Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF
Combined slip 2DOF wheel with disc, drum, or mapped brake

Libraries:
Vehicle Dynamics Blockset /
Wheels and Tires
Description
Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF incorporates two degrees of freedom (DOF's) of wheel motion, and 6 DOF's of tire forcing, in combined longitudinal and lateral slip conditions.
Wheel motion: Rotation about spin axis, and vertical displacement.
Tire forces and moments: Fx, Fy, and Fz; Mx, My, and Mz.
It models the tire using the Magic Formula 6.2.[1] and [2] Set the Magic Formula 6.2 coefficients by either importing your own tire model file, or selecting one of the built-in tire models.
Use this block in simulations like the following.
Vehicle braking and acceleration, including rolling resistance.
Vehicle ride motions, including effects of suspension modes.
Maneuvers with combined lateral and longitudinal slip, such as lateral vehicle motion and yaw stability.
If you install the Extended Tire Features for Vehicle Dynamics Blockset support package, these additional capabilities are available:
Plot generation — Click the Plot steady state force, moment response button to generate these plots:
Lateral force [N] vs Slip angle [rad]
Self-aligning moment [Nm] vs Slip angle [rad]
Longitudinal force [N] vs Longitudinal slip []
Longitudinal force [N] vs Lateral force [N]
Import tire parameters — Use the
tireModel.getmethod to import tire parameter values defined in the Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF block to atireModelobject.Export tire parameters — Use the
setmethod to export tire parameter values from atireModelobject to the Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF block.Tire model conversion — Use the
convertmethod to convert a tire model of one of these types to a Magic Formula 6.2 tire model that you can import to the Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF block:Magic Formula 5.2
Fiala
Dugoff
Use the Tire type parameter to select the source of the tire data.
| Goal | Action |
|---|---|
Import your own external file containing Magic Formula coefficients, and use them to drive the empirical equations modeling the tire1 and 2. The file you import can be a .mat, .tir, or .txt type, and must contain parameter names corresponding to those in the tire block. |
Update the block parameters with fitting coefficients from a file:
|
Select one of the Magic Formula built-in tire models to drive the empirical equations modeling the tire 1 and 2. | Update the applicable block parameters with values from a built-in tire model:
|
Use the Brake Type parameter to select the brake.
| Action | Brake Type Setting |
|---|---|
No braking |
|
Implement brake that converts the brake cylinder pressure into a braking force |
|
Implement simplex drum brake that converts the applied force and brake geometry into a net braking torque |
|
Implement lookup table that is a function of the wheel speed and applied brake pressure |
|
Rotational Wheel Dynamics
The block calculates the inertial response of the wheel subject to:
Axle losses
Brake and drive torque
Tire rolling resistance
Ground contact through the tire-road interface
To implement the Magic Formula 6.2, the block uses these equations from the cited references:
| Calculation | Equations |
|---|---|
Longitudinal force | Tire and Vehicle Dynamics2 equations 4.E9 through 4.E57 |
Lateral force - pure sideslip | Tire and Vehicle Dynamics2 equations 4.E19 through 4.E30 |
Lateral force - combined slip | Tire and Vehicle Dynamics2 equations 4.E58 through 4.E67 |
Vertical dynamics | Tire and Vehicle Dynamics2 equations 4.E68, 4.E1, 4.E2a, and 4.E2b |
Overturning couple | Tire and Vehicle Dynamics2 equation 4.E69 |
Rolling resistance |
|
Aligning moment | Tire and Vehicle Dynamics2 equation 4.E31 through 4.E49 |
Aligning torque - combined slip | Tire and Vehicle Dynamics2 equation 4.E71 through 4.E78 If you clear Include turn slip, the block sets some of these equations to 1. |
The input torque is the summation of the applied axle torque, braking torque, and moment arising from the combined tire torque.
For the moment arising from the combined tire torque, the block implements tractive wheel forces and rolling resistance with first-order dynamics. The rolling resistance has a time constant parameterized in terms of a relaxation length.
Braking torque is based on an idealized dry clutch friction model (if brakes are selected). Depending on the lockup condition, the block implements these friction and dynamic models:
| If | Lockup Condition | Friction Model | Dynamic Model |
|---|---|---|---|
Unlocked | |||
Locked |
The equations use these variables.
| ω | Wheel angular velocity |
| a | Velocity independent force component |
| b | Linear velocity force component |
| c | Quadratic velocity force component |
| Le | Tire relaxation length |
| J | Moment of inertia |
| My | Rolling resistance torque |
| Ta | Applied axle torque about wheel spin axis |
| Tb | Braking torque |
| Td | Combined tire torque |
| Tf | Frictional torque |
| Ti | Net input torque |
| Tk | Kinetic frictional torque |
| To | Net output torque |
| Ts | Static frictional torque |
| Fc | Applied clutch force |
| Fx | Longitudinal force developed by the tire road interface due to slip |
| Reff | Effective clutch radius |
| Ro | Annular disk outer radius |
| Ri | Annular disk inner radius |
| Re | Effective tire radius while under load and for a given pressure |
| Vx | Longitudinal axle velocity |
| Fz | Vehicle normal force |
| ɑ | Tire pressure exponent |
| β | Normal force exponent |
| pi | Tire pressure |
| μs | Coefficient of static friction |
| μk | Coefficient of kinetic friction |
Tire and Wheel Coordinate Systems
To resolve the forces and moments, the block uses the Z-Up orientation of the tire and wheel coordinate systems.
Tire coordinate system axes (XT, YT, ZT) are fixed in a reference frame attached to the tire. The origin is at the tire contact with the ground.
Wheel coordinate system axes (XW, YW, ZW) are fixed in a reference frame attached to the wheel. The origin is at the wheel center.
Z-Up Orientation1

Brakes
If you specify the Brake Type parameter as
Disc, the block implements a disc brake. This figure
shows the side and front views of a disc brake.
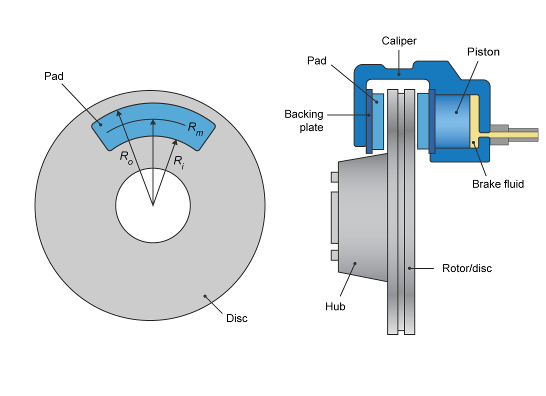
A disc brake converts brake cylinder pressure from the brake cylinder into force. The disc brake applies the force at the brake pad mean radius.
The block uses these equations to calculate brake torque for the disc brake.
The equations use these variables.
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| T | Brake torque |
| P | Applied brake pressure |
| N | Wheel speed |
| Npads | Number of brake pads in disc brake assembly |
| μstatic | Disc pad-rotor coefficient of static friction |
| μ | Disc pad-rotor coefficient of kinetic friction |
| Ba | Brake actuator bore diameter |
| Rm | Mean radius of brake pad force application on brake rotor |
| Ro | Outer radius of brake pad |
| Ri | Inner radius of brake pad |
If you specify the Brake Type parameter as
Drum, the block implements a static (steady-state)
simplex drum brake. A simplex drum brake consists of a single two-sided hydraulic
actuator and two brake shoes. The brake shoes do not share a common hinge pin.
The simplex drum brake model uses the applied force and brake geometry to calculate a net torque for each brake shoe. The drum model assumes that the actuators and shoe geometry are symmetrical for both sides, allowing a single set of geometry and friction parameters to be used for both shoes.
The block implements equations that are derived from these equations in Fundamentals of Machine Elements.

The equations use these variables.
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| T | Brake torque |
| P | Applied brake pressure |
| N | Wheel speed |
| μstatic | Disc pad-rotor coefficient of static friction |
| μ | Disc pad-rotor coefficient of kinetic friction |
| Trshoe | Right shoe brake torque |
| Tlshoe | Left shoe brake torque |
| a | Distance from drum center to shoe hinge pin center |
| c | Distance from shoe hinge pin center to brake actuator connection on brake shoe |
| r | Drum internal radius |
| Ba | Brake actuator bore diameter |
| Θ1 | Angle from shoe hinge pin center to start of brake pad material on shoe |
| Θ2 | Angle from shoe hinge pin center to end of brake pad material on shoe |
If you specify the Brake Type parameter as
Mapped, the block uses a lookup table to determine the
brake torque.
The equations use these variables.
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| T | Brake torque |
Brake torque lookup table | |
| P | Applied brake pressure |
| N | Wheel speed |
| μstatic | Friction coefficient of drum pad-face interface under static conditions |
| μ | Friction coefficient of disc pad-rotor interface |
The lookup table for the brake torque, , is a function of applied brake pressure and wheel speed, where:
T is brake torque, in N·m.
P is applied brake pressure, in bar.
N is wheel speed, in rpm.

Examples
Scene Interrogation with Camera and Ray Tracing Reference Application
Interrogate a 3D Unreal Engine® scene with a vehicle dynamics model by using a camera and ray tracing reference application project.
Ports
Input
Brake pressure, in Pa.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set the Brake Type parameter, to one of these types:
DiscDrumMapped
Axle torque, Ta, about wheel spin axis, in N·m.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Axle longitudinal velocity, Vx, along tire-fixed x-axis, in m/s.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Axle lateral velocity, Vy, along tire-fixed y-axis, in m/s.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Camber angle, ɣ, or inclination angle, ε, in rad.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Tire angular velocity, r, about the tire-fixed z-axis (yaw rate), in rad/s.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Tire inflation pressure, pi, in Pa.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Ground displacement along tire-fixed z-axis, in m. Positive input produces wheel lift.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Axle force applied to tire, Fext, along vehicle-fixed z-axis (positive input compresses the tire), in N.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Vertical Motion to
None or Magic
Formula.
Tire radial deflection, RadialDeflct, in m. This value will be used in all internal dependent magic formula equations that rely on deflection.
Vector is the number of wheels,
N, by 1. If you provide a
scalar value, the block assumes that number of wheels is one.
Dependencies
To enable this port, set Vertical Motion to
External Deflection.
Magic Formula 6.2 scale factor array. Array dimensions are 27 by
the number of wheels, N.
The Magic Formula 6.2 equations use scale factors to account for static or simulation
run-time variations. Nominally, most are set to 1.
| Array Element | Variable | Scale Factor |
|---|---|---|
ScaleFctrs(1,1) | lam_Fzo | Nominal load |
ScaleFctrs(2,1) | lam_mux
| Longitudinal peak friction coefficient |
ScaleFctrs(3,1) | lam_muy
| Lateral peak friction coefficient |
ScaleFctrs(4,1) | lam_muV | Slip speed, Vs, decaying friction |
ScaleFctrs(5,1) | lam_Kxkappa
| Brake slip stiffness |
ScaleFctrs(6,1) | lam_Kyalpha
| Cornering stiffness |
ScaleFctrs(7,1) | lam_Cx | Longitudinal shape factor |
ScaleFctrs(8,1) | lam_Cy | Lateral shape factor |
ScaleFctrs(9,1) | lam_Ex
| Longitudinal curvature factor |
ScaleFctrs(10,1) | lam_Ey
| Lateral curvature factor |
ScaleFctrs(11,1) | lam_Hx
| Longitudinal horizontal shift |
ScaleFctrs(12,1) | lam_Hy | Lateral horizontal shift |
ScaleFctrs(13,1) | lam_Vx
| Longitudinal vertical shift |
ScaleFctrs(14,1) | lam_Vy | Lateral vertical shift |
ScaleFctrs(15,1) | lam_Kygamma
| Camber force stiffness |
ScaleFctrs(16,1) | lam_Kzgamma | Camber torque stiffness |
ScaleFctrs(17,1) | lam_t | Pneumatic trail (effecting aligning torque stiffness) |
ScaleFctrs(18,1) | lam_Mr | Residual torque |
ScaleFctrs(19,1) | lam_xalpha
| Alpha influence on Fx (kappa) |
ScaleFctrs(20,1) | lam_ykappa | Kappa influence on Fy (alpha) |
ScaleFctrs(21,1) | lam_Vykappa
| Induced ply steer Fy |
ScaleFctrs(22,1) | lam_s
| Moment arm of Fx |
ScaleFctrs(23,1) | lam_Cz
| Radial tire stiffness |
ScaleFctrs(24,1) | lam_Mx
| Overturning couple stiffness |
ScaleFctrs(25,1) | lam_VMx
| Overturning couple vertical shift |
ScaleFctrs(26,1) | lam_My | Rolling resistance moment |
ScaleFctrs(27,1) | lam_Mphi | Parking torque Mz |
Output
Block data, returned as a bus signal containing these block values.
| Signal | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Axle torque about wheel-fixed y-axis | N·m |
| Wheel angular velocity about wheel-fixed y-axis | rad/s |
| Longitudinal vehicle force along tire-fixed x-axis | N |
| Lateral vehicle force along tire-fixed y-axis | N |
| Vertical vehicle force along tire-fixed z-axis | N |
| Overturning moment about tire-fixed x-axis | N·m |
| Rolling resistance torque about tire-fixed y-axis | N·m |
Mz | Aligning moment about tire-fixed z-axis | N·m |
| Vehicle longitudinal velocity along tire-fixed x-axis | m/s |
| Vehicle lateral velocity along tire-fixed y-axis | m/s |
| Loaded effective radius | m |
| Longitudinal slip ratio | NA |
| Side slip angle | rad |
| Contact patch half length | m |
| Contact patch half width | m |
| Loaded radius | m |
| Tire radial deflection | m |
| Wheel torque | N·m |
| Camber angle | rad |
| Tire angular velocity about the tire-fixed z-axis (yaw rate) | rad/s |
| Brake torque about vehicle-fixed y-axis | N·m |
| Brake pressure | Pa |
| Axle local vertical displacement along tire-fixed z-axis | m |
| Axle vertical velocity along tire-fixed z-axis | m/s |
| Ground displacement along tire-fixed z-axis (positive input produces wheel lift) | m |
| Vertical sidewall force on ground along tire-fixed z-axis | N |
| Tire inflation pressure | Pa |
Wheel angular velocity, ω, about wheel-fixed y-axis, in rad/s.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Longitudinal force acting on axle, Fx, along tire-fixed x-axis, in N. Positive force acts to move the vehicle forward.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Lateral force acting on axle, Fy, along tire-fixed y-axis, in N.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Vertical force acting on axle, Fz, along tire-fixed z-axis, in N.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Longitudinal moment acting on axle, Mx, about tire-fixed x-axis, in N·m.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Lateral moment acting on axle, My, about tire-fixed y-axis, in N·m.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Vertical moment acting on axle, Mz, about tire-fixed z-axis, in N·m.
Vector is the number of wheels, N,
by 1. If you provide a scalar value, the block assumes that number of
wheels is one.
Parameters
Tire Options
Use the Tire type parameter to select the source of the tire data.
| Goal | Action |
|---|---|
Import your own external file containing Magic Formula coefficients, and use them to drive the empirical equations modeling the tire1 and 2. The file you import can be a .mat, .tir, or .txt type, and must contain parameter names corresponding to those in the tire block. |
Update the block parameters with fitting coefficients from a file:
|
Select one of the Magic Formula built-in tire models to drive the empirical equations modeling the tire 1 and 2. | Update the applicable block parameters with values from a built-in tire model:
|
Programmatic Use
To set the block
parameter value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block
parameter value programmatically, use the get_param
function.
| Parameter: | tireType |
| Values: | External file | Light passenger car
205/60R15 | Light passenger car
245/60R16 | Mid-size passenger car
235/45R18 | Performance car
225/40R19 | SUV 265/50R20 | Light truck 275/65R18 | Commercial truck
295/75R22.5 |
| Data Types: | character vector |
Tire file .tir or object containing empirical data
to model tire longitudinal and lateral behavior with the Magic Formula.
If you provide an .txt file, make sure the file
contains names that correspond to the block parameters.
Update the block parameters with fitting coefficients from a file:
Set Tire type to
External file.On the Wheel and Tire Parameters > External tire source pane, select Select file.
Select the tire coefficient file.
Select Update mask values from file. In the dialog box that prompts you for confirmation, click OK. The block updates the parameters.
Select Apply.
Programmatic Use
To set the block
parameter value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block
parameter value programmatically, use the get_param
function.
| Parameter: | tireParamSet |
| Values: | vdynPassCar.mat (default) | .tir | .txt |
| Data Types: | character vector |
Type of vertical motion. By default, the block uses the Magic Formula to calculate the vertical motion of the tire.
Programmatic Use
To set the block
parameter value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block
parameter value programmatically, use the get_param
function.
| Parameter: | vertType |
| Values: | Magic
Formula (default) | None | External deflection |
| Data Types: | character vector |
Select to include ply steer in the Magic Formula 6.2 equations.
By default, the blocks include ply steer and turn slip in the Magic Formula 6.2 equations. The equations are fit to flat-belt test data and predict a number of tire effects, including ply steer and turn slip. Consider removing the effects if your:
Test data does not include ply steer or turn slip data.
Analysis does not require ply steer or turn slip effects.
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets these parameters to 0:
Vertical shift of overturning moment, QSX1
Combined slip Fx shift factor reduction, RHX1
Efy curvature constant camber dependency, PEY3
SHY horizontal shift at FZNOM, PHY1
SHY variation with load, PHY2
Svy/Fz vertical shift at FZNOM, PVY1
Svy/Fz variation with load, PVY2
Fy shift reduction with slip angle, RBY3
Slip ratio side force Svyk/Muy*Fz at FZNOM, RVY1
Side force Svyk/Muy*Fz variation with load, RVY2
Bpt slope variation with camber, QBZ4
Dpt peak trail variation with camber, QDZ3
Dmr peak residual torque, QDZ6
Dmr peak residual torque variation with load, QDZ7
Ept variation with sign of alpha-t, QEZ4
Sht horizontal trail shift at FZNOM, QHZ1
Sht variation with load, QHZ2
Nominal value of s/R0: effect of Fx on Mz, SSZ1
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value
programmatically, use the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | plySteer |
| Values: | on (default) | off |
| Data Types: | character vector |
Select to include ply steer in Magic Formula 6.2 equations.
By default, the blocks include ply steer and turn slip in the Magic Formula 6.2 equations. The equations are fit to flat-belt test data and predict a number of tire effects, including ply steer and turn slip. Consider removing the effects if your:
Test data does not include ply steer or turn slip data.
Analysis does not require ply steer or turn slip effects.
If you clear Turn slip, the block internally:
Sets the Magic Formula turn slip equations to 1. Specifically, equations 4.E77, 4.E79, 4.E81, 4.E83, 4.E84, 4.E92, 4.E102, 4.E101, and 4.E1052.
Uses Magic Formula terms that effect horizontal shift.
Uses Magic Formula small turn slip values in 4.E272.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value
programmatically, use the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | turnslip |
| Values: | on (default) | off |
| Data Types: | character vector |
Use the Brake Type parameter to select the brake.
| Action | Brake Type Setting |
|---|---|
No braking |
|
Implement brake that converts the brake cylinder pressure into a braking force |
|
Implement simplex drum brake that converts the applied force and brake geometry into a net braking torque |
|
Implement lookup table that is a function of the wheel speed and applied brake pressure |
|
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value
programmatically, use the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | BrakeType |
| Values: | None | Disc | Drum | Mapped |
| Data Types: | character vector |
Plotting
Click Install Extended Tire Features to install the Extended Tire Features for Vehicle Dynamics Blockset support package. With the support package, you can plot steady-state force and moment tire responses from the Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF Block Parameters dialog box.
Click Plot steady state force, moment response to generate these plots:
Lateral force [N] vs Slip angle [rad]
Self-aligning moment [Nm] vs Slip angle [rad]
Longitudinal force [N] vs Longitudinal slip []
Longitudinal force [N] vs Lateral force [N]
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, click Install Extended Tire Features.
Brake
Static friction coefficient, specified as a
scalar or N-by-1 vector, dimensionless. If
you specify a scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a
vector, you must specify vectors for the other brake parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Disc, Drum, or
Mapped.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | mu_static |
| Values: | 0.3 (default) | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Kinematic friction coefficient, specified as
a scalar or N-by-1 vector, dimensionless.
If you specify a scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you
specify a vector, you must specify vectors for the other brake
parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Disc, Drum, or
Mapped.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | mu_kinetic |
| Values: | 0.2 (default) | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Disc
Disc brake actuator bore, specified as a
scalar or N-by-1 vector, in m. If you
specify a scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a
vector, you must specify vectors for the other brake parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Disc.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | disc_abore |
| Values: | 0.05 (default) | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Brake pad mean radius, specified as a scalar
or N-by-1 vector, in m. If you specify a
scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a vector, you
must specify vectors for the other brake parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Disc.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Rm |
| Values: | 0.177 (default) | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Number of brake pads, specified as a scalar
or N-by-1 vector, dimensionless. If you
specify a scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a
vector, you must specify vectors for the other brake parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Disc.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | num_pads |
| Values: | 2 (default) | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Drum
Drum brake actuator bore, specified as a
scalar or N-by-1 vector, in m. If you
specify a scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a
vector, you must specify vectors for the other brake parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Drum.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | drum_abore |
| Values: | 0.0508 (default) | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Shoe pin to drum center distance, in m.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Drum.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | drum_a |
| Values: | 0.123 (default) | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Shoe pin center to force application point distance, in m.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Drum.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | drum_c |
| Values: | 0.212 (default) | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Drum internal radius, in m.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Drum.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | drum_r |
| Values: | 0.15 (default) | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Shoe pin to pad start angle, in deg.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Drum.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | drum_theta1 |
| Values: | 0 (default) | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Shoe pin to pad end angle, in deg.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Drum.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | drum_theta2 |
| Values: | 126 (default) | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Mapped
Brake actuator pressure breakpoints, in bar.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Mapped.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | brake_p_bpt |
| Values: | vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Wheel speed breakpoints, in rpm.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Mapped.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | brake_n_bpt |
| Values: | vector |
| Data Types: | double |
The lookup table for the brake torque, , is a function of applied brake pressure and wheel speed, where:
T is brake torque, in N·m.
P is applied brake pressure, in bar.
N is wheel speed, in rpm.

Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Brake Type to
Mapped.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | f_brake_t |
| Values: | vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Simulation
Initial wheel rotational velocity, specified as a
scalar or N-by-1 vector, in rad/s. If you specify
a scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a vector, you must
specify vectors for the other rotational parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value
programmatically, use the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | omegao |
| Values: | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Dimension
Inertial and Damping
Tire mass, specified as a scalar or
N-by-1 vector, in kg. If you specify a
scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a vector, you
must specify vectors for the other inertial parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Vertical Motion to
Magic Formula.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | MASS |
| Values: | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Tire rotational inertia (rolling axis), specified as
a scalar or N-by-1 vector, in
kg·m2. If you specify a scalar, the block uses that value
for all wheels. If you specify a vector, you must specify vectors for the other
rotational parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value
programmatically, use the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | IYY |
| Values: | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Rotational damping, specified as a scalar or
N-by-1 vector, in N·m·s/rad. If you specify a
scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a vector, you must
specify vectors for the other rotational parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value
programmatically, use the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | br |
| Values: | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Gravity, GRAVITY, in m/s^2.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Vertical Motion to
Magic Formula.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | GRAVITY |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Vertical
Initial tire displacement, specified as a
scalar or N-by-1 vector, in m. If you
specify a scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a
vector, you must specify vectors for the other vertical parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | zo |
| Values: | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Initial wheel vertical velocity, specified as
a scalar or N-by-1 vector, in m/s. If you
specify a scalar, the block uses that value for all wheels. If you specify a
vector, you must specify vectors for the other vertical parameters.
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | zdoto |
| Values: | scalar | N-by-1 vector |
| Data Types: | double |
Linear load change with deflection and quadratic camber, Q_FZ3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Q_FZ3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Vertical stiffness change due to lateral load dependency on lateral stiffness, Q_FCY2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Q_FCY2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Linear load dependent camber angle effect on vertical stiffness, Q_CAM1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Q_CAM1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Quadratic load dependent camber angle effect on vertical stiffness, Q_CAM2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Q_CAM2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Linear reduction of stiffness with load and camber angle, Q_CAM3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Q_CAM3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Constant camber and slip angle effect on vertical stiffness, Q_FYS1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Q_FYS1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Linear camber and slip angle effect on vertical stiffness, Q_FYS2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Q_FYS2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Quadratic camber and slip angle effect on vertical stiffness, Q_FYS3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | Q_FYS3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Structural
Linear vertical deflection influence on longitudinal stiffness, PCFX1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PCFX1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Quadratic vertical deflection influence on longitudinal stiffness, PCFX2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PCFX2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Linear vertical deflection influence on lateral stiffness, PCFY1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PCFY1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Quadratic vertical deflection influence on lateral stiffness, PCFY2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PCFY2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Contact Patch
Longitudinal
Linear variation of longitudinal slip stiffness with tire pressure, PPX1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PPX1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Quadratic variation of longitudinal slip stiffness with tire pressure, PPX2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PPX2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Linear variation of peak longitudinal friction with tire pressure, PPX3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PPX3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Quadratic variation of peak longitudinal friction with tire pressure, PPX4, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PPX4 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Combined slip longitudinal force, Fx, slope factor reduction, RBX1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RBX1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Slip ratio longitudinal force, Fx, slope reduction variation, RBX2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RBX2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Camber influence on combined slip longitudinal force, Fx, stiffness, RBX3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RBX3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Shape factor for combined slip longitudinal force, Fx, reduction, RCX1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RCX1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Combined longitudinal force, Fx, curvature factor with load, REX2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | REX2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Combined slip longitudinal force, Fx, shift factor reduction, RHX1, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RHX1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Overturning
Vertical shift of overturning moment, QSX1, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QSX1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Overturning moment, Mx, combined lateral force load and camber, QSX4, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QSX4 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Overturning moment, Mx, load effect due to lateral force and camber, QSX5, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QSX5 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Overturning moment, Mx, due to B-factor of lateral force and load, QSX9, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QSX9 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Overturning moment, Mx, due to vertical force and camber, QSX10, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QSX10 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Overturning moment, Mx, due to B-factor of vertical force and camber, QSX11, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QSX11 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Overturning moment, Mx, due to lateral force with camber, QSX14, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QSX14 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral
Lateral curvature, Efy, constant camber dependency, PEY3, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PEY3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Maximum lateral force stiffness, KFy, to nominal force, FZNOM, ratio, PKY1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PKY1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Load at maximum lateral force stiffness, KFy, to nominal force, FZNOM, ratio, PKY2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PKY2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force stiffness, KFy, to nominal force, FZNOM, stiffness variation with camber, PKY3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PKY3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Horizontal shift, SHY, at nominal force, FZNOM, PHY1, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PHY1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Horizontal shift, SHY, variation with load, PHY2, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PHY2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Vertical shift, Svy, at nominal force, FZNOM, PVY1, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PVY1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Vertical shift, Svy, variation with load, PVY2, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PVY2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Cornering stiffness variation with inflation pressure induced nominal load dependency, PPY2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PPY2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, shift reduction with slip angle, RBY3, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RBY3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, combined stiffness variation from camber, RBY4, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RBY4 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, combined reduction shift factor with load, RHY2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RHY2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Slip ratio side force at nominal force, FZNOM, RVY1, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RVY1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Side force variation with load, RVY2, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | RVY2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Rolling
Aligning
Trail slope factor for trail Bpt at nominal force, FZNOM, QBZ1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QBZ1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Slope variation with camber, QBZ4, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QBZ4 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Peak trail, Dpt, variation with camber, QDZ3, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QDZ3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Peak residual torque, Dmr, QDZ6, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QDZ6 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Peak residual torque, Dmr, variation with load, QDZ7, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QDZ7 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Peak residual torque, Dmr, variation with camber and load, QDZ9, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QDZ9 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Peak residual torque, Dmr, variation with square of camber, QDZ10, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QDZ10 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Peak residual torque, Dmr, variation with square of load, QDZ11, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QDZ11 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Trail curvature, Ept variation with sign of alpha-t, QEZ4, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QEZ4 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Trail curvature, Ept variation with sign of alpha-t and camber, QEZ5, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QEZ5 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Horizontal trail shift, Sht, at nominal load, FZNOM, QHZ1, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QHZ1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Horizontal trail shift, Sht, variation with load, QHZ2, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QHZ2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Horizontal trail shift, Sht, variation with load and camber, QHZ4, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QHZ4 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Inflation pressure influence on residual aligning torque, PPZ2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PPZ2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Nominal value of s/R0: effect of longitudinal force, Fx, on aligning torque, Mz, SSZ1, dimensionless.
Dependencies
If you clear Ply steer, the block internally sets this parameter to 0 in the Magic Formula equations.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | SSZ1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Turnslip
Longitudinal force, Fx, peak reduction due to spin with varying load, PDXP2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PDXP2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Longitudinal force, Fx, peak reduction due to spin with slip ratio, PDXP3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PDXP3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, peak reduction due to spin with varying load, PDYP2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PDYP2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, peak reduction due to spin with slip angle, PDYP3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PDYP3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, peak reduction due to square root of spin, PDYP4, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PDYP4 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, versus slip angle response lateral shift limit, PHYP1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PHYP1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, versus slip angle response max lateral shift limit, PHYP2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PHYP2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, versus slip angle response max lateral shift limit with load, PHYP3, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PHYP3 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Lateral force, Fy, versus slip angle response lateral shift curvature factor, PHYP4, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | PHYP4 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Turn moment for constant turning and zero longitudinal speed, QCRP1, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QCRP1 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
Turn slip moment increase with spin at 90-degree slip angle, QCRP2, dimensionless.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter
value programmatically, use the set_param
function.
To get the block parameter
value programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | QCRP2 |
| Values: | scalar |
| Data Types: | double |
References
[1] Besselink, Igo, Antoine J. M. Schmeitz, and Hans B. Pacejka, "An improved Magic Formula/Swift tyre model that can handle inflation pressure changes," Vehicle System Dynamics - International Journal of Vehicle Mechanics and Mobility 48, sup. 1 (2010): 337–52, https://doi.org/10.1080/00423111003748088.
[2] Pacejka, H. B. Tire and Vehicle Dynamics. 3rd ed. Oxford, United Kingdom: SAE and Butterworth-Heinemann, 2012.
[3] Schmid, Steven R., Bernard J. Hamrock, and Bo O. Jacobson. Fundamentals of Machine Elements, SI Version. 3rd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2018aStarting in R2024b, you can specify Tire type to use the new built-in
tire model, Light passenger car 245/60R16.
Starting in R2024b, these parameters have been renamed.
| Old Name | New Name |
|---|---|
| Wheel width | Tire nominal section width |
| Unloaded radius | Tire unloaded radius |
| Initial rotational velocity | Initial wheel rotational velocity |
| Wheel mass | Tire mass |
| Rotational inertia | Tire rotational inertia |
Starting in R2024b, specifying Vertical Motion as External Deflection enables the RadialDeflct port. Use this port to define the sidewall deflection when interfacing with a tire in cases where forces are not provided.
Starting in R2024b, the Info port bus contains these new signals.
| Signal | Description |
|---|---|
RadialDeflct | Tire radial deflection |
RL | Loaded radius |
WhlTrq | Wheel torque |
If you have the Extended Tire Features for Vehicle Dynamics Blockset support package installed, you can use the new Plot steady state force, moment response button to generate plots.
Starting from R2023a, the Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF block includes the Vertical Motion parameter. By default, the Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF block uses the Magic Formula to calculate the vertical motion of the tire.
Starting from R2022b, you can to use the Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF block to specify brake and
tire characteristics for each wheel on your vehicle. Specifically, the block allows
N-by-1 vectors for these parameters:
Static friction coefficient, mu_static
Kinetic friction coefficient, mu_kinetic
Disc brake actuator bore, disc_abore
Brake pad mean radius, Rm
Number of brake pads, num_pads
Drum brake actuator bore, disc_abore
Initial rotational velocity, omegao
Rotational damping, br
Wheel mass, MASS
Rotational inertia (rolling axis), IYY
Initial tire displacement, zo
Initial wheel vertical velocity (wheel fixed frame), zdoto
N is the number of wheels and must match the input signal dimensions.
Starting from R2022b, the Combined Slip Wheel 2DOF block includes Ply steer and Turn slip parameters. To remove ply steer and turn slip from the Magic Formula implementation of these blocks, clear the Ply steer and Turn slip parameters.
See Also
Blocks
- Combined Slip Wheel CPI | Combined Slip Wheel STI | Fiala Wheel 2DOF | Longitudinal Wheel | Dugoff Wheel 2DOF
Functions
1 Reprinted with permission Copyright © 2008 SAE International. Further distribution of this material is not permitted without prior permission from SAE.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)
