a