gnssconstellation
Syntax
Description
[
returns the satellite positions and velocities at the satPos,satVel] = gnssconstellation(t)datetime
t. The function returns positions and velocities in the Earth-centered
Earth-fixed (ECEF) coordinate system in meters and meters per second, respectively. If the
time zone for the datetime is not specified, it is assumed to be UTC.
[
additionally specifies the GNSS file type from which you obtained the navigation message
data. This syntax enables you to process navigation data obtained from either a RINEX file,
a SEM almanac file, a YUMA almanac file, or a Galileo XML almanac file.satPos,satVel,satID] = gnssconstellation(t,navData,GNSSFileType=gnssFileType)
Note
The gnssconstellation function determines the satellite position and
satellite velocities by propagating the current orbital parameters specified by the
RINEX file, SEM almanac file, a YUMA almanac file, or a Galileo XML almanac file to the
query time. To get more accurate satellite positions and velocities, ensure you are
using the navigation file released for the time that you are querying at. For more
information about orbital parameter validity, see Orbital Parameters.
Examples
Get the current satellite positions and velocities from the GNSS satellites. Access the orbital parameters from IS-GPS-200M Interface Specification and calculate the position and velocities in ECEF coordinates for the given time. Display the satellite positions.
t = datetime('now','TimeZone','Local'); [satPos,satVel] = gnssconstellation(t); disp(satPos)
1.0e+07 *
1.4419 -1.8695 -1.2166
-2.2526 0.2278 -1.3886
1.5333 0.7401 2.0385
0.3961 1.5158 2.1447
-2.4055 -0.5273 0.9948
-1.9160 0.3842 1.7988
-0.8862 -1.8420 -1.6958
2.2055 1.4496 0.2971
0.4132 -1.4954 -2.1558
-0.3260 -2.6073 0.3871
-1.4088 0.9526 2.0401
-0.8837 2.1251 1.3257
1.3540 1.2768 -1.8949
2.3915 -1.0450 -0.4931
-1.8792 1.7314 -0.7245
-1.0802 1.8950 -1.5154
-0.6681 -1.3739 2.1726
2.1602 -0.0441 -1.5446
-0.1029 1.6219 -2.1007
-2.3215 -1.2902 0.0178
1.9083 -0.3933 1.8050
-1.5993 -1.7888 1.1387
-1.3851 -1.1670 -1.9426
1.2669 -1.4214 1.8517
0.7572 -2.2715 1.1494
0.4967 2.5311 0.6332
-0.2939 2.5923 -0.4975
Use the lookangles function to get the azimuth and elevation angles of satellites for given satellite and receiver positions. Specify a mask angle of 5 degrees. Get the satellite positions using the gnssconstellation function.
Specify a receiver position in geodetic coordinates (latitude, longitude, altitude).
recPos = [42 -71 50];
Get the satellite positions for the current time.
t = datetime('now');
gpsSatPos = gnssconstellation(t);Specify a mask angle of 5 degrees.
maskAngle = 5;
Get the azimuth and elevation look angles for the satellite positions. The vis output indicates which satellites are visible. Get the total using nnz.
[az,el,vis] = lookangles(recPos,gpsSatPos,maskAngle);
fprintf('%d satellites visible at %s.\n',nnz(vis),t);10 satellites visible at 13-Feb-2026 20:59:29.
Read one set of GPS satellites from the GPS navigation message in a RINEX file.
filename = "GODS00USA_R_20211750000_01D_GN.rnx";
data = rinexread(filename);
gpsData = data.GPS;
[~,satIdx] = unique(gpsData.SatelliteID);
gpsData = gpsData(satIdx,:);Get the satellite positions, velocities, and IDs at the first time step.
t = gpsData.Time(1); [satPos,satVel,satID] = gnssconstellation(t,gpsData)
satPos = 31×3
107 ×
-1.5630 -0.1882 2.1186
1.3808 2.1970 -0.4861
-2.0061 0.7606 1.5492
-2.5625 -0.0140 -0.7096
1.4896 0.5448 -2.1487
0.6129 2.5407 0.4615
-1.0081 1.3751 -1.9877
-2.5811 -0.6135 -0.3246
-1.9289 0.8690 -1.6134
0.9542 -2.2526 1.0113
2.0186 -0.5308 1.6093
2.0993 1.3376 -0.9594
-1.0551 2.2204 1.0002
2.6312 0.3802 -0.3333
-1.0047 -1.1218 -2.2112
⋮
satVel = 31×3
103 ×
-0.8888 -2.5914 -0.8416
0.0362 0.7543 3.1043
1.1203 -1.6505 2.2591
-0.8301 -0.4385 2.9967
-1.6023 2.1607 -0.5493
-0.3948 -0.4708 3.1591
-1.0322 -2.4133 -1.1748
0.4370 -0.1710 -3.1339
-1.9860 -0.5032 2.1087
0.9968 -0.8308 -2.8502
-1.3152 1.6379 2.1695
-1.2059 -0.1406 -2.8610
-1.0488 0.7681 -2.8132
-0.3937 0.3259 -3.0428
1.9524 -1.9313 0.1383
⋮
satID = 31×1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
13
14
15
16
⋮
Read GPS navigation message data from a SEM almanac file.
data = semread("semalmanac_2022-4-10.al3")data=31×16 timetable
Time GPSWeekNumber GPSTimeOfApplicability PRNNumber SVN AverageURANumber Eccentricity InclinationOffset RateOfRightAscension SqrtOfSemiMajorAxis GeographicLongitudeOfOrbitalPlane ArgumentOfPerigee MeanAnomaly ZerothOrderClockCorrection FirstOrderClockCorrection SatelliteHealth SatelliteConfiguration
____________________ _____________ ______________________ _________ ___ ________________ ____________ _________________ ____________________ ___________________ _________________________________ _________________ ___________ __________________________ _________________________ _______________ ______________________
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 1 63 0 0.01171 0.014391 -2.4484e-09 5153.6 -0.9271 0.28359 -0.23387 0.00038624 -7.276e-12 0 11
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 2 61 0 0.020515 0.0074596 -2.5029e-09 5153.6 -0.95587 -0.45355 -0.18869 -0.00065327 0 0 9
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 3 69 0 0.0040326 0.0096912 -2.5757e-09 5153.6 -0.59787 0.29979 -0.59118 -0.00020409 -1.4552e-11 0 11
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 4 74 0 0.0017715 0.0059814 -2.4665e-09 5153.6 -0.25353 -0.95004 0.31619 -0.00017643 3.638e-12 0 12
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 5 50 0 0.0059118 0.0055599 -2.6193e-09 5153.6 -0.61097 0.32122 0.61334 -7.8201e-05 0 0 10
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 6 67 0 0.0026565 0.014187 -2.452e-09 5153.7 -0.92973 -0.28158 -0.1523 0.00026417 1.4552e-11 0 11
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 7 48 0 0.015865 0.0028152 -2.5138e-09 5153.6 0.07053 -0.72524 -0.44853 0.00032043 0 0 10
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 8 72 0 0.0074387 0.0068531 -2.4738e-09 5153.7 0.72894 0.048076 0.467 -6.3896e-05 0 0 11
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 9 68 0 0.0021076 0.0037479 -2.5029e-09 5153.5 -0.27053 0.59743 0.61325 -0.00034428 3.638e-12 0 11
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 10 73 0 0.0075555 0.0096321 -2.5793e-09 5153.6 -0.59875 -0.79359 -0.88495 -0.0003767 -1.0914e-11 0 11
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 11 78 0 0.00031376 0.0064716 -2.5393e-09 5153.7 -0.9136 0.85276 0.49013 -4.1962e-05 7.276e-12 63 12
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 12 58 0 0.0087256 0.008585 -2.5575e-09 5153.5 0.42482 0.40497 -0.64747 -0.00019932 -7.276e-12 0 10
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 13 43 0 0.0058503 0.0083656 -2.4374e-09 5153.6 -0.22159 0.29646 0.31699 0.00029278 7.276e-12 0 9
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 14 77 0 0.0016966 0.0033073 -2.6121e-09 5153.6 0.41456 0.97049 -0.63662 -0.00010204 -3.638e-12 0 12
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 15 55 0 0.013989 -0.003952 -2.5866e-09 5153.7 -0.30476 0.34521 0.16087 -6.9618e-05 3.638e-12 0 10
12-Apr-2022 16:50:54 2205 2.3347e+05 16 56 0 0.012782 0.0085545 -2.5611e-09 5153.6 0.43073 0.23073 0.76066 -0.00049114 -3.638e-12 0 9
⋮
Get the satellite positions, velocities, and IDs at the first time step.
t = data.Time(1);
[satPos,satVel,satID] = gnssconstellation(t,data,GNSSFileType="SEM")satPos = 31×3
107 ×
1.3899 -2.2151 0.3074
-1.6755 0.5872 -1.9147
1.5377 -1.2781 -1.7528
0.6332 -1.6385 -1.9887
-2.5716 0.5413 0.4215
-1.0251 -1.1336 -2.1646
0.2694 -2.3585 1.1775
1.3414 -0.7139 2.1761
-0.3881 -2.2626 -1.3395
1.5043 1.1879 1.8656
-1.7866 0.4175 -1.9205
-1.9188 1.0246 -1.5421
-1.6711 -0.2575 2.0374
-1.3516 -1.3127 1.8746
-1.2509 0.9486 2.1022
⋮
satVel = 31×3
103 ×
0.0014 0.4854 3.2261
0.8625 -2.4217 -1.4348
2.2113 0.0321 1.9394
1.4081 2.1049 -1.2936
-0.5761 -0.2150 -3.1036
1.2999 -2.4327 0.6643
0.9229 -1.1620 -2.6758
1.5581 2.2893 -0.1743
1.1480 1.2668 -2.4877
-2.3150 0.2417 1.6982
1.1085 -2.1747 -1.5056
-1.9099 -0.2154 2.2852
-1.0411 -2.3996 -1.1323
2.3787 -0.1846 1.5773
-1.7983 -2.1160 -0.0817
⋮
satID = 31×1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
⋮
Read GPS navigation message data from a YUMA almanac file.
data = yumaread("yumaAlmanac_2022-9-27.alm")data=31×13 timetable
Time PRN Health Eccentricity TimeOfApplicability OrbitalInclination RateOfRightAscen SQRTA RightAscenAtWeek ArgumentOfPerigee MeanAnom Af0 Af1 Week
____________________ ___ ______ ____________ ___________________ __________________ ________________ ______ ________________ _________________ ________ ___________ __________ ____
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 1 0 0.012008 4.055e+05 0.98891 -7.5432e-09 5153.6 0.3651 0.9438 -1.095 0.00027561 -7.276e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 2 0 0.02 4.055e+05 0.96685 -7.7946e-09 5154.9 0.27125 -1.393 -1.6195 -0.00064468 0 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 3 0 0.0044999 4.055e+05 0.97519 -7.726e-09 5153.5 1.3977 1.0651 -2.1966 -0.00035858 -3.638e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 4 0 0.0020423 4.055e+05 0.96187 -7.966e-09 5153.7 2.4795 -3.1045 0.81839 -0.00011158 7.276e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 5 0 0.0060811 4.055e+05 0.96224 -7.8403e-09 5153.7 1.3543 1.1188 1.415 -9.8228e-05 0 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 6 0 0.0024514 4.055e+05 0.98822 -7.5546e-09 5153.5 0.35683 -0.8974 -0.87447 0.00047684 1.0914e-11 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 7 0 0.016406 4.055e+05 0.95104 -7.7832e-09 5153.6 -2.7871 -2.2412 -1.7241 0.00030327 -3.638e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 8 0 0.0075631 4.055e+05 0.96192 -8.2403e-09 5153.5 -0.71955 0.16395 1.1555 -8.6784e-05 0 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 9 0 0.0025387 4.055e+05 0.95495 -8.0575e-09 5153.7 2.4248 1.9083 1.5732 -0.00028992 3.638e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 10 0 0.0079675 4.055e+05 0.97498 -7.7489e-09 5153.6 1.395 -2.5116 -3.0858 -5.722e-06 0 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 11 0 0.00075054 4.055e+05 0.96415 -7.7832e-09 5153.6 0.40358 -3.1036 0.81271 -2.0981e-05 -3.638e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 12 0 0.0085082 4.055e+05 0.96755 -7.966e-09 5153.7 -1.6731 1.3158 -2.4318 -0.0002861 -7.276e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 13 0 0.0065126 4.055e+05 0.96921 -7.8518e-09 5153.6 2.5812 0.94039 0.67456 0.00039673 7.276e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 14 0 0.002305 4.055e+05 0.95095 -8.1261e-09 5153.6 -1.708 -3.0302 -2.4903 -0.00010014 3.638e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 15 0 0.014625 4.055e+05 0.93093 -8.3203e-09 5153.6 2.3127 1.1401 0.17435 -2.4796e-05 3.638e-12 2229
29-Sep-2022 16:38:06 16 0 0.012809 4.055e+05 0.96738 -7.9889e-09 5153.7 -1.6547 0.73255 2.0697 -0.00052547 0 2229
⋮
Get the satellite positions, velocities, and IDs at the first time step.
t = data.Time(1);
[satPos,satVel,satID] = gnssconstellation(t,data,GNSSFileType="YUMA")satPos = 31×3
107 ×
-1.3549 2.2358 -0.3793
1.4926 -2.1942 -0.1952
-1.2477 1.2357 -2.0018
-0.4096 2.0385 -1.6467
2.2427 -0.7207 1.2218
1.4711 0.4089 -2.1680
-0.0841 2.0989 1.6373
-1.0615 1.1949 2.1111
0.5989 2.4816 -0.7333
-1.9686 -1.1518 1.4018
1.9842 -0.6457 -1.6411
1.3664 -1.1517 -1.9882
1.4721 -0.2873 2.1756
1.7638 1.3202 1.4920
0.9458 -1.3494 2.0339
⋮
satVel = 31×3
103 ×
-0.4388 0.2295 3.2113
0.0460 0.4065 -3.1646
-2.4900 -0.3576 1.3500
-0.9647 -1.8691 -2.0833
1.5583 0.3175 -2.6224
-1.6003 2.2475 -0.6531
-1.3741 1.5034 -2.0994
-1.2344 -2.3991 0.7711
-0.6518 -0.7124 -2.9785
1.7466 0.0160 2.4627
-1.1680 1.7362 -2.0987
2.4120 0.5344 1.3766
0.7821 2.6885 -0.1548
-1.9034 -0.0429 2.2785
1.5170 2.2368 0.7915
⋮
satID = 31×1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
⋮
Read navigation data from a Galileo almanac file and use the navigation data to:
Get satellite positions, velocities, and IDs at a given timestamp.
Compute satellite visibility and look angles for a given receiver position by using the extracted satellite positions.
First, read GPS navigation message data from a Galileo almanac file.
filename = "galAlmanac_2019-08-06.xml";
data = galalmanacread(filename)data=22×16 timetable
Time SVID aSqRoot ecc deltai omega0 omegaDot w m0 af0 af1 iod t0a wna statusE5a statusE5b statusE1B
____________________ ____ ________ __________ __________ ________ ___________ ________ _________ ___________ ___________ ___ _________ ____ _________ _________ _________
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 1 0.011719 0.00022888 0.0030518 -0.11984 -1.8626e-09 -0.81259 -0.053925 -0.00066185 -7.276e-12 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 2 0.017578 0.00010681 0.0030518 -0.11984 -1.8626e-09 -0.50497 0.63766 7.2479e-05 0 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 3 0.042969 0.00036621 -0.0076904 -0.78656 -1.7462e-09 -0.1449 0.94464 -0.00019646 -3.638e-12 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 4 0.039062 0.00027466 -0.0076904 -0.78653 -1.7462e-09 -0.40698 -0.041412 -0.00033951 -7.276e-12 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 5 0.042969 0.00021362 -0.0076904 -0.78656 -1.7462e-09 -0.33777 -0.61145 -0.00045967 3.638e-12 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 7 0.042969 0.00041199 -0.0076904 -0.78656 -1.7462e-09 -0.285 0.58496 -0.00024033 -7.276e-12 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 8 0.039062 0.00036621 -0.0057983 -0.789 -1.7462e-09 -0.19412 0.74414 0.0063114 -7.276e-12 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 9 0.039062 0.00045776 -0.0057983 -0.789 -1.7462e-09 -0.21506 -0.4855 0.0063572 -1.0914e-11 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 11 0.017578 0.00038147 0.0021973 0.54333 -1.7462e-09 0.28098 -0.3125 0.0056324 -1.0914e-11 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 12 0.015625 0.0002594 0.0021973 0.54333 -1.7462e-09 0.10056 0.12363 0.0062618 -1.819e-11 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 13 0.021484 1.5259e-05 0.0032349 0.54181 -1.7462e-09 0.23178 0.73837 0.00039101 0 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:29:42 15 0.017578 3.0518e-05 0.0032349 0.54178 -1.7462e-09 -0.60843 -0.19565 0.00090027 0 3 2.034e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 19 0.027344 0.00024414 -0.0058594 -0.78732 -1.7462e-09 -0.47565 0.30069 -3.8147e-06 0 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 21 0.021484 0.00022888 0.0029297 -0.12067 -1.8626e-09 -0.91656 0.30164 -0.00054741 -3.638e-12 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 24 0.011719 0.00024414 0.0022583 -0.11884 -1.8626e-09 0.27414 0.35886 0.0059395 -1.819e-11 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
06-Aug-2019 08:39:42 25 0.027344 0.00032043 0.0029297 -0.1207 -1.8626e-09 -0.7215 -0.89252 0.0017204 -1.0914e-11 4 2.04e+05 1041 0 0 0
⋮
Specify the timestamp for which to find the satellite positions, velocities, and IDs.
t = datetime(2021,06,24,01,59,44)
t = datetime
24-Jun-2021 01:59:44
Get the satellite positions, velocities, and IDs at the specified timestamp by using the gnssconstellation function.
[satPos,satVel,satID] = gnssconstellation(t,data,GNSSFileType="galalmanac");Specify a receiver position in geodetic coordinates (latitude, longitude, altitude) to compute the satellite look angles and visibility.
recPos = [42.3013162 -71.3782972 0];
Specify the elevation mask angle for the receiver.
maskAngle = 5;
Compute the look angles and visibilities of satellite positions for the given receiver position. The vis output indicates which satellites are visible. Get the total using nnz.
[az,el,vis] = lookangles(recPos,satPos,maskAngle);
fprintf('%d satellites visible at %s.\n',nnz(vis),t)10 satellites visible at 24-Jun-2021 01:59:44.
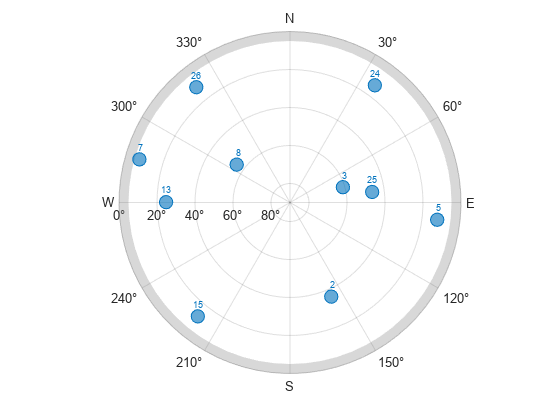
Plot the visible satellite positions with the elevation mask.
figure skyplot(az(vis),el(vis),satID(vis),MaskElevation=maskAngle)
Input Arguments
Current time for the satellite simulation, specified as a scalar datetime array.
The default time zone for a datetime array is UTC. For information
on specifying a different time zone, see datetime.
GPS start time is January 6, 1980 at 00:00 (UTC). Specifying any
datetime prior to this time will use the GPS start time.
Example:
datetime('now','TimeZone','Local');
Data Types: datetime
Navigation data, specified as a timetable.
For a RINEX file, you can obtain the timetable from the structure returned by the
rinexreadfunction.For a SEM almanac file, you can use the timetable returned by the
semreadfunction.For a YUMA almanac file, you can use the timetable returned by the
yumareadfunction.For a Galileo XML almanac file, you can use the timetable returned by the
galalmanacreadfunction.
Read Navigation Data from RINEX File
The gnssconstellation function can process the GPS or Galileo
data read from a RINEX file. The contents of the structure returned by the rinexread
function vary depending on the type of satellite system described by the RINEX file. For
more information on the contents of the structure, see the
rinexread function More About section.
To read GPS navigation message data from a RINEX file, extract the
GPS field from the returned structure. For example:
rinexData = rinexread("GODS00USA_R_20211750000_01D_GN.rnx");
navData = rinexData.GPS;To read Galileo navigation message data from a RINEX file, extract the
Galileo field from the returned structure. For example:
rinexData = rinexread("GODS00USA_R_20211750000_01D_EN.rnx");
navData = rinexData.Galileo;To read GLONASS navigation message data from a RINEX file, extract the
GLONASS field from the returned structure. For example:
rinexData = rinexread("GODS00USA_R_20211750000_01D_RN.rnx");
navData = rinexData.GLONASS;To read BeiDou navigation message data from a RINEX file, extract the
BeiDou field from the returned structure. For example:
rinexData = rinexread("GODS00USA_R_20211750000_01D_CN.rnx");
navData = rinexData.BeiDou;To read NavIC/IRNSS navigation message data from a RINEX file, extract the
NavIC field from the returned structure. For example:
rinexData = rinexread("ARHT00ATA_R_20211750000_01D_IN.rnx");
navData = rinexData.NavIC;To read QZSS navigation message data from a RINEX file, extract the
QZSS field from the returned structure. For example:
rinexData = rinexread("ARHT00ATA_R_20211750000_01D_JN.rnx");
navData = rinexData.QZSS;To read SBAS navigation message data from a RINEX file, extract the
SBAS field from the returned structure. For example:
rinexData = rinexread("GOP600CZE_R_20211750000_01D_SN.rnx");
navData = rinexData.SBAS;Read Navigation Data from SEM Almanac File
The gnssconstellation function can process the GPS data read
from a SEM almanac file. The timetable returned by the semread
function contains the parameters of each satellite in the almanac file associated with
the specified date. For more information on the contents of the timetable, see the
data argument of
the semread function.
Because semread returns a timetable, you can directly specify
navData as the semread output argument. For
example:
navData = semread("semalmanac_2022-1-18.al3")Read Navigation Data from YUMA Almanac File
The gnssconstellation function can process the GPS and QZSS
data read from a YUMA almanac file. The timetable returned by the yumaread
function contains the parameters of each satellite in the almanac file associated with
the specified date. For more information on the contents of the timetable, see the
data argument of
the yumaread function.
Because yumaread returns a timetable, you can directly specify
navData as the yumaread output argument. For
example:
navData = yumaread("yumaAlmanac_2022-4-20.alm")Read Navigation Data from Galileo XML Almanac File
The gnssconstellation function can process the Galileo data
read from a Galileo XML almanac file. The timetable returned by the galalmanacread
function contains the parameters of each satellite in the almanac file associated with
the specified date. For more information on the contents of the timetable, see the
data argument of
the galalmanacread function.
Because galalmanacread returns a timetable, you can directly
specify navData as the galalmanacread output
argument. For example:
navData = galalmanacread("galAlmanac_2023-02-17.xml")Note
When you read Galileo data in RINEX format, the week number is aligned with the GPS week. The GPS time of week starts at the midnight between 5th and 6th January 1980.
When you read Galileo data in Almanac format, the week number is aligned with the Galileo system time (GST). The GST start epoch is 13 seconds before 00:00 UTC on Sunday 22nd August 1999 (midnight between 21st and 22nd August).
GNSS file type, specified as "RINEX", "SEM",
"YUMA", or "galalmanac".
Specify the GNSS file type as,
"RINEX"when specifying the navigation data as a timetable obtained from the structure returned by therinexreadfunction."SEM"when specifying the navigation data as a timetable returned by thesemreadfunction."YUMA"when specifying the navigation data as a timetable returned by theyumareadfunction."galalmanac"when specifying the navigation data as a timetable returned by thegalalmanacreadfunction.
Example: GNSSFileType="RINEX"
Example: GNSSFileType="SEM"
Example: GNSSFileType="YUMA"
Example: GNSSFileType="galalmanac"
Data Types: char | string
Output Arguments
Satellite positions in the Earth-centered Earth-fixed (ECEF) coordinate system in meters, returned as an N-by-3 matrix of scalars. N is the number of satellites in the constellation.
Data Types: single | double
Satellite velocities in the Earth-centered Earth-fixed (ECEF) coordinate system in meters per second, returned as an N-by-3 matrix of scalars. N is the number of satellites in the constellation.
Data Types: single | double
Satellite identification numbers, returned as an N-element column vector. N is the number of satellites in the constellation.
Data Types: single | double
More About
Orbital parameters define the initial positions and velocities of a satellite and enable you to calculate past and future positions and velocities of the satellites based on those initial positions and velocities. These orbital parameters produce accurate results within a time range of the time of ephemeris, or initial time for satellites that do not record time of ephemeris. To get accurate position and velocity calculations, ensure that you are using the correct orbital parameters for the corresponding querying time.
These are the time windows in which the orbital parameters are valid for position and velocity calculations:
GPS, Galileo, BeiDou, NavIC, QZSS — [ti-2 hours, ti+2 hours].
GLONASS, SBAS — [ti-15 minutes, ti+15 minutes].
ti is the time of ephemeris or initial time for satellites that do not record time of ephemeris.
For GPS, Galileo, BeiDou, NavIC, and QZSS satellites, Table A.2-2 in GPS SPS Performance Standard defines the satellite positions and velocities in Earth-centered Earth-fixed (ECEF) coordinates. Position calculations use equations from Table 30-II in the same IS-GPS-200M Interface Specification. Velocity calculations use equations 8.21–8.27 in Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multisensor Integrated Navigation Systems [1].
For GLONASS, and SBAS satellites, Section A.3.1.2 in GLONASS ICD Edition 5.1 2008 defines equations for both the positions and velocities in Earth-centered Earth-fixed (ECEF) coordinates.
References
[1] Groves, Paul D. Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multisensor Integrated Navigation Systems. Boston: Artech House, 2013.
[2] International GNSS Service (IGS), Daily 30-Second GPS Broadcast Ephemeris Data, NASA Crustal Dynamics Data Information System (CDDIS), Greenbelt, MD, USA, Jun. 24, 2021. Accessed Jun. 25, 2021. https://dx.doi.org/10.5067/GNSS/gnss_daily_n_001.
[3] United States Coast Guard. "GPS Almanacs, NANUs, and OPS Advisories Archives." US Coast Guard Navigation Center. Accessed May 6, 2022. https://www.navcen.uscg.gov/archives.
[4] QZSS almanac archives, Quasi-Zenith Satellite System(QZSS). "QZSS (Quasi-Zenith Satellite System) - Cabinet Office (Japan)" Accessed September 20, 2022. https://sys.qzss.go.jp/dod/en/archives/pnt.html.
[5] European GNSS Service Centre (GSC). "Galileo Open Service Signal-In-Space Interface Control Document." Accessed March 13, 2023. https://www.gsc-europa.eu/sites/default/files/sites/all/files/Galileo_OS_SIS_ICD_v2.1.pdf.
Extended Capabilities
Only MEX functions are supported for code generation.
Version History
Introduced in R2021aRead navigation data from a RINEX file containing these additional GNSS satellites:
GLONASS
BeiDou
NavIC
QZSS
SBAS
See the navData argument
for examples of how to read data from these satellites from RINEX files.
Specify input argument gnssFileType as
"galalmanac" if the input navigation data navData is
read from Galileo XML almanac file.
See Also
Objects
Functions
skyplot|lookangles|pseudoranges|receiverposition|rinexread|rinexinfo|semread|yumaread|galalmanacread
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)