C Function
Integrate and call external C/C++ code from a Simulink model
Libraries:
Simulink /
User-Defined Functions
Description
The C Function block integrates and calls external C/C++ code from a Simulink® model. Use this block to define external code and customize the integration of your code by preprocessing or postprocessing the data. In addition, you can specify customized code for simulation and C code generation. You can conditionally call functions defined in your code, and you can also call multiple functions in one block. Using this block, you can initialize persistent data and pass it to an external function.
The C Function block supports initializing persistent data and calling external functions from the block dialog box. Persistent data can include an object of a C++ class defined in your custom code. See Interface with C++ Classes Using C Function Block. The block supports only initializing and terminating persistent data. The block does not support updating the data during simulation. To model a dynamic system with continuous states, use an S-Function block. To learn more about S-functions, see What Is an S-Function?
Note
C99 is the standard version of C language supported for custom C code integration into Simulink.
Specify Custom Code
Since R2024a
Starting in R2024a, the Configure custom code settings parameter provides you with a range of options to specify custom C/C++ code for the block.
To integrate a code component that is fully contained in a single block, use the Use Block Custom Code option. For example, to integrate a custom filter defined using C/C++ code into your model, specify the custom code locally using this option. The block then behaves like the specified filter.
To share custom C/C++ code across multiple blocks in a model or across multiple models, use the Use Configuration Parameters Custom Code option. To share the custom code across multiple models you must define the custom code in the Configuration Parameters dialog box of a Simulink library model. Then, use the code in a block within the library and fetch that block from that library in other models.
Call C Library Functions
You can call these C Math Library functions directly from the C Function block.
abs | acos | asin | atan | atan2 | ceil |
cos | cosh | exp | fabs | floor | fmod |
labs | ldexp | log | log10 | pow | sin |
sinh | sqrt | tan | tanh |
When you call these functions, double precision applies unless all the input arguments
are explicitly single precision. When a type mismatch occurs, a cast of the input arguments
to the expected type replaces the original arguments. For example, if you call the
sin function with an integer argument, a cast of the input argument to
a floating-point number of type double replaces the original
argument.
Starting in R2025a, you can call these string library functions inside the C function block.
strlen | strncpy | strncat | strcmp | strncmp | strstr |
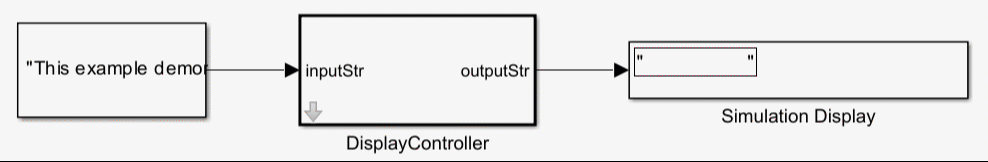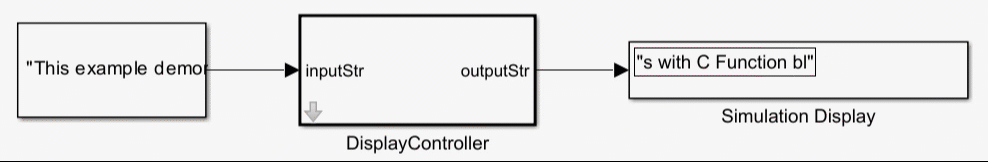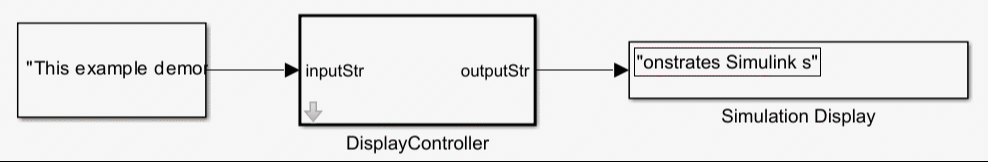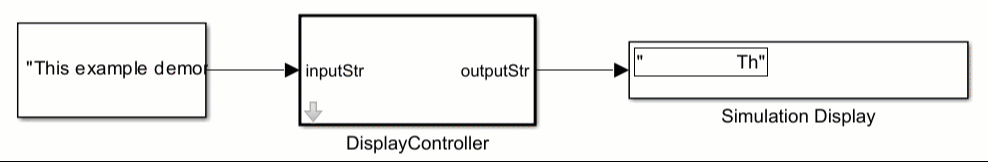
For more information, see Use Simulink Strings inside C Function Block to Model Scrolling Display.
To call other C library functions, create and call an external wrapper function that calls the C library function.
abs, fabs, and labs
FunctionsInterpretation of the abs, fabs, and
labs functions in C Function block goes beyond the
standard C version to include integer and floating-point arguments:
If
xis an integer, the standard C functionabsapplies tox, orabs(x).If
xis a double, the standard C functionlabsapplies tox, orlabs(x).If
xis a single, the standard C functionfabsapplies tox, orfabs(x).
The call to the function should call the correct CRL based on the type of data passed into the function. If no CRL is specified, the call to the function should call to type-specific library. The CRL for C99 generates a type-specific function. For example:
| Type passed in | Code generation call |
|---|---|
sin(doubleIn) | sin(doubleIn) |
sin(floatIn) | sinf(floatIn) |
You can call printf,
memcpy and memset functions in the C
Function block. (since R2023a)
Report Run-time Errors and Warnings in Simulink
Since R2024a
In custom C code that you specify in the C Function block , use the
slError and slWarning functions to report
run-time errors and warnings, respectively. An error terminates the simulation and must be
resolved before simulation continues. A warning indicates a potential issue with the code
but does not terminate the simulation.
Both slError and slWarning functions support
different data type format specifiers (for example, %d for integer,
%f for float) that are similar to C.
Examples :
slError("Error message");slError("Input %f should be non-negative", x);slWarning("Warning message");slWarning("Input %d should be non-zero", y);
The following code executes at the start of the simulation. It uses the
slError function to issue an error message if the data store fails to
initialize at the start of simulation.

Specify Row-Major and Column-Major Array Layouts in Custom Code
Since R2024a
Use the slSetRowMajor and slSetColumnMajor
functions to specify row-major and column-major array layouts, respectively. Specify these
functions in the Simulation Target pane of the Configuration Parameters
dialog box using Use Configuration Parameters Custom Code parameter
from block dialog box.
For a row-major layout, the row elements of a matrix are stored contiguously in memory. Similarly, for a column-major layout, the column elements of a matrix are stored contiguously in memory. For more information, see Row-Major and Column-Major Array Layouts (MATLAB Coder).
Function prototypes:
void slSetRowMajor(const char* functionName)void slSetColumnMajor(const char* functionName)
functionName must be a string literal and fully qualified.
For example, consider the following code:
namespace NS1 { class ACLASS{ public: void foo_row(); }; namespace NS2{ void foo_col(double*, double*); } }
For a fully qualified function name.
If the function is inside a namespace, all the nested namespaces should be included in the function name string. Based on the above code, for the column-major function,
foo_col, useslSetColumnMajor("NS1::NS2::foo_col")in the configuration parameters custom code.For all class members, the class name along with any nested namespaces should be included in the function name string. Based on the above code, for the row-major function
foo_row, useslSetRowMajor("NS1::ACLASS::foo_row")in the configuration parameters custom code.
For a C Function block that uses classes, if the constructor takes majority, the majority must be specified in the Start code.
Examples
Limitations
Limitations apply when using these Simulink features with the C Function block.
Starting in R2025a, code coverage is supported.
For versions prior to R2025a, Simulink Coverage™ is not supported. Only execution coverage of the C Function block is measured.
Simulink Design Verifier™
Simulink Design Verifier does not generate test cases for coverage objectives inside the C Function block. The limitations that apply to C/C++ S-functions also apply to C/C++ code in a C Function block. In particular, calls to external or library functions are replaced by stubs for analysis. For more information on these limitations, see Support Limitations and Considerations for S-Functions and C/C++ Code (Simulink Design Verifier).
Simulink Code Inspector™
Simulink Code Inspector does not inspect the code generated from the C Function block.
These limitations apply to the C code that you specify in a C Function block.
Local static variables using the
statickeyword are not supported. To cache values across time steps, define a symbol asPersistentin the Symbols table of the block dialog box.Taking the address of a
Constantsymbol is not supported.Directly calling C library functions other than the C Math Library functions listed above under Call C Library Functions is not supported. To call other C library functions, create and call a wrapper function that calls the C library function.
C Function block that uses local custom code is not supported inside a Dataflow Subsystem (DSP System Toolbox).