Sistemi elettrici
Scoprire gli esempi che illustrano la modellazione, il controllo e la simulazione di sistemi elettrici.
Esempi in primo piano
Circuito RC in Simulink e Simscape
Questo esempio mostra due modelli di un circuito RC, di cui uno utilizza i blocchi di input/output di Simulink® e l'altro le reti fisiche di Simscape™.
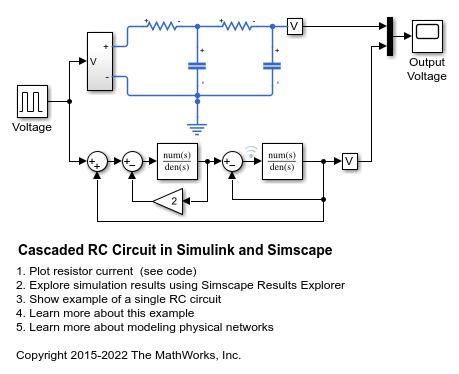
Cascaded RC Circuit in Simulink and Simscape
Two models of a cascaded RC circuit, one using Simulink® input/output blocks and one using Simscape™ physical networks.
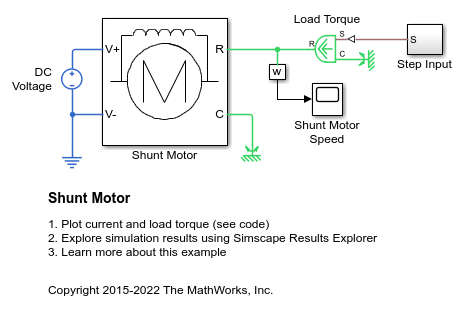
Shunt Motor
A model of a shunt motor. In a shunt motor, the field and armature windings are connected in parallel. Equivalent circuit parameters are armature resistance Ra = 110 Ohms, field resistance Rf = 2.46KOhms, and back emf coefficient Laf = 5.11. The back-emf is given by Laf*If*Ia*w, where If is the field current, Ia is the armature current, and w is the rotor speed in radians/s. The rotor inertia J is 2.2e-4kgm^2, and rotor damping B is 2.8e-6Nm/(radian/s).
Motore CC a magnete permanente
Questo modello è basato su un micromotore CC della Faulhaber, Serie 0615. I valori dei parametri sono impostati in modo da corrispondere alla variante da 1,5 V di questo motore. Il modello utilizza questi parametri per verificare la velocità a vuoto, la corrente a vuoto e la coppia di stallo indicate dal produttore.
Lead-Acid Battery
Model a lead-acid battery cell using the Simscape™ language to implement the nonlinear equations of the equivalent circuit components. In this way, as opposed to modeling entirely in Simulink®, the connection between model components and the defining physical equations is more easily understood. For the defining equations and their validation, see Jackey, R. "A Simple, Effective Lead-Acid Battery Modeling Process for Electrical System Component Selection", SAE World Congress & Exhibition, April 2007, ref. 2007-01-0778.
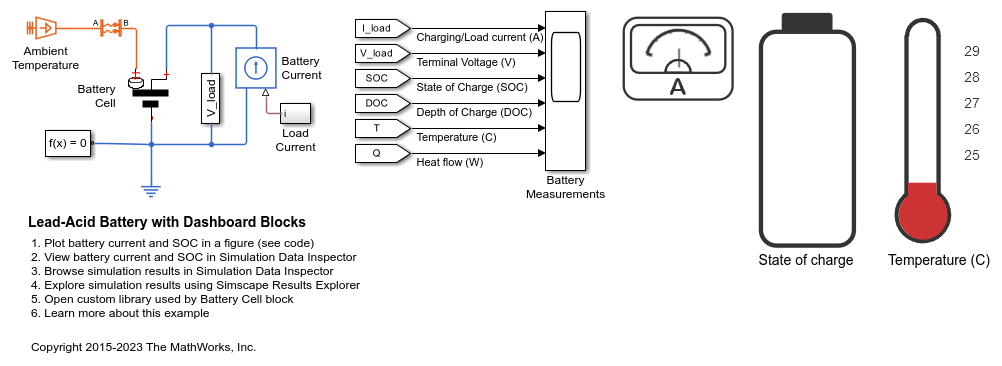
Lead-Acid Battery with Dashboard Blocks
Model a lead-acid battery cell using the Simscape™ language.
Pacco batterie agli ioni di litio con guasto
Questo esempio mostra come simulare in modo efficiente un pacco batterie composto da più celle collegate in serie. Mostra inoltre come sia possibile introdurre un guasto in una delle celle per vedere l'impatto sulle prestazioni della batteria e sulle temperature delle celle. Per quanto riguarda l'efficienza, le celle identiche collegate in serie non sono semplicemente modellate collegando i modelli delle celle in serie. Si utilizza invece una singola cella e la tensione al terminale viene scalata dal numero di celle. Il guasto viene rappresentato modificando i parametri del sottosistema Guasto cella 10, riducendo sia la capacità che la tensione a circuito aperto e aumentando i valori della resistenza.
Lithium-Ion Battery Pack with Fault Using Arrays
Simulate a battery pack that consists of multiple series-connected cells. It also shows how you can introduce a fault into one of the cells to see the impact on battery performance and cell temperatures. The battery pack is modeled in Simscape™ language by connecting cell models in series using arrays. You can represent the fault by defining different parameters for the faulty cell.
Cella della batteria al litio - Circuito equivalente a un ramo RC
Questo esempio mostra come modellare una cella al litio utilizzando il linguaggio Simscape™ per implementare gli elementi di un modello di circuito equivalente con un ramo RC. Per le equazioni di definizione e la loro validazione, vedere T. Huria, M. Ceraolo, J. Gazzarri, R. Jackey. “Modello elettrico ad alta fedeltà con dipendenza termica per la caratterizzazione e la simulazione di celle di batterie al litio ad alta potenza”, Conferenza Internazionale IEEE sui Vecoli Elettrici, marzo 2012.
Cella della batteria al litio - Circuito equivalente a due rami RC
Questo esempio mostra come modellare una cella al litio utilizzando il linguaggio Simscape™ per implementare gli elementi di un modello di circuito equivalente con due rami RC. Per le equazioni di definizione e la loro validazione, vedere T. Huria, M. Ceraolo, J. Gazzarri, R. Jackey. “Modello elettrico ad alta fedeltà con dipendenza termica per la caratterizzazione e la simulazione di celle di batterie al litio ad alta potenza”, Conferenza Internazionale IEEE sui Vecoli Elettrici, marzo 2012.
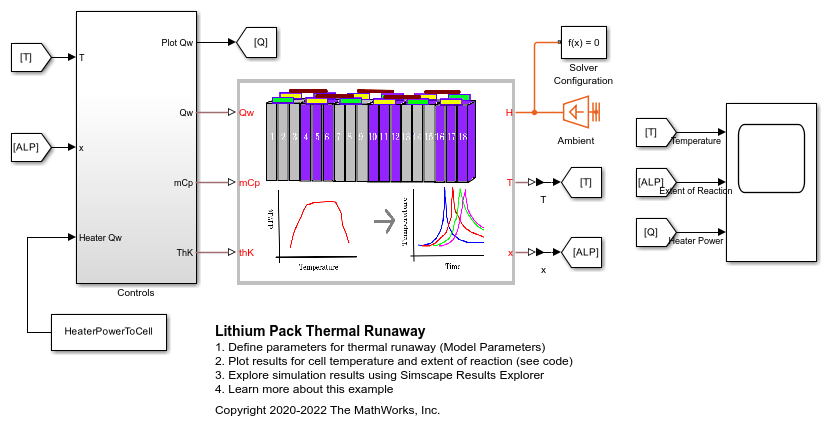
Lithium Pack Thermal Runaway
Model a thermal runaway in a lithium-ion battery pack. The model measures the cell heat generation, the cell-to-cell heat cascade, and the subsequent temperature rise in the cells, based on the design. The cell thermal runaway abuse heat is calculated using calorimeter data. Simulation is run to evaluate the number of cells that go into runaway mode, when just one cell is abused. To delay or cancel the cell-to-cell thermal cascading, this example models a thermal barrier between the cells.
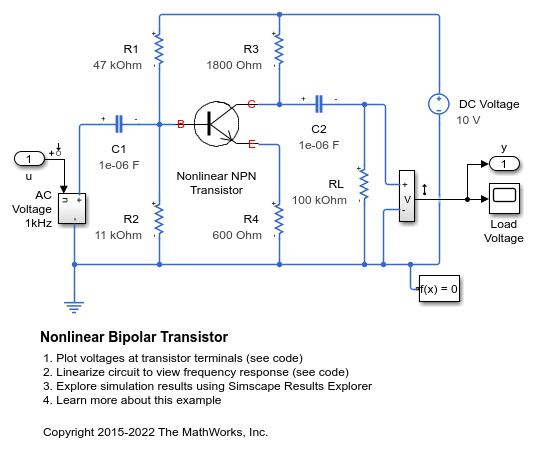
Nonlinear Bipolar Transistor
An implementation of a nonlinear bipolar transistor based on the Ebers-Moll equivalent circuit. R1 and R2 set the nominal operating point, and the small signal gain is approximately set by the ratio R3/R4. The 1uF decoupling capacitors have been chosen to present negligible impedance at 1KHz. The model is configured for linearization so that a frequency response can be generated.
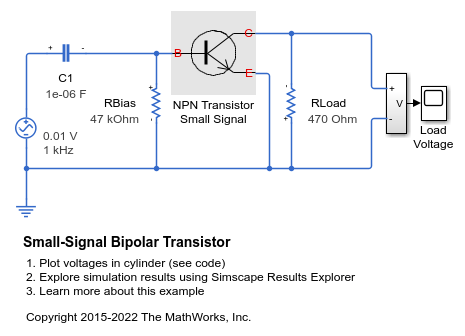
Small-Signal Bipolar Transistor
The use of a small-signal equivalent transistor model to assess performance of a common-emitter amplifier. The 47K resistor is the bias resistor required to set nominal operating point, and the 470 Ohm resistor is the load resistor. The transistor is represented by a hybrid-parameter equivalent circuit with circuit parameters h_ie (base circuit resistance), h_oe (output admittance), h_fe (forward current gain), and h_re (reverse voltage transfer ratio). Parameters set are typical for a BC107 Group B transistor. The gain is approximately given by -h_fe*470/h_ie =-47. The 1uF decoupling capacitor has been chosen to present negligible impedance at 1KHz compared to the input resistance h_ie, so the output voltage should be 47*10mV = 0.47V peak.
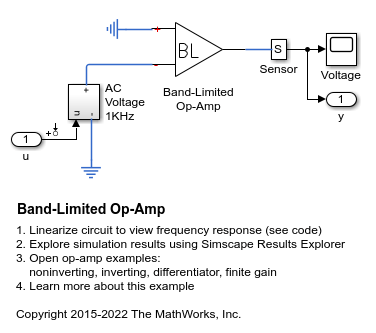
Band-Limited Op-Amp
How higher fidelity or more detailed component models can be built from the Foundation library blocks. The model implements a band-limited op-amp. It includes a first-order dynamic from inputs to outputs, and gives much faster simulation than if using a device-level equivalent circuit, which would normally include multiple transistors. This model also includes the effects of input and output impedance (Rin and Rout in the circuit), but does not include nonlinear effects such as slew-rate limiting.
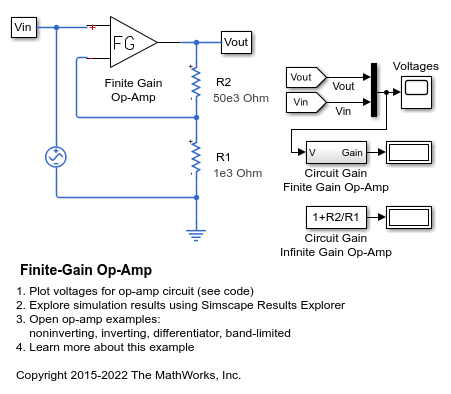
Finite-Gain Op-Amp
How higher fidelity or more detailed component models can be built from the Foundation library blocks. The Op-Amp block in the Foundation library models the ideal case whereby the gain is infinite, input impedance infinite, and output impedance zero. The Finite Gain Op-Amp block in this example has an open-loop gain of 1e5, input resistance of 100K ohms and output resistance of 10 ohms. As a result, the gain for this amplifier circuit is slightly lower than the gain that can be analytically calculated if the op-amp gain is assumed to be infinite.
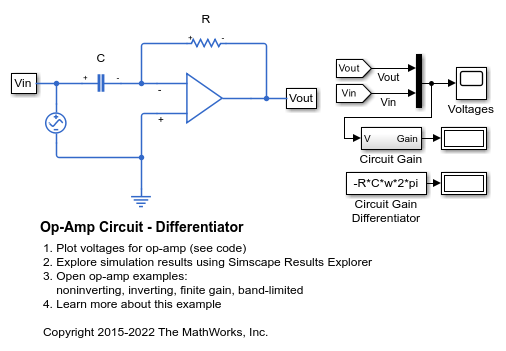
Op-Amp Circuit - Differentiator
A differentiator, such as might be used as part of a PID controller. It also illustrates how numerical simulation issues can arise in some idealized circuits. The model runs with the capacitor series parasitic resistance set to its default value of 1e-6 Ohms. Setting it to zero results in a warning and a very slow simulation. See the User's Guide for further information.
Circuito op-amp - Amplificatore invertente
Questo modello mostra un circuito op-amp invertente standard. Il guadagno è dato da -R2/R1 e, con i valori impostati a R1=1K Ohm e R2=10K Ohm, la tensione di ingresso da 0,1V picco-picco viene amplificata a 1V picco-picco. Poiché il blocco Op-Amp implementa un dispositivo ideale (ossia a guadagno infinito), questo guadagno si ottiene indipendentemente dal carico di output.
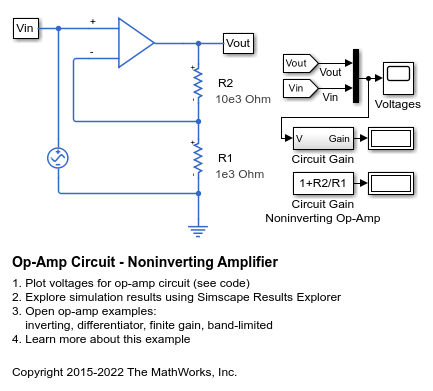
Circuito op-amp - Amplificatore non invertente
Questo modello mostra un circuito op-amp non invertente. Il guadagno è dato da 1+R2/R1 e, con i valori impostati a R1=1K Ohm e R2=10K Ohm, la tensione di ingresso da 0,1V picco-picco viene amplificata a 1,1V picco-picco. Poiché il blocco Op-Amp implementa un dispositivo ideale (ossia a guadagno infinito), questo guadagno si ottiene indipendentemente dal carico di output.
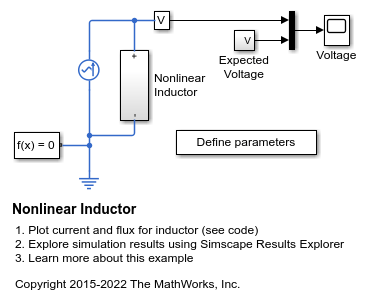
Nonlinear Inductor
An implementation of a nonlinear inductor where inductance depends on current. A tanh function defines the nonlinear flux-current relationship. The flux saturates for large currents, which can occur, for example, in iron core inductors.
Rettificatore a ponte full-wave
Questo esempio mostra un trasformatore CA ideale e un raddrizzatore a ponte full-wave che converte 120 volt CA in 12 volt CC. Il trasformatore ha un rapporto di spire di 14 e riduce l'alimentazione a 8,6 volt rms, ovvero 8,6*radice quadrata di (2) = 12 volt picco-picco. Il rettificatore a ponte full-wave combinato con un condensatore converte quindi il segnale in CC. La resistenza rappresenta un carico tipico.
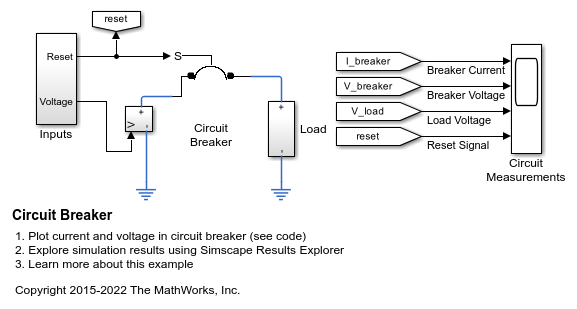
Circuit Breaker
Model a circuit breaker. The electromechanical breaker mechanism is approximated with a first-order time constant, and it is assumed that the mechanical force is proportional to load current. This simple representation is suitable for use in a larger model of a complete system. When the 20V supply is applied at one second, it results in a current that exceeds the circuit breaker current rating, and hence the breaker trips. The reset is then pressed at three seconds, and the voltage is ramped up. The breaker then trips just beyond the circuit breaker current rating.
Solenoide
Questo esempio mostra un solenoide con ritorno a molla. Il solenoide è modellato come un'induttanza il cui valore L dipende dalla posizione x dello stantuffo. La forza elettromotrice inversa (EMF) per un'induttanza variabile nel tempo è data da:
Operating Point RLC Transient Response
The response of a DC power supply connected to a series RLC load. The goal is to plot the output voltage response when a load is suddenly attached to the fully powered-up supply. This is done using a Simscape operating point.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleziona un sito web
Seleziona un sito web per visualizzare contenuto tradotto dove disponibile e vedere eventi e offerte locali. In base alla tua area geografica, ti consigliamo di selezionare: .
Puoi anche selezionare un sito web dal seguente elenco:
Come ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito
Per ottenere le migliori prestazioni del sito, seleziona il sito cinese (in cinese o in inglese). I siti MathWorks per gli altri paesi non sono ottimizzati per essere visitati dalla tua area geografica.
Americhe
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)