fimplicit
Plot implicit function
Syntax
Description
fimplicit( plots
the implicit function defined by f)f(x,y) = 0 over
the default interval [-5 5] for x and y.
fimplicit( plots
into the axes specified by ax,___)ax instead of into the
current axes. Specify the axes as the first input argument, prior
to any of the previous input arguments.
fimplicit(___, specifies
the line style, marker symbol, and line color. For example, LineSpec)'-r' plots
a red line.
fimplicit(___, specifies
line properties using one or more name-value pair arguments. For example, Name,Value)'LineWidth',2 specifies
a line width of 2 points.
fp = fimplicit(___)ImplicitFunctionLine object. Use fp to
access and modify properties of the line after it is created. For
a list of properties, see ImplicitFunctionLine Properties.
Examples
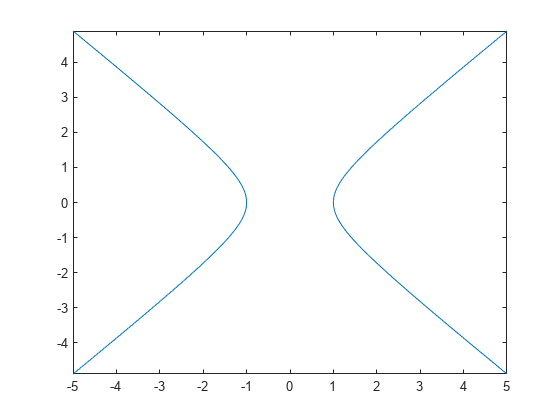
Plot the hyperbola described by the function over the default interval of [-5 5] for x and y.
fimplicit(@(x,y) x.^2 - y.^2 - 1)
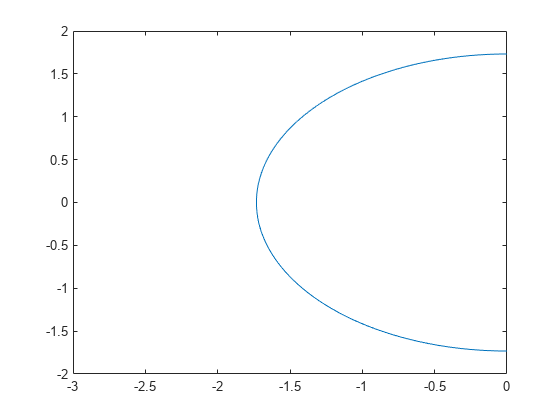
Plot the function over the intervals [-3 0] for x and [-2 2] for y.
f = @(x,y) x.^2 + y.^2 - 3; fimplicit(f,[-3 0 -2 2])
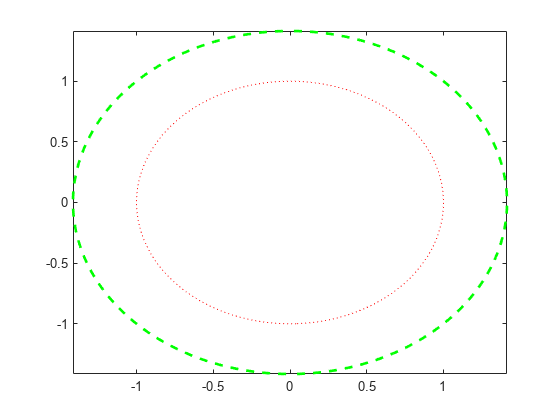
Plot two circles centered at (0,0) with different radius values. For the first circle, use a dotted, red line. For the second circle, use a dashed, green line with a line width of 2 points.
f1 = @(x,y) x.^2 + y.^2 - 1; fimplicit(f1,':r') hold on f2 = @(x,y) x.^2 + y.^2 - 2; fimplicit(f2,'--g','LineWidth',2) hold off
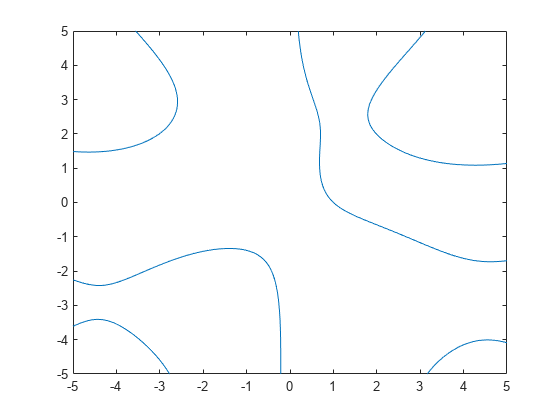
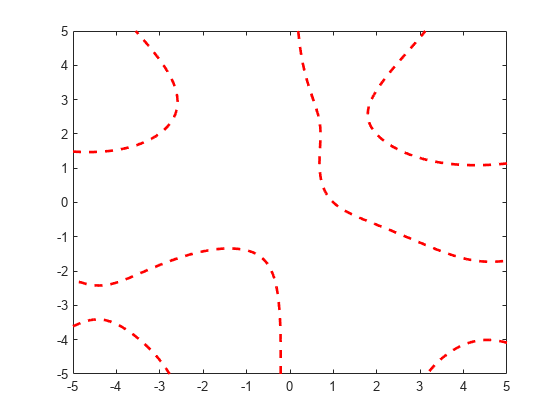
Plot the implicit function and assign the implicit function line object to the variable fp.
fp = fimplicit(@(x,y) y.*sin(x) + x.*cos(y) - 1)
fp =
ImplicitFunctionLine with properties:
Function: @(x,y)y.*sin(x)+x.*cos(y)-1
Color: [0.0660 0.4430 0.7450]
LineStyle: '-'
LineWidth: 0.5000
Show all properties
Use fp to access and modify properties of the implicit function line object after it is created. For example, change the color, line style, and line width.
fp.Color = 'r'; fp.LineStyle = '--'; fp.LineWidth = 2;
Input Arguments
Implicit function to plot, specified as a function handle to a named or anonymous function.
Specify a function of the form z = f(x,y).
The function must accept two matrix input arguments and return a matrix
output argument of the same size. Use array operators instead of matrix
operators for the best performance. For example, use .* (times)
instead of * (mtimes).
Example: fimplicit(@(x,y) x.^2 - y.^2 + 1)
Plotting interval for x and y,
specified in one of these forms:
Two-element vector of the form
[min max]— Use the same plotting interval of[min max]for bothxandy.Four-element vector of the form
[xmin xmax ymin ymax]— Use different plotting intervals forxandy. Plot over the interval[xmin xmax]forxand[ymin ymax]fory.
Example: fimplicit(f,[-2 3 -5 0])
Line style, marker, and color, specified as a string scalar or character vector containing symbols. The symbols can appear in any order. You do not need to specify all three characteristics (line style, marker, and color). For example, if you omit the line style and specify the marker, then the plot shows only the marker and no line.
Example: "--or" is a red dashed line with circle markers.
| Line Style | Description | Resulting Line |
|---|---|---|
"-" | Solid line |
|
"--" | Dashed line |
|
":" | Dotted line |
|
"-." | Dash-dotted line |
|
| Marker | Description | Resulting Marker |
|---|---|---|
"o" | Circle |
|
"+" | Plus sign |
|
"*" | Asterisk |
|
"." | Point |
|
"x" | Cross |
|
"_" | Horizontal line |
|
"|" | Vertical line |
|
"square" | Square |
|
"diamond" | Diamond |
|
"^" | Upward-pointing triangle |
|
"v" | Downward-pointing triangle |
|
">" | Right-pointing triangle |
|
"<" | Left-pointing triangle |
|
"pentagram" | Pentagram |
|
"hexagram" | Hexagram |
|
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] |
|
Axes object. If you do not specify the axes, then fimplicit uses
the current axes.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: fimplicit(f,'MeshDensity',50,'LineWidth',2) specifies
the number of evaluation points and the line width.
The ImplicitFunctionLine properties listed
here are only a subset. For a complete list, see ImplicitFunctionLine Properties.
Number of evaluation points per direction, specified as a scalar.
Line color, specified as an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
Example: "blue"
Example: [0
0 1]
Example: "#0000FF"
Line style, specified as one of the options listed in this table.
| Line Style | Description | Resulting Line |
|---|---|---|
"-" | Solid line |
|
"--" | Dashed line |
|
":" | Dotted line |
|
"-." | Dash-dotted line |
|
"none" | No line | No line |
Line width, specified as a positive value in points, where 1 point = 1/72 of an inch. If the line has markers, then the line width also affects the marker edges.
The line width cannot be thinner than the width of a pixel. If you set the line width to a value that is less than the width of a pixel on your system, the line displays as one pixel wide.
Marker symbol, specified as one of the values listed in this table. By default, the object does not display markers. Specifying a marker symbol adds markers at each data point or vertex.
| Marker | Description | Resulting Marker |
|---|---|---|
"o" | Circle |
|
"+" | Plus sign |
|
"*" | Asterisk |
|
"." | Point |
|
"x" | Cross |
|
"_" | Horizontal line |
|
"|" | Vertical line |
|
"square" | Square |
|
"diamond" | Diamond |
|
"^" | Upward-pointing triangle |
|
"v" | Downward-pointing triangle |
|
">" | Right-pointing triangle |
|
"<" | Left-pointing triangle |
|
"pentagram" | Pentagram |
|
"hexagram" | Hexagram |
|
"none" | No markers | Not applicable |
Marker size, specified as a positive value in points, where 1 point = 1/72 of an inch.
Marker outline color, specified as "auto", an RGB triplet, a
hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name. The default value of
"auto" uses the same color as the Color
property.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
Marker fill color, specified as "auto", an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color
code, a color name, or a short name. The "auto" value uses the same
color as the MarkerEdgeColor property.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
Example: [0.3 0.2 0.1]
Example: "green"
Example: "#D2F9A7"
Tips
Use element-wise operators for the best performance and to avoid a warning message. For example, use
x.*yinstead ofx*y. For more information, see Array vs. Matrix Operations.When you zoom in on the chart,
fimplicitrecalculates the data, which can reveal hidden details.
Version History
Introduced in R2016b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)