Assignment
Assegnare valori a elementi specifici del segnale
Librerie:
Simulink /
Math Operations
HDL Coder /
Math Operations
Descrizione
Il blocco Assignment assegna valori a elementi specifici del segnale. Si specificano gli indici degli elementi a cui assegnare i valori inserendo gli indici nella finestra di dialogo del blocco oppure collegando al blocco una o più sorgenti esterne di indici. Il segnale sulla porta dati del blocco U specifica i valori da assegnare a Y. Il blocco sostituisce gli elementi specificati di Y con elementi provenienti dal segnale dati.
In base al valore inserito per il parametro Number of output dimensions, viene visualizzata una tabella delle opzioni dell'indice. Ciascuna riga della tabella corrisponde ad una delle dimensioni di output in Number of output dimensions. Per ciascuna dimensione, è possibile definire gli elementi del segnale con cui lavorare. Specificare un segnale vettoriale come segnale monodimensionale e un segnale matriciale come segnale bidimensionale. Per abilitare una porta di indice esterna, nella riga corrispondente della tabella, impostare Index Option su Index vector (port), Starting index (port) o .
Ad esempio, si assuma un segnale in 5 D con una modalità di indice a base unica. La tabella nella finestra di dialogo del blocco Assignment cambia per includere una riga per ciascuna dimensione. Se si definisce ciascuna dimensione con le seguenti voci:
| Riga | Opzione di indice | Indice |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Assign all | |
| 2 | Index vector (dialog) | [1 3 5] |
| 3 | Starting index (dialog) | 4 |
| 4 | Starting index (port) | |
| 5 | Index vector (port) |
i valori assegnati sono Y(1:end,[1 3 5],4:3+size(U,3),Idx4:Idx4+size(U,4)-1,Idx5)=U, dove Idx4 e Idx5 sono le porte di input per le dimensioni 4 e 5.
Quando si utilizza il blocco Assignment in modalità normale, Simulink® inizializza gli output del blocco a zero anche se il modello non li inizializza esplicitamente. In modalità di accelerazione, Simulink converte il modello in una S-Function. Questo comporta la generazione di codice. Il codice generato potrebbe non eseguire l'inizializzazione implicita degli output dei blocchi. In tali casi, è necessario inizializzare esplicitamente gli output del modello.
È possibile utilizzare il blocco per assegnare valori a segnali vettoriali, matriciali o multidimensionali.
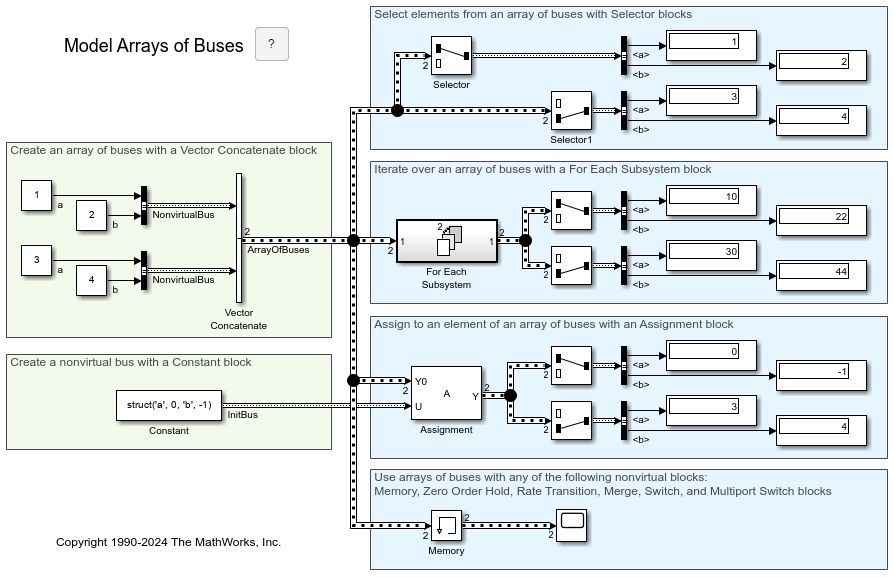
È possibile utilizzare un array di bus come segnale di input per un blocco Assignment.
Blocco Assignment nel sottosistema condizionale
Se si posiziona un blocco Assignment in un blocco sottosistema condizionale, in molti casi viene inserito un buffer di segnale nascosto (equivalente a un blocco Signal Conversion) e l'unione dei segnali provenienti dai blocchi Assignment con scritture parziali può causare un errore.
Tuttavia, se si seleziona il parametro Ensure outport is virtual per il blocco Outport del sottosistema condizionale, tali casi sono supportati ed è possibile eseguire scritture parziali negli array utilizzando i blocchi Assignment. Vedere Ensure Output Port Is Virtual.

Esempi
Limitazioni
Il parametro Index non è sincronizzabile durante la simulazione. Se Index Option per una dimensione è impostato su
Index vector (dialog)oStarting index (dialog)e si specifica un valore simbolico, compreso un oggettoSimulink.Parameter, per il corrispondente Index nella finestra di dialogo del blocco, il valore istantaneo all'inizio della simulazione sarà utilizzato per tutta la simulazione e il parametro apparirà come valore in linea nel codice generato. Vedere Tune and Experiment with Block Parameter Values. È possibile modificare l'indice di assegnazione in modo dinamico utilizzando le porte di indice.
Porte
Input
Output
Parametri
Caratteristiche del blocco
Tipi di dati: |
|
Passaggio diretto |
|
Segnali multidimensionali |
|
Segnali di dimensioni variabili |
|
Rilevamento zero-crossing |
|