gaussianAntenna
Description
gaussianAntenna(
adds a Gaussian antenna to each transmitter or receiver in the vector
trx,Name=Value)trx and specifies options using name-value arguments. For example,
DishDiameter=1.7 defines the diameter of the antenna dish.
ant = gaussianAntenna(___)ant.
Examples
Create a satellite scenario object.
startTime = datetime(2020,11,25,0,0,0);
stopTime = startTime + days(1);
sampleTime = 60; % seconds
sc = satelliteScenario(startTime,stopTime,sampleTime)sc =
satelliteScenario with properties:
StartTime: 25-Nov-2020
StopTime: 26-Nov-2020
SampleTime: 60
AutoSimulate: 1
Satellites: [1×0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Satellite]
GroundStations: [1×0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.GroundStation]
Platforms: [1×0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Platform]
Viewers: [0×0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Viewer]
AutoShow: 1
Add a satellite to the scenario.
semiMajorAxis = 10000000; % meters eccentricity = 0; inclination = 60; % degrees rightAscensionOfAscendingNode = 0; % degrees argumentOfPeriapsis = 0; % degrees trueAnomaly = 0; % degrees sat = satellite(sc,semiMajorAxis,eccentricity,inclination,rightAscensionOfAscendingNode, ... argumentOfPeriapsis,trueAnomaly,Name="Satellite");
Add gimbals to the satellite. These gimbals enable the satellite receiver antenna to steer to the first ground station, and its transmitter antenna to steer to the second ground station.
gimbalrxSat = gimbal(sat); gimbaltxSat = gimbal(sat);
Add a receiver to the first gimbal of the satellite.
gainToNoiseTemperatureRatio = 5; % dB/K systemLoss = 3; % dB rxSat = receiver(gimbalrxSat,Name="Satellite Receiver",GainToNoiseTemperatureRatio= ... gainToNoiseTemperatureRatio,SystemLoss=systemLoss)
rxSat =
Receiver with properties:
Name: Satellite Receiver
ID: 4
MountingLocation: [0; 0; 0] meters
MountingAngles: [0; 0; 0] degrees
Antenna: [1x1 satcom.satellitescenario.GaussianAntenna]
SystemLoss: 3 decibels
PreReceiverLoss: 3 decibels
GainToNoiseTemperatureRatio: 5 decibels/Kelvin
RequiredEbNo: 10 decibels
CoordinateAxes: [1x1 matlabshared.satellitescenario.CoordinateAxes]
Add a transmitter to the second gimbal of the satellite.
frequency = 27e9; % Hz power = 20; % dBW bitRate = 20; % Mbps systemLoss = 3; % dB txSat = transmitter(gimbaltxSat,Name="Satellite Transmitter",Frequency=frequency, ... power=power,BitRate=bitRate,SystemLoss=systemLoss)
txSat =
Transmitter with properties:
Name: Satellite Transmitter
ID: 5
MountingLocation: [0; 0; 0] meters
MountingAngles: [0; 0; 0] degrees
Antenna: [1x1 satcom.satellitescenario.GaussianAntenna]
SystemLoss: 3 decibels
Frequency: 2.7e+10 Hertz
BitRate: 20 Mbps
Power: 20 decibel-watts
Links: [1x0 satcom.satellitescenario.Link]
CoordinateAxes: [1x1 matlabshared.satellitescenario.CoordinateAxes]
Specify the antenna specifications of the repeater.
dishDiameter = 0.5; % meters
apertureEfficiency = 0.5;
gaussianAntenna(txSat,DishDiameter=dishDiameter,ApertureEfficiency=apertureEfficiency);
gaussianAntenna(rxSat,DishDiameter=dishDiameter,ApertureEfficiency=apertureEfficiency);Add two ground stations to the scenario.
gs1 = groundStation(sc,Name="Ground Station 1"); latitude = 52.2294963; % degrees longitude = 0.1487094; % degrees gs2 = groundStation(sc,latitude,longitude,Name="Ground Station 2");
Point gimbals of the satellite towards the two ground stations for the simulation duration.
pointAt(gimbaltxSat,gs2); pointAt(gimbalrxSat,gs1);
Add gimbals to the ground stations. These gimbals enable the ground station antennas to steer towards the satellite.
gimbalgs1 = gimbal(gs1); gimbalgs2 = gimbal(gs2);
Add a transmitter to ground station gs1.
frequency = 30e9; % Hz power = 40; % dBW bitRate = 20; % Mbps txGs1 = transmitter(gimbalgs1,Name="Ground Station 1 Transmitter",Frequency=frequency, ... Power=power,BitRate=bitRate);
Add a receiver to ground station gs2.
requiredEbNo = 14; % dB rxGs2 = receiver(gimbalgs2,Name="Ground Station 2 Receiver",RequiredEbNo=requiredEbNo);
Define the antenna specifications of the ground stations.
dishDiameter = 5; % meters
gaussianAntenna(txGs1,DishDiameter=dishDiameter);
gaussianAntenna(rxGs2,DishDiameter=dishDiameter);Point gimbals of the ground stations towards the satellite for the simulation duration.
pointAt(gimbalgs1,sat); pointAt(gimbalgs2,sat);
Add link analysis to transmitter txGs1.
lnk = link(txGs1,rxSat,txSat,rxGs2)
lnk =
Link with properties:
Sequence: [10 4 5 11]
LineWidth: 2
LineColor: [0.3922 0.8314 0.0745]
Determine the times when ground station gs1 can send data to ground station gs2 via the satellite.
linkIntervals(lnk)
ans=4×8 table
Source Target IntervalNumber StartTime EndTime Duration StartOrbit EndOrbit
______________________________ ___________________________ ______________ ____________________ ____________________ ________ __________ ________
"Ground Station 1 Transmitter" "Ground Station 2 Receiver" 1 25-Nov-2020 00:20:00 25-Nov-2020 00:40:00 1200 NaN NaN
"Ground Station 1 Transmitter" "Ground Station 2 Receiver" 2 25-Nov-2020 03:19:00 25-Nov-2020 03:36:00 1020 NaN NaN
"Ground Station 1 Transmitter" "Ground Station 2 Receiver" 3 25-Nov-2020 06:15:00 25-Nov-2020 06:36:00 1260 NaN NaN
"Ground Station 1 Transmitter" "Ground Station 2 Receiver" 4 25-Nov-2020 22:20:00 25-Nov-2020 22:38:00 1080 NaN NaN
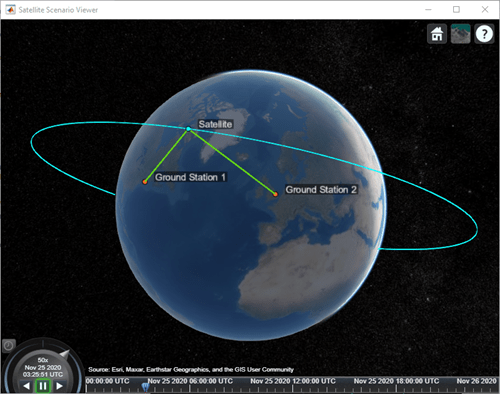
Visualize the link by using the Satellite Scenario Viewer.
play(sc);
startTime = datetime(2020,11,25,0,0,0);
stopTime = startTime + days(1);
sampleTime = 60; % seconds
sc = satelliteScenario(startTime,stopTime,sampleTime)sc =
satelliteScenario with properties:
StartTime: 25-Nov-2020
StopTime: 26-Nov-2020
SampleTime: 60
AutoSimulate: 1
CentralBodyOptions: [1×1 Aero.satellitescenario.CentralBodyOptions]
Satellites: [1×0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Satellite]
GroundStations: [1×0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.GroundStation]
Platforms: [1×0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Platform]
Viewers: [0×0 matlabshared.satellitescenario.Viewer]
AutoShow: 1
Define the orbital parameters of the satellite.
semiMajorAxis = 10000000; % meters eccentricity = 0; inclination = 60; % degrees rightAscensionOfAscendingNode = 0; % degrees argumentOfPeriapsis = 0; % degrees trueAnomaly = 0; % degrees
Create a satellite object and attach a gimbal to the satellite.
sat = satellite(sc,semiMajorAxis,eccentricity,inclination,rightAscensionOfAscendingNode, ... argumentOfPeriapsis,trueAnomaly,Name="Satellite"); gimbalSat = gimbal(sat); frequency = 27e9; % Hz
Define the transmitter parameters. Create a transmitter object and attach it to the gimbal.
power = 20; % dBW bitRate = 20; % Mbps systemLoss = 3; % dB txSat = transmitter(gimbalSat,Name="Satellite Transmitter",Frequency=frequency, ... power=power,BitRate=bitRate,SystemLoss=systemLoss)
txSat =
Transmitter with properties:
Name: Satellite Transmitter
ID: 3
MountingLocation: [0; 0; 0] meters
MountingAngles: [0; 0; 0] degrees
Antenna: [1x1 satcom.satellitescenario.GaussianAntenna]
SystemLoss: 3 decibels
Frequency: 2.7e+10 Hertz
BitRate: 20 Mbps
Power: 20 decibel-watts
Links: [1x0 satcom.satellitescenario.Link]
CoordinateAxes: [1x1 matlabshared.satellitescenario.CoordinateAxes]
Define the antenna parameters.
rho_a = 0.5; % Aperture efficiency d = 0.5; lambda = 0.01110342; % Wavelength in meters
Calculate the boresight gain and 3dB beamwidth for the gaussian antenna properties.
boresightGain = rho_a * ((pi * d / lambda)^2); % This is in linear scale beamwidth_3dB = 70 * lambda / d; % in degrees
Convert boresight gain from linear scale to dB. Create a gaussian antenna object and attach it to the transmitter.
boresightGain_dB = 10 * log10(boresightGain); antenna = gaussianAntenna(txSat,DishDiameter=d,ApertureEfficiency=rho_a);
Define the angle range from -180 to 180 degrees for gain calculation. Calculate the gain pattern and convert the gain to dB.
theta = -180:1:180; gain = boresightGain * exp(-(4 * log(2) * ((theta/beamwidth_3dB).^2))); gain_dB = 10 * log10(gain);
Generate a plot visualize the gain pattern of the Gaussian antenna.
figure; plot(theta, gain_dB); xlabel('Angle off the boresight (degrees)'); ylabel('Gain (dB)'); title('Gaussian Antenna Gain Pattern Using Algorithm'); grid on; axis tight; ylim([-40, max(gain_dB)+5]); % Adjust y-axis limits for better visualization

The X-axis represents the angle off the boresight in degrees, and the Y-axis represents the gain in dB.
Input Arguments
Transmitter or receiver object to which the Gaussian antenna is added, specified as either a scalar or a vector.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: 'DishDiameter'=1.7 sets the dish diameter of the antenna to
1.7 meters upon creation.
This property is read-only.
You can set this property only when calling gaussianAntenna.
After you call gaussianAntenna, this property is read-only.
Diameter of the Gaussian antenna dish in meters, specified as a scalar or a vector.
If
DishDiameteris a scalar, the same value is assigned to all transmitters or receivers intrx.If
DishDiameteris a vector, the length of the vector must equal that oftrx, and each transmitter or receiver intrxis assigned the corresponding element in theDishDiametervector.
This property is read-only.
You can set this property only when calling gaussianAntenna. After you call gaussianAntenna, this property is read-only.
Aperture efficiency of the Gaussian antenna, specified as a scalar in the range (0,1].
If
ApertureEfficiencyis a scalar, the same value is assigned to all transmitters or receivers intrx.If
ApertureEfficiencyis a vector, the length of the vector must equal that oftrx, and each transmitter or receiver intrxis assigned the corresponding element in theApertureEfficiencyvector.
Output Arguments
Gaussian antenna object added to the specified transmitter or receiver, returned as either a scalar or a vector.
Note
When the AutoSimulate property of satellite scenario is false, you
can call the gaussianAntenna function only when SimulationStatus is NotStarted. You can use the restart
function to reset the SimulationStatus to NotStarted, but doing so erases the
simulation data.
Algorithms
The Gaussian antenna approximates a parabolic reflector using a Gaussian curve as
gain(theta) = boresightGain*exp(-(4*log(2)*((theta/3dBbeamwidth)^2)))
Note that log(2) is a natural log, where:
boresightGain = rho_a*((pi*d/lambda)^2)
-
3dBbeamwidth = 70*lambda/d
(in degrees)
theta is the angle between the direction in which the gain is computed and the boresight direction is in degrees.
rho_a is the aperture efficiency.
d is the dish diameter in meters.
lambda is the wavelength in meters.
The gain in dBi is
gain_dBi(theta) = 10*log10(gain(theta)
Version History
Introduced in R2021a
See Also
Objects
Functions
hide|show|play|satellite|access|groundStation|receiver|transmitter
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)