Cartesian 3-D Printer
This example models a Cartesian 3-D printer. The model allows you to specify the rotational motion of the motor on each axis to define a printing path. In this example, the printing head moves along the edges of two letters, S and M, using the predefined rotational motions.
The printer has three linear actuators that drive the motion of the printing head along x-, y-, and z-directions. These actuators are modeled by the Lead Screw Joint blocks. The lead screw joints convert the rotational inputs to translational motions.
Model

Subsystems
The 3-D printer has three degrees of freedom and consists of five subsystems: the printing bed, printer base assembly, gantry assembly, sliding block assembly, and printing head assembly. The prismatic and lead screw joints constrain the subsystems and permit movements along x-, y-, and z- axes.
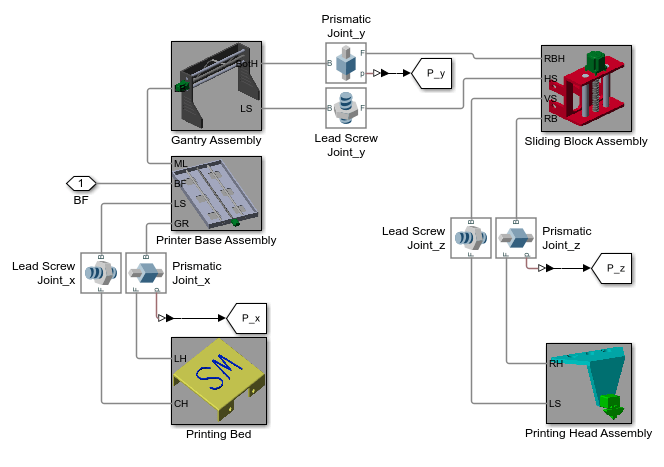
Multibody Explorer Animation
Simulation Results
This plot shows the x-, y-, and z-positions of the printing head during the printing.

See Also
Lead Screw Joint | Revolute Joint