Contenuto principale
Risultati per
I have been finding the AI Chat Playground very useful for daily MATLAB use. In particular it has been very useful for me in basically replacing or supplementing dives into MATLAB documentation. The documentation for MATLAB is in my experience uniformly excellent and thorough but it is sometimes lengthy and hard to parse and the AI Chat is a great one stop shop for many questions I have. However, I would find it very useful if the AI Chat could answer my queries and then also supply a link directly to the documentation. E.g. a box at the bottom of the answer that is basically
"Here is the documentation on the functions AI Chat referred to in this response"
could be neat.
Over at Reddit, a MATLAB user asked about when to use a script vs. a live script. How would you answer this?
Hi
I am using simulink for the frequency response analysis of the three phase induction motor stator winding.
The problem is that i can't optimise the pramaeter values manually, for this i have to use genetic algrothem. But iam stucked how to use genetic algorithum to optimise my circuit paramter values like RLC. Any guidence will be highly appreciated.
Starting with MATLAB can be daunting, but the right resources make all the difference. In my experience, the combination of MATLAB Onramp and Cody offers an engaging start.
MATLAB Onramp introduces you to MATLAB's basic features and workflows. Then practice your coding skill on Cody. Challenge yourself to solve 1 basic problem every day for a month! This consistent practice can significantly enhance your proficiency.
What other resources have helped you on your MATLAB journey? Share your recommendations and let's create a comprehensive learning path for beginners!
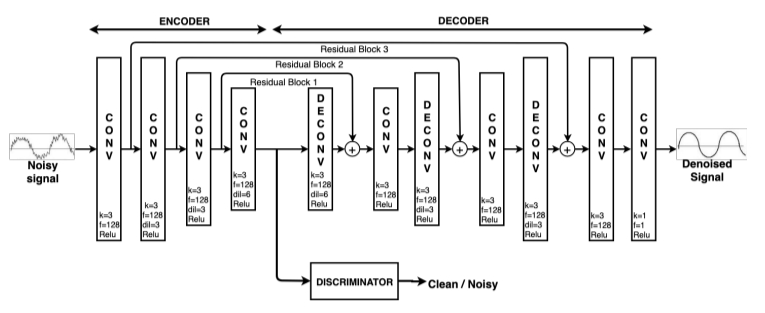
I am a beginner of deep learning, and meet with some problems in learning the MATLAB example "Denoise Signals with Adversarial Learning Denoiser Model", hope very much to get help!
1. visualizaition of the features
It is my understanding that the encoded representation of the autoencoder is the features of the original signal. However in this example, the output dimension of the encoder is 64xSignalLength. Does it mean that every sample point of the signal has 64 features?
2. usage of the residual blocks
The encoder-decoder model uses residual blocks (which contribute to reconstructing the denoised signal from the latent space, ). However, only the encoder output is connected to the discriminator. Doesn't it cause the prolem that most features will be learned by the residual blocks, and only a few features that could confuse the discriminator will be learned by the encoder and sent to the discriminator?
I would tell myself to understand vectorization. MATLAB is designed for operating on whole arrays and matrices at once. This is often more efficient than using loops.
I have been developing a neural net to extract a set of generative parameters from an image of a 2-D NMR spectrum. I use a pair of convolution layers each followed by a fullyconnected layer; the pair are joined by an addtion layer and that fed to a regression layer. This trains fine, but answers are sub-optimal. I woudl like to add a fully connected layer between the addtion layer and regression, but training using default training scripts simply won't converge. Any suggestions? Maybe I can start with the pre-trained weights for the convolution layers, but I don't know how to do this.
JHP

how can I do to get those informations?
This is not a question, it is my attempt at complying with the request for thumbs up/down voting. I vote thumbs up, for having AI.....
I am not sure if specific AI errors are to be reported. Other messages I just read from others here and the AI Chat itself clearly state that errors abound.
My AI request was: "Plot 300 points of field 2"
AI Chat gave me, in part:
data = thingSpeakRead(channelID, 'Fields', 2, 'NumPoints', 300, 'ReadKey', readAPIKey);
% Extract the field values
field1Values = data.Field1;
% Plot the data
plot(field1Values);
The AI code failed due to "Dot indexing is not supported for variables of this type"
So, I corrected the code thus to get the correct plot:
data = thingSpeakRead(channelID, 'Fields', 2, 'NumPoints', 300, 'ReadKey', readAPIKey);
% Extract the field values
%field1Values = data.Field1;
% Plot the data
plot(data);
I see great promise in AI Chat.
Opie
Explore all the capabilities for Modeling Dynamic Systems while keeping them handy with this Cheat Sheet - Download Now.
Write a matlab script that will print the odd numbers, 1 through 20, in reverse.
I cannot figure out how to do this correctly, please help.
I saw this post on Answers.
I was impressed at the capability of the AI, as I have been at other times when I posed a question to it, at least some of the time. So much so that I wondered...
What if the AI were automatically applied to EVERY question on Answers? Would that be a good or bad thing? For example, suppose the AI automatically offers an answer to every question as soon as it gets posted? Of course, users would still be allowed to post their own, possibly better answers. But would it tend to disincentivise individuals from ansering questions?
Perhaps as bad, would it push Answers into the mode of a homework solving forum? Since if every homework question gets a possibly pretty good automatic AI generated solution, then every student will just post all HW questions, and the forum would quickly become overwhelmed.
I suppose one idea could be to set up the AI to post an answer to all un-answered questions that are at least one month old. Then students would not gain by posting their homework.
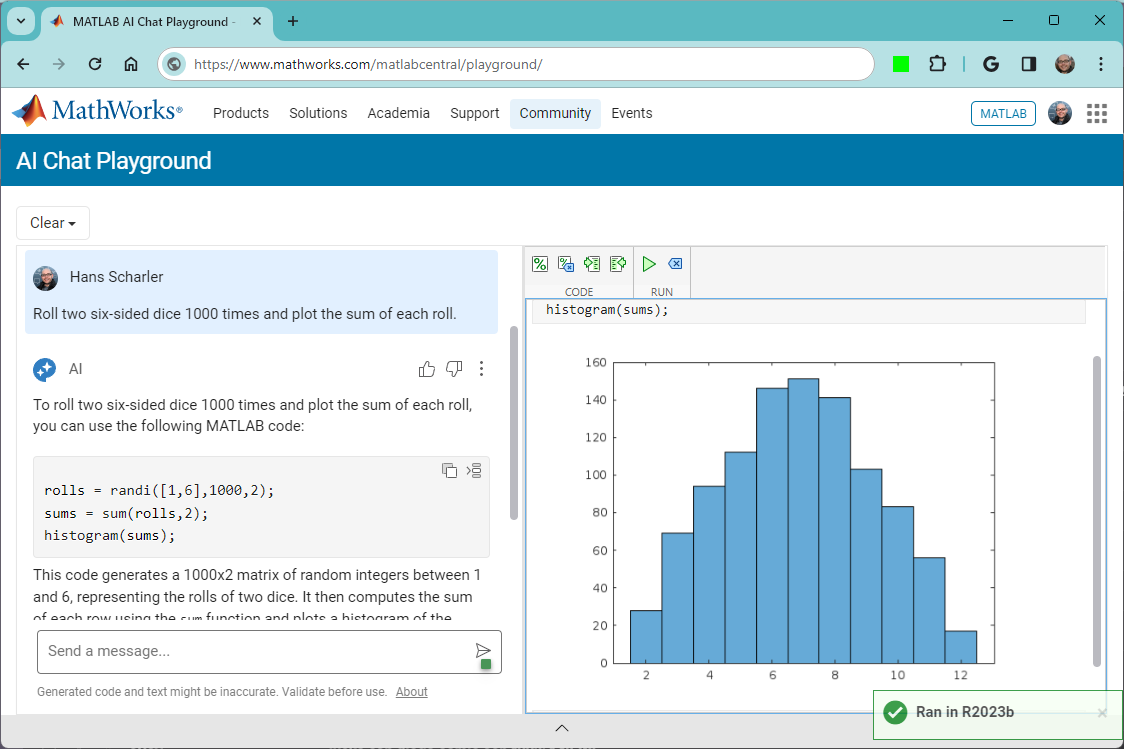
The MATLAB AI Chat Playground is open to everyone!
Check it out here on the community: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/playground
Here's a MATLAB class I wrote that leverages the MATLAB Central Interface for MATLAB toolbox, which in turn uses the publicy available Community API. Using this class, I've created a few Favorites that show me what's going on in MATLAB Central - without having to leave MATLAB 🙂
The class has a few convenient queries:
- Results for the last 7 days
- Results for the last 30 days
- Results for the current month
- Results for today
And supporting a bunch of different content scopes:
- All MATLAB Central
- MATLAB Answers
- Blogs
- Cody
- Contests
- File Exchange
- Exclude Answers content
The results are displayed in the command window (which worked best for me) and link to each post. Here's what that looks like for this command
>> CommunityFeed.thisMonth("app designer", CommunityFeed.Scope.ExcludeAnswers)

Let me know if you find this class useful and feel free to suggest changes.
New Cheat Sheet Alert!
Level up your data organization and access skills in MATLAB with our latest cheat sheet! Download the full cheat sheet on MATLAB GitHub for Students here.
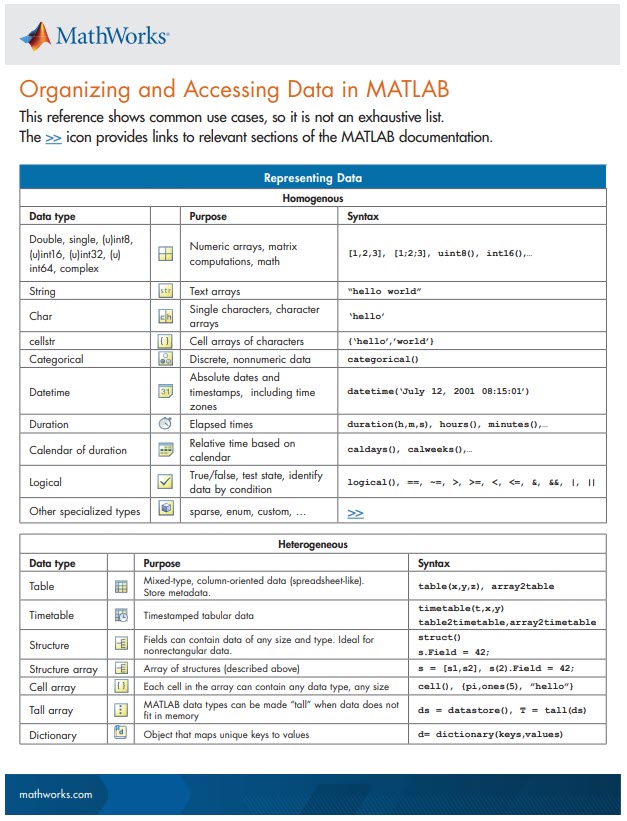
Calling all students! New to MATLAB or need helpful resources? Check out our MATLAB GitHub for Students repository! Find MATLAB examples, videos, cheat sheets, and more!
Visit the repository here: MATLAB GitHub for Students
Imagine x is a large vector and you want the smallest 10 elements. How might you do it?

I've now seen linear programming questions pop up on Answers recently, with some common failure modes for linprog that people seem not to understand.
One basic failure mode is an infeasible problem. What does this mean, and can it be resolved?
The most common failure mode seems to be a unbounded problem. What does this mean? How can it be avoided/solved/fixed? Is there some direction I can move where the objective obviously grows without bounds towards +/- inf?
Finally, I also see questions where someone wants the tool to produce all possible solutions.
A truly good exposition about linear programming would probably result in a complete course on the subject, and Aswers is limited in how much I can write (plus I'll only have a finite amount of energy to keep writing.) I'll try to answer each sub-question as separate answers, but if someone else would like to offer their own take, feel free to do so as an answer, since it has been many years for me since I learned linear programming.
Introduction
Comma-separated lists are really very simple. You use them all the time. Here is one:
a,b,c,d
That is a comma-separated list containing four variables, the variables a, b, c, and d. Every time you write a list separated by commas then you are writing a comma-separated list. Most commonly you would write a comma-separated list as inputs when calling a function:
fun(a,b,c,d)
or as arguments to the concatenation operator or cell construction operator:
[a,b,c,d]
{a,b,c,d}
or as function outputs:
[a,b,c,d] = fun();
It is very important to understand that in general a comma-separated list is NOT one variable (but it could be). However, sometimes it is useful to create a comma-separated list from one variable (or define one variable from a comma-separated list), and MATLAB has several ways of doing this from various container array types:
struct_array.field % all elements
struct_array(idx).field % selected elements
cell_array{:} % all elements
cell_array{idx} % selected elements
string_array{:} % all elements
string_array{idx} % selected elements
Note that in all cases, the comma-separated list consists of the content of the container array, not subsets (or "slices") of the container array itself (use parentheses to "slice" any array). In other words, they will be equivalent to writing this comma-separated list of the container array content:
content1, content2, content3, .. , contentN
and will return as many content arrays as the original container array has elements (or that you select using indexing, in the requested order). A comma-separated list of one element is just one array, but in general there can be any number of separate arrays in the comma-separated list (zero, one, two, three, four, or more). Here is an example showing that a comma-separated list generated from the content of a cell array is the same as a comma-separated list written explicitly:
>> C = {1,0,Inf};
>> C{:}
ans =
1
ans =
0
ans =
Inf
>> 1,0,Inf
ans =
1
ans =
0
ans =
Inf
How to Use Comma-Separated Lists
Function Inputs: Remember that every time you call a function with multiple input arguments you are using a comma-separated list:
fun(a,b,c,d)
and this is exactly why they are useful: because you can specify the arguments for a function or operator without knowing anything about the arguments (even how many there are). Using the example cell array from above:
>> vertcat(C{:})
ans =
1
0
Inf
which, as we should know by now, is exactly equivalent to writing the same comma-separated list directly into the function call:
>> vertcat(1,0,Inf)
ans =
1
0
Inf
How can we use this? Commonly these are used to generate vectors of values from a structure or cell array, e.g. to concatenate the filenames which are in the output structure of dir:
S = dir(..);
F = {S.name}
which is simply equivalent to
F = {S(1).name, S(2).name, S(3).name, .. , S(end).name}
Or, consider a function with multiple optional input arguments:
opt = {'HeaderLines',2, 'Delimiter',',', 'CollectOutputs',true);
fid = fopen(..);
C = textscan(fid,'%f%f',opt{:});
fclose(fid);
Note how we can pass the optional arguments as a comma-separated list. Remember how a comma-separated list is equivalent to writing var1,var2,var3,..., then the above example is really just this:
C = textscan(fid,'%f%f', 'HeaderLines',2, 'Delimiter',',', 'CollectOutputs',true)
with the added advantage that we can specify all of the optional arguments elsewhere and handle them as one cell array (e.g. as a function input, or at the top of the file). Or we could select which options we want simply by using indexing on that cell array. Note that varargin and varargout can also be useful here.
Function Outputs: In much the same way that the input arguments can be specified, so can an arbitrary number of output arguments. This is commonly used for functions which return a variable number of output arguments, specifically ind2sub and gradient and ndgrid. For example we can easily get all outputs of ndgrid, for any number of inputs (in this example three inputs and three outputs, determined by the number of elements in the cell array):
C = {1:3,4:7,8:9};
[C{:}] = ndgrid(C{:});
which is thus equivalent to:
[C{1},C{2},C{3}] = ndgrid(C{1},C{2},C{3});
Further Topics:
MATLAB documentation:
Click on these links to jump to relevant comments below:
Dynamic Indexing (indexing into arrays with arbitrary numbers of dimensions)
Summary
Just remember that in general a comma-separated list is not one variable (although they can be), and that they are exactly what they say: a list (of arrays) separated with commas. You use them all the time without even realizing it, every time you write this:
fun(a,b,c,d)
