cot
Cotangent of angle in radians
Syntax
Description
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
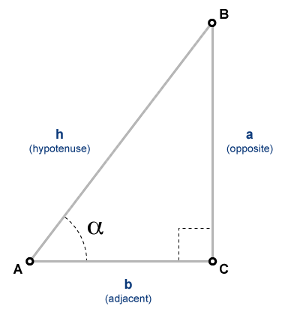
More About
Tips
In floating-point arithmetic,
cotis a bounded function. That is,cotdoes not return values ofInfor-Infat points of divergence that are multiples ofpi, but a large magnitude number instead. This stems from the inaccuracy of the floating-point representation of π.