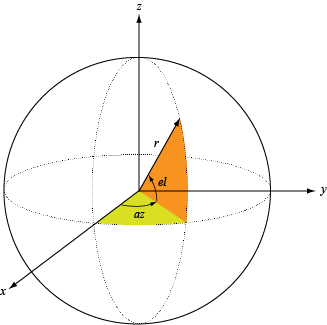
patternElevation
Plot antenna or transducer element directivity and pattern versus elevation
Syntax
Description
patternElevation(
plots the element pattern with additional options specified by one or more
element,FREQ,AZ,Name=Value)Name=Value pair arguments.
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
More About
Version History
Introduced in R2019a