Identify Classes in Markov Chain
This example shows how to programmatically and visually identify classes in a Markov chain. The example also extracts a recurrent class from the chain for further analysis.
Create an eight-state Markov chain from a randomly generated transition matrix with 50 infeasible transitions in random locations. An infeasible transition is a transition whose probability of occurring is zero. Assign arbitrary names to the states.
numStates = 8; Zeros = 50; stateNames = strcat(repmat("Regime ",1,8),string(1:8)); rng(1617676169) % For reproducibility mc = mcmix(8,'Zeros',Zeros,'StateNames',stateNames);
Visually classify the states in the Markov chain by plotting a digraph. Specify node markers and colors for transient and recurrent states and communicating classes.
figure;
graphplot(mc,'ColorNodes',true);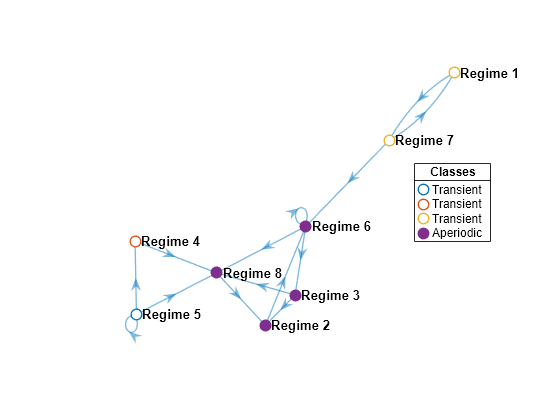
The chain has four classes, three transient and one aperiodic. The aperiodic class is composed of four recurrent states.
Programmatically classify states in the Markov chain. Return the following:
Class indices,
binsClass memberships,
ClassStatesWhether the classes are recurrent,
ClassRecurrenceClass periods,
ClassPeriod
[bins,ClassStates,ClassRecurrence,ClassPeriod] = classify(mc)
bins = 1×8
3 4 4 2 1 4 3 4
ClassStates=1×4 cell array
{["Regime 5"]} {["Regime 4"]} {["Regime 1" "Regime 7"]} {["Regime 2" "Regime 3" "Regime 6" "Regime 8"]}
ClassRecurrence = 1×4 logical array
0 0 0 1
ClassPeriod = 1×4
1 1 1 1
ClassStates{:}ans = "Regime 5"
ans = "Regime 4"
ans = 1×2 string
"Regime 1" "Regime 7"
ans = 1×4 string
"Regime 2" "Regime 3" "Regime 6" "Regime 8"
classify assigns bin numbers to each state to identify class membership. The programmatic results match the visual results.
To characterize the asymptotic behavior of the chain, isolate the recurrent class by forming a subchain. To create a subchain:
Identify the recurrent class in the Markov chain.
Identify the bin number of the recurrent class.
Pass the Markov chain object and bin number to
subchain.
recurrentClass = find(ClassRecurrence,1); recurrentState = find((bins == recurrentClass),1); sc = subchain(mc,recurrentState);
sc is a dtmc model object representing the recurrent class in mc.
Plot a digraph of the subchain. Indicate transition probabilities by using edge colors. Specify node markers and colors for transient and recurrent states and communicating classes.
figure; graphplot(sc,'ColorEdges',true,'ColorNodes',true);

As expected, the subchain has one class composed of the four recurrent states.