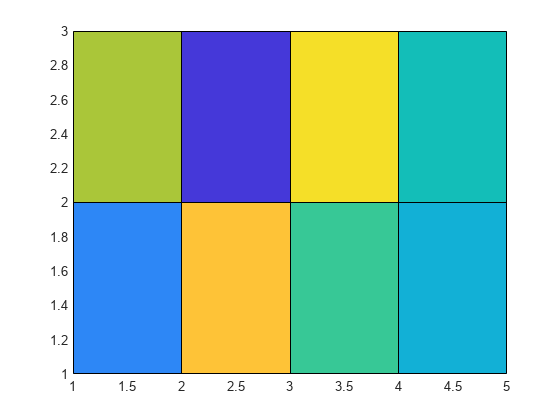pcolor
Pseudocolor plot
Description
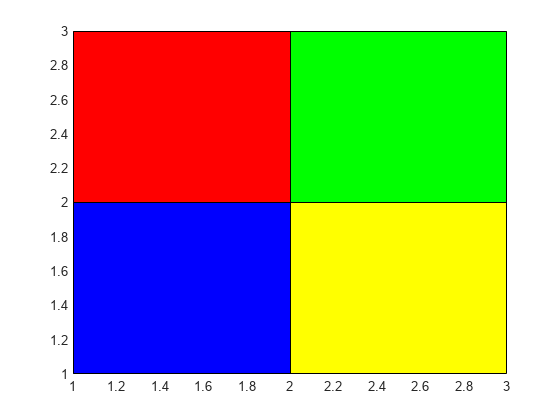
pcolor( creates a pseudocolor plot using the
values in matrix C)C. A pseudocolor plot displays matrix data as an array
of colored cells (known as faces). MATLAB® creates this plot as a flat surface in the
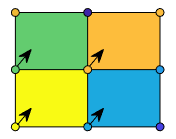
x-y plane. The surface is defined by a grid of
x- and y-coordinates that correspond to the corners
(or vertices) of the faces. The grid covers the region X=1:n and
Y=1:m, where [m,n] = size(C). Matrix
C specifies the colors at the vertices. The color of each face depends
on the color at one of its four surrounding vertices. Of the four vertices, the one that
comes first in the x-y grid determines the color of
the face.
pcolor(___, sets
properties of the plot using one or more name-value arguments. For example, you can specify
the color or hide the mesh lines of the plot. For a list of properties, see Surface Properties. (since R2024b)Name=Value)
pcolor( specifies the
target axes for the plot. Specify ax,___)ax as the first argument in any of the
previous syntaxes.
s = pcolor(___) returns a Surface
object. Use s to set properties on the plot after creating it. For a list
of properties, see Surface Properties.
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Algorithms
Use the pcolor, image, and imagesc functions to display rectangular arrays
of colored cells. The relationship between the color matrix C and the
colored cells is different in each case.
pcolor(C)uses the values inCto define the vertex colors by scaling the values to the full range of the colormap. The size ofCdetermines the number of vertices. The values inCmap colors from the current colormap to the vertices surrounding each cell.image(C)usesCto define the cell colors by mapping the values directly into the colormap. The size ofCdetermines the number of cells.imagesc(C)usesCto define the cell colors by scaling the values to the full range of the colormap. The size ofCdetermines the number of cells.