Contenuto principale
Risultati per
Hello everyone.
I have modelled a three phase inverter to run a 5Kw PMSM motor (MATLAB preparametrized). The torque load is applied through ideal torque source and step junction, and the speed of the motor is visualized. When I provide the gate signal only through SPWM generator (No control, only SPWM signal generation through carrier and sine wave comparison),
- The speed stabilizes around 62 rad/sec after some initial oscillations, but when I try to run the same model using PMSM field oriented control block set, the speed is negative (negative rotation) and it keeps on increasing eventhough the speed reference provided is only upto 60. The waveform of both speed and torque has been attached hereby.
- Moreover, is there anyway to tune the PI controllers (inner and outer loops) of PMSM Field oriented blockset automatically.
- It can be seen from the torque waveform, there is soemkind of disturbance around 0.4-0.45 sec, which creates too much noise in current, torque waveforms. What could be the reason behind this.
Your help would be highly appreciated.
Thank you.
Before we begin, you will need to make sure you have 'sir_age_model.m' installed. Once you've downloaded this folder into your working directory, which can be located at your current folder. If you can see this file in your current folder, then it's safe to use it. If you choose to use MATLAB online or MATLAB Mobile, you may upload this to your MATLAB Drive.
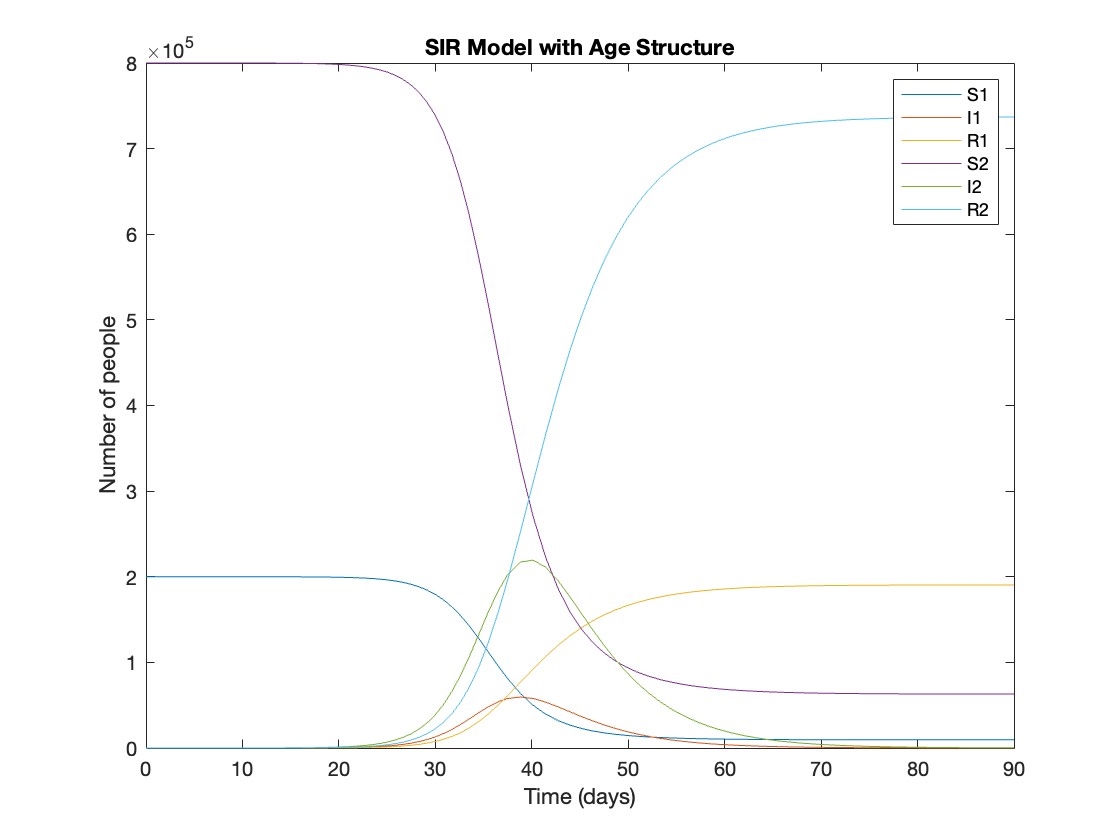
This is the code for the SIR model stratified into 2 age groups (children and adults). For a detailed explanation of how to derive the force of infection by age group.
% Main script to run the SIR model simulation
% Initial state values
initial_state_values = [200000; 1; 0; 800000; 0; 0]; % [S1; I1; R1; S2; I2; R2]
% Parameters
parameters = [0.05; 7; 6; 1; 10; 1/5]; % [b; c_11; c_12; c_21; c_22; gamma]
% Time span for the simulation (3 months, with daily steps)
tspan = [0 90];
% Solve the ODE
[t, y] = ode45(@(t, y) sir_age_model(t, y, parameters), tspan, initial_state_values);
% Plotting the results
plot(t, y);
xlabel('Time (days)');
ylabel('Number of people');
legend('S1', 'I1', 'R1', 'S2', 'I2', 'R2');
title('SIR Model with Age Structure');
What was the cumulative incidence of infection during this epidemic? What proportion of those infections occurred in children?
In the SIR model, the cumulative incidence of infection is simply the decline in susceptibility.
% Assuming 'y' contains the simulation results from the ode45 function
% and 't' contains the time points
% Total cumulative incidence
total_cumulative_incidence = (y(1,1) - y(end,1)) + (y(1,4) - y(end,4));
fprintf('Total cumulative incidence: %f\n', total_cumulative_incidence);
% Cumulative incidence in children
cumulative_incidence_children = (y(1,1) - y(end,1));
% Proportion of infections in children
proportion_infections_children = cumulative_incidence_children / total_cumulative_incidence;
fprintf('Proportion of infections in children: %f\n', proportion_infections_children);
927,447 people became infected during this epidemic, 20.5% of which were children.
Which age group was most affected by the epidemic?
To answer this, we can calculate the proportion of children and adults that became infected.
% Assuming 'y' contains the simulation results from the ode45 function
% and 't' contains the time points
% Proportion of children that became infected
initial_children = 200000; % initial number of susceptible children
final_susceptible_children = y(end,1); % final number of susceptible children
proportion_infected_children = (initial_children - final_susceptible_children) / initial_children;
fprintf('Proportion of children that became infected: %f\n', proportion_infected_children);
% Proportion of adults that became infected
initial_adults = 800000; % initial number of susceptible adults
final_susceptible_adults = y(end,4); % final number of susceptible adults
proportion_infected_adults = (initial_adults - final_susceptible_adults) / initial_adults;
fprintf('Proportion of adults that became infected: %f\n', proportion_infected_adults);
Throughout this epidemic, 95% of all children and 92% of all adults were infected. Children were therefore slightly more affected in proportion to their population size, even though the majority of infections occurred in adults.
Are you going to be in the path of totality? How can you predict, track, and simulate the solar eclipse using MATLAB?
In one line of MATLAB code, compute how far you can see at the seashore. In otherwords, how far away is the horizon from your eyes? You can assume you know your height and the diameter or radius of the earth.
Me at the beginning of every meeting
Hey MATLAB Community! 🌟
March has been bustling with activity on MATLAB Central, bringing forth a treasure trove of insights, innovations, and fun. Whether you're delving into the intricacies of spline conversions or seeking inspiration from Pi Day celebrations, there's something for everyone.
Here’s a roundup of the top posts from the past few weeks that you won't want to miss:
Interesting questions
Dive into the technicalities of converting spline forms with a focus on calculating coefficients. A must-read for anyone dealing with spline representations.
Explore the challenges and solutions in tuning autopilot gains within a non-linear model of a business jet aircraft.
Popular discussions
Celebrate Pi Day with cool MATLAB implementations and code. A delightful read filled with π-inspired creativity.
Get a glimpse of fun with MATLAB through an engaging visual shared by Athanasios. A light-hearted thread that showcases the fun side of mathematics.
From File Exchange
Unlock the secrets of global climate data with MATLAB. This thread offers tools and insights for analyzing precipitation variability.
Interact with a numerical puddle in real-time and explore the dynamics of disturbances. A fascinating exploration of fluid dynamics simulation.
From the Blogs
Revisit Pi Day with Jiro's picks of the coolest π visualizations. A post that combines art, math, and the joy of exploration.
Discover the synergy between MATLAB and Visual Studio Code, enhanced by GitHub Copilot support. A game-changer for MATLAB developers.
These threads are just the tip of the iceberg. Each post is a gateway to new knowledge, ideas, and community connections. Dive in, explore, and don't forget to contribute your insights and questions. Together, we make MATLAB Central a vibrant hub of innovation and support.
Happy Coding!
The latest release is pretty much upon us. Official annoucements will be coming soon and the eagle-eyed among you will have started to notice some things shifting around on the MathWorks website as we ready for this.
The pre-release has been available for a while. Maybe you've played with it? I have...I've even been quietly using it to write some of my latest blog posts...and I have several queued up for publication after MathWorks officially drops the release.
At the time of writing, this page points to the pre-release highlights. Prerelease Release Highlights - MATLAB & Simulink (mathworks.com)
What excites you about this release? why?
sort(v)
8%
unique(v)
16%
union(v, [ ])
17%
intersect(v, v)
14%
setdiff(v, [ ])
12%
All return sorted output
33%
1193 voti
The stationary solutions of the Klein-Gordon equation refer to solutions that are time-independent, meaning they remain constant over time. For the non-linear Klein-Gordon equation you are discussing:
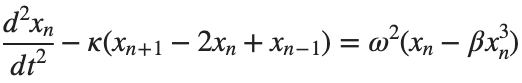
Stationary solutions arise when the time derivative term, 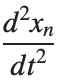 , is zero, meaning the motion of the system does not change over time. This leads to a static differential equation:
, is zero, meaning the motion of the system does not change over time. This leads to a static differential equation:
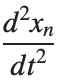 , is zero, meaning the motion of the system does not change over time. This leads to a static differential equation:
, is zero, meaning the motion of the system does not change over time. This leads to a static differential equation:This equation describes how particles in the lattice interact with each other and how non-linearity affects the steady state of the system.
The solutions to this equation correspond to the various possible stable equilibrium states of the system, where each represents different static distribution patterns of displacements 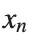 . The specific form of these stationary solutions depends on the system parameters, such as κ , ω, and β , as well as the initial and boundary conditions of the problem.
. The specific form of these stationary solutions depends on the system parameters, such as κ , ω, and β , as well as the initial and boundary conditions of the problem.
To find these solutions in a more specific form, one might need to solve the equation using analytical or numerical methods, considering the different cases that could arise in such a non-linear system.
By interpreting the equation in this way, we can relate the dynamics described by the discrete Klein - Gordon equation to the behavior of DNA molecules within a biological system . This analogy allows us to understand the behavior of DNA in terms of concepts from physics and mathematical modeling .
% Parameters
numBases = 100; % Number of spatial points
omegaD = 0.2; % Common parameter for the equation
% Preallocate the array for the function handles
equations = cell(numBases, 1);
% Initial guess for the solution
initialGuess = 0.01 * ones(numBases, 1);
% Parameter sets for kappa and beta
paramSets = [0.1, 0.05; 0.5, 0.05; 0.1, 0.2];
% Prepare figure for subplot
figure;
set(gcf, 'Position', [100, 100, 1200, 400]); % Set figure size
% Newton-Raphson method parameters
maxIterations = 1000;
tolerance = 1e-10;
% Set options for fsolve to use the 'levenberg-marquardt' algorithm
options = optimoptions('fsolve', 'Algorithm', 'levenberg-marquardt', 'MaxIterations', maxIterations, 'FunctionTolerance', tolerance);
for i = 1:size(paramSets, 1)
kappa = paramSets(i, 1);
beta = paramSets(i, 2);
% Define the equations using a function
for n = 2:numBases-1
equations{n} = @(x) -kappa * (x(n+1) - 2 * x(n) + x(n-1)) - omegaD^2 * (x(n) - beta * x(n)^3);
end
% Boundary conditions with specified fixed values
someFixedValue1 = 10; % Replace with actual value if needed
someFixedValue2 = 10; % Replace with actual value if needed
equations{1} = @(x) x(1) - someFixedValue1;
equations{numBases} = @(x) x(numBases) - someFixedValue2;
% Combine all equations into a single function
F = @(x) cell2mat(cellfun(@(f) f(x), equations, 'UniformOutput', false));
% Solve the system of equations using fsolve with the specified options
x_solution = fsolve(F, initialGuess, options);
norm(F(x_solution))
% Plot the solution in a subplot
subplot(1, 3, i);
plot(x_solution, 'o-', 'LineWidth', 2);
grid on;
xlabel('n', 'FontSize', 12);
ylabel('x[n]', 'FontSize', 12);
title(sprintf('\\kappa = %.2f, \\beta = %.2f', kappa, beta), 'FontSize', 14);
end
% Improve overall aesthetics
sgtitle('Stationary States for Different \kappa and \beta Values', 'FontSize', 16); % Super title for the figure
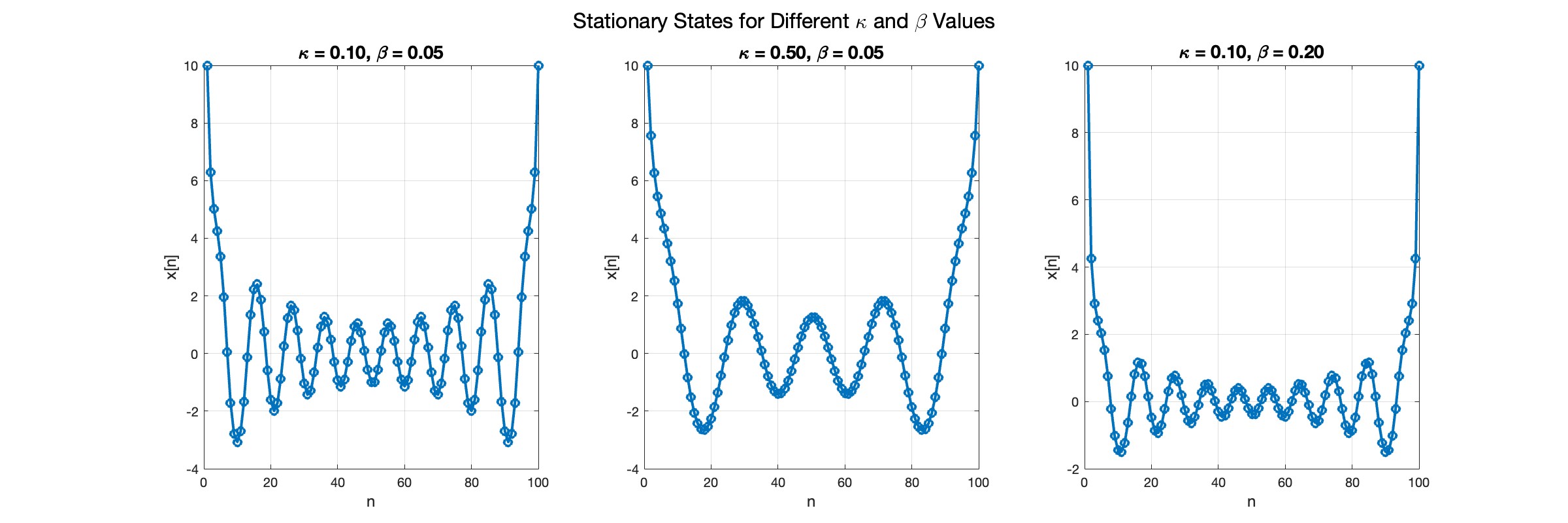
In the second plot, the elasticity constant κis increased to 0.5, representing a system with greater stiffness . This parameter influences how resistant the system is to deformation, implying that a higher κ makes the system more resilient to changes . By increasing κ, we are essentially tightening the interactions between adjacent units in the model, which could represent, for instance, stronger bonding forces in a physical or biological system .
In the third plot the nonlinearity coefficient β is increased to 0.2 . This adjustment enhances the nonlinear interactions within the system, which can lead to more complex dynamic behaviors, especially in systems exhibiting bifurcations or chaos under certain conditions .
The following expression 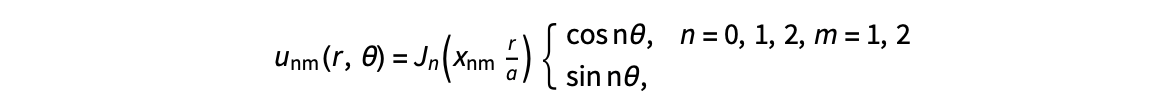
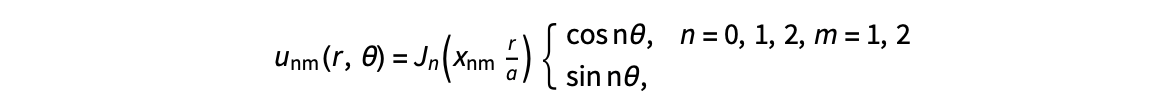
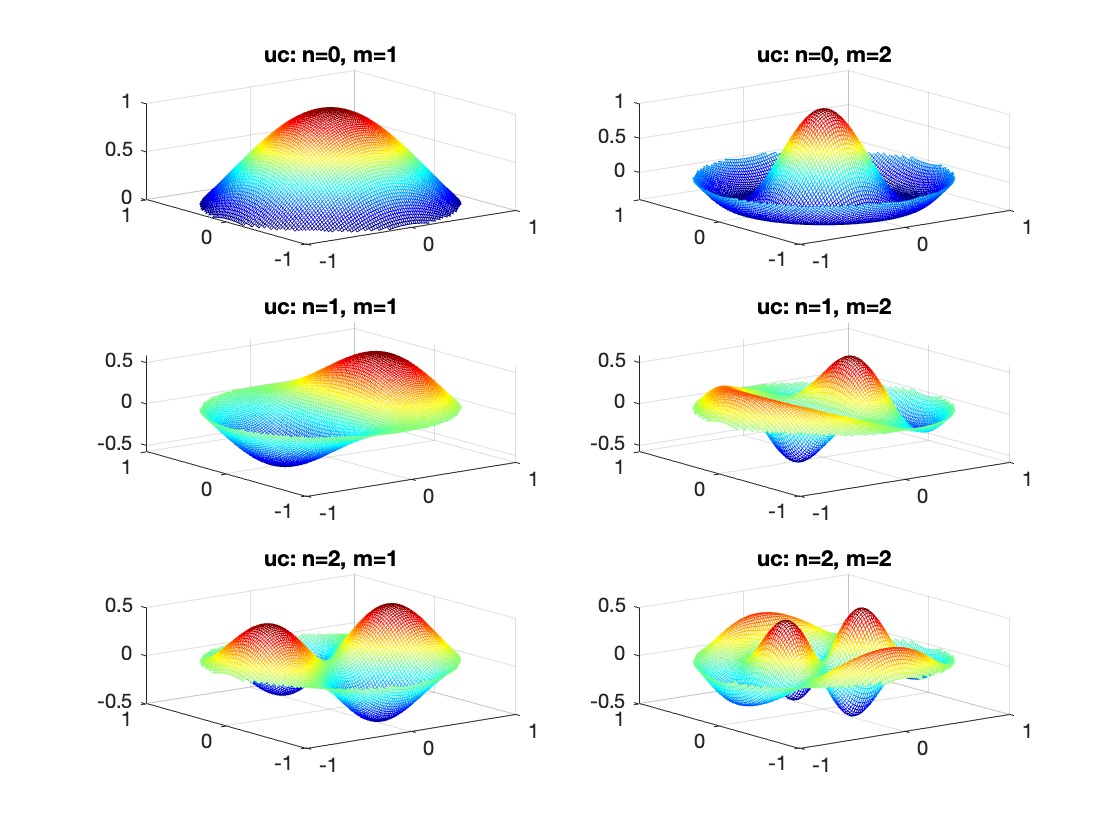
gives the solution for the Helmholtz problem. On the circular disc with center 0 and radius a. For  the plot in 3-dimensional graphics of the solutions on Matlab for
the plot in 3-dimensional graphics of the solutions on Matlab for  and then calculate some eigenfunctions with the following expression.
and then calculate some eigenfunctions with the following expression.
It could be better to separate functions with  and
and  as follows
as follows
diska = 1; % Radius of the disk
mmax = 2; % Maximum value of m
nmax = 2; % Maximum value of n
% Function to find the k-th zero of the n-th Bessel function
% This function uses a more accurate method for initial guess
besselzero = @(n, k) fzero(@(x) besselj(n, x), [(k-(n==0))*pi, (k+1-(n==0))*pi]);
% Define the eigenvalue k[m, n] based on the zeros of the Bessel function
k = @(m, n) besselzero(n, m);
% Define the functions uc and us using Bessel functions
% These functions represent the radial part of the solution
uc = @(r, t, m, n) cos(n * t) .* besselj(n, k(m, n) * r);
us = @(r, t, m, n) sin(n * t) .* besselj(n, k(m, n) * r);
% Generate data for demonstration
data = zeros(5, 3);
for m = 1:5
for n = 0:2
data(m, n+1) = k(m, n); % Storing the eigenvalues
end
end
% Display the data
disp(data);
% Plotting all in one figure
figure;
plotIndex = 1;
for n = 0:nmax
for m = 1:mmax
subplot(nmax + 1, mmax, plotIndex);
[X, Y] = meshgrid(linspace(-diska, diska, 100), linspace(-diska, diska, 100));
R = sqrt(X.^2 + Y.^2);
T = atan2(Y, X);
Z = uc(R, T, m, n); % Using uc for plotting
% Ensure the plot is only within the disk
Z(R > diska) = NaN;
mesh(X, Y, Z);
title(sprintf('uc: n=%d, m=%d', n, m));
colormap('jet');
plotIndex = plotIndex + 1;
end
end
First, I felt that the three answers provided by a user in this thread might have been generated by AI. How do you think?
Second, I found that "Responsible usage of generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT, is allowed in MATLAB Answers."
If the answers are indeed AI generated, then the user didn't do "clearly indicating when AI generated content is incorporated".
That leads to my question that how do we enforce the guideline.
I am not against using AI for answers but in this case, I felt the answering text is mentioning all the relevant words but missing the point. For novice users who are seeking answers, this would be misleading and waste of time.
Calculation of RMS like dc signal for a sinusoidal signal using Sim...
I have Line-to-line sinusoidal voltage reading as L1-L2, L2-L3 and L3-L1. I want to get RMS-like DC-signal that is equal to 400V when input voltage is 400V when there is no unbalance. I want to im...

Happy Pi Day!
3.14 π Day has arrived, and this post provides some very cool pi implementations and complete MATLAB code.
Firstly, in order to obtain the first n decimal places of pi, we need to write the following code (to prevent inaccuracies, we need to take a few more tails and perform another operation of taking the first n decimal places when needed):
function Pi=getPi(n)
if nargin<1,n=3;end
Pi=char(vpa(sym(pi),n+10));
Pi=abs(Pi)-48;
Pi=Pi(3:n+2);
end
With this function to obtain the decimal places of pi, our visualization journey has begun~Step by step, from simple to complex~(Please try to use newer versions of MATLAB to run, at least R17b)
1 Pie chart
Just calculate the proportion of each digit to the first 1500 decimal places:
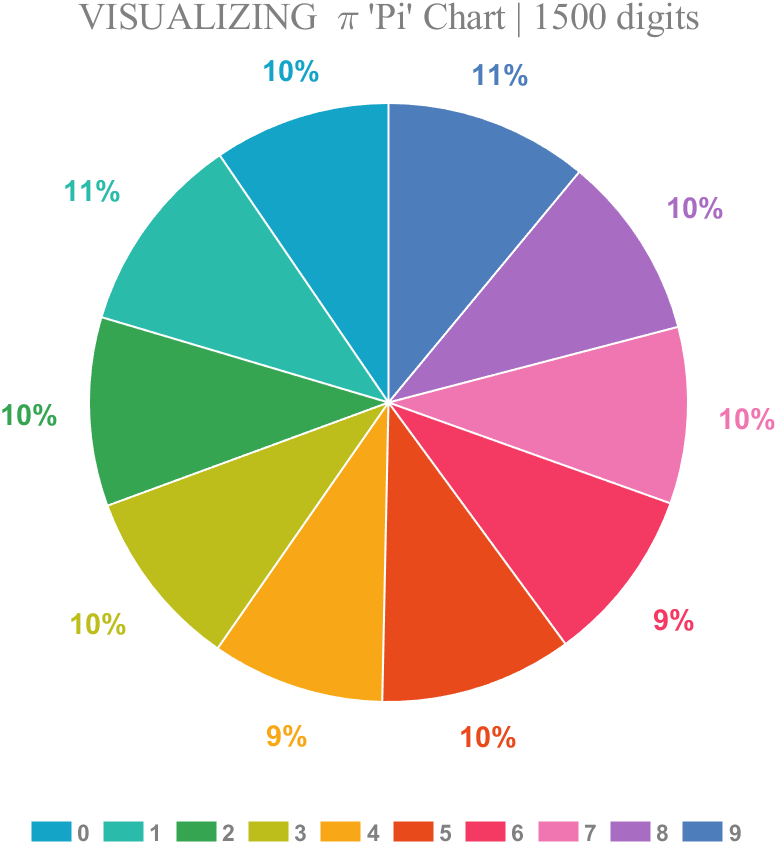
% 获取pi前1500位小数
Pi=getPi(1500);
% 统计各个数字出现次数
numNum=find([diff(sort(Pi)),1]);
numNum=[numNum(1),diff(numNum)];
% 配色列表
CM=[20,164,199;43,187,170;53,165,81;189,190,28;248,167,22;
232,74,27;244,57,99;240,118,177;168,109,195;78,125,187]./255;
% 绘图并修饰
pieHdl=pie(numNum);
set(gcf,'Color',[1,1,1],'Position',[200,100,620,620]);
for i=1:2:20
pieHdl(i).EdgeColor=[1,1,1];
pieHdl(i).LineWidth=1;
pieHdl(i).FaceColor=CM((i+1)/2,:);
end
for i=2:2:20
pieHdl(i).Color=CM(i/2,:);
pieHdl(i).FontWeight='bold';
pieHdl(i).FontSize=14;
end
% 绘制图例并修饰
lgdHdl=legend(num2cell('0123456789'));
lgdHdl.FontWeight='bold';
lgdHdl.FontSize=11;
lgdHdl.TextColor=[.5,.5,.5];
lgdHdl.Location='southoutside';
lgdHdl.Box='off';
lgdHdl.NumColumns=10;
lgdHdl.ItemTokenSize=[20,15];
title("VISUALIZING \pi 'Pi' Chart | 1500 digits",'FontSize',18,...
'FontName','Times New Roman','Color',[.5,.5,.5])
2 line chart
Calculate the change in the proportion of each number:
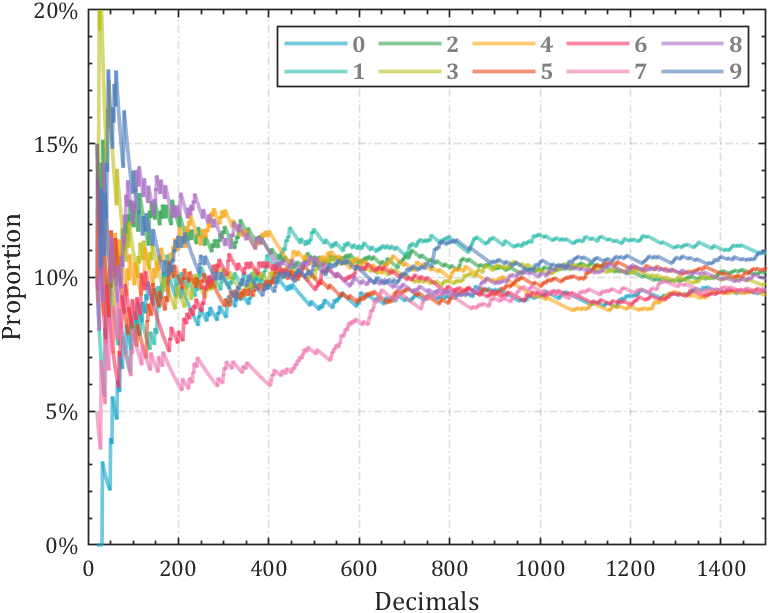
% 获取pi前1500位小数
Pi=getPi(1500);
% 计算比例变化
Ratio=cumsum(Pi==(0:9)',2);
Ratio=Ratio./sum(Ratio);
D=1:length(Ratio);
% 配色列表
CM=[20,164,199;43,187,170;53,165,81;189,190,28;248,167,22;
232,74,27;244,57,99;240,118,177;168,109,195;78,125,187]./255;
hold on
% 循环绘图
for i=1:10
plot(D(20:end),Ratio(i,20:end),'Color',[CM(i,:),.6],'LineWidth',1.8)
end
% 坐标区域修饰
ax=gca;box on;grid on
ax.YLim=[0,.2];
ax.YTick=0:.05:.2;
ax.XTick=0:200:1400;
ax.YTickLabel={'0%','5%','10%','15%','20%'};
ax.XMinorTick='on';
ax.YMinorTick='on';
ax.LineWidth=.8;
ax.GridLineStyle='-.';
ax.FontName='Cambria';
ax.FontSize=11;
ax.XLabel.String='Decimals';
ax.YLabel.String='Proportion';
ax.XLabel.FontSize=13;
ax.YLabel.FontSize=13;
% 绘制图例并修饰
lgdHdl=legend(num2cell('0123456789'));
lgdHdl.NumColumns=5;
lgdHdl.FontWeight='bold';
lgdHdl.FontSize=11;
lgdHdl.TextColor=[.5,.5,.5];
3 stacked area diagram
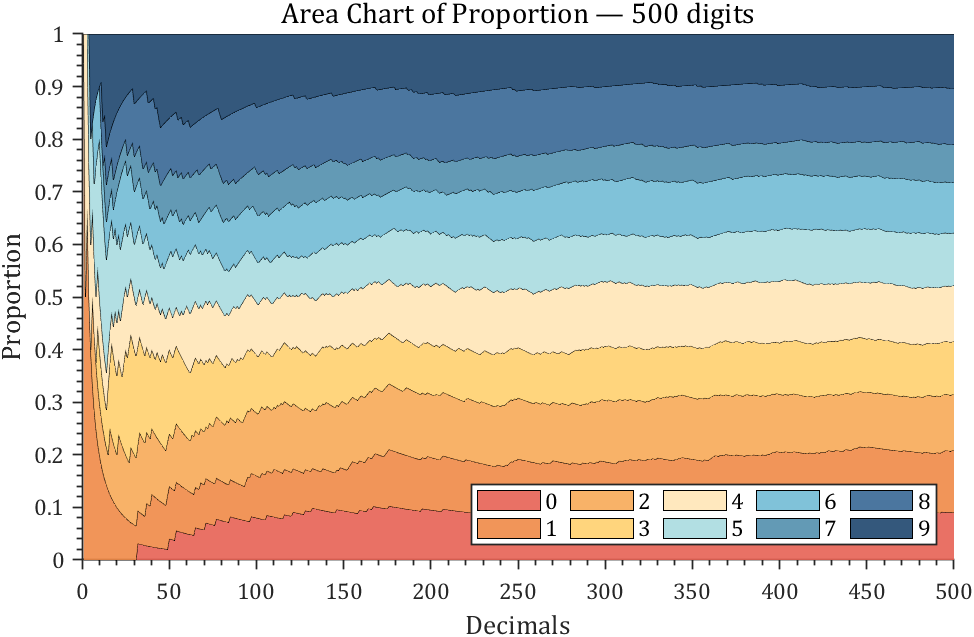
% 获取pi前500位小数
Pi=getPi(500);
% 计算比例变化
Ratio=cumsum(Pi==(0:9)',2);
Ratio=Ratio./sum(Ratio);
% 配色列表
CM=[231,98,84;239,138,71;247,170,88;255,208,111;255,230,183;
170,220,224;114,188,213;82,143,173;55,103,149;30,70,110]./255;
% 绘制堆叠面积图
hold on
areaHdl=area(Ratio');
for i=1:10
areaHdl(i).FaceColor=CM(i,:);
areaHdl(i).FaceAlpha=.9;
end
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,720,420]);
ax=gca;
ax.YLim=[0,1];
ax.XMinorTick='on';
ax.YMinorTick='on';
ax.LineWidth=.8;
ax.FontName='Cambria';
ax.FontSize=11;
ax.TickDir='out';
ax.XLabel.String='Decimals';
ax.YLabel.String='Proportion';
ax.XLabel.FontSize=13;
ax.YLabel.FontSize=13;
ax.Title.String='Area Chart of Proportion — 500 digits';
ax.Title.FontSize=14;
% 绘制图例并修饰
lgdHdl=legend(num2cell('0123456789'));
lgdHdl.NumColumns=5;
lgdHdl.FontSize=11;
lgdHdl.Location='southeast';
4 connected stacked bar chart
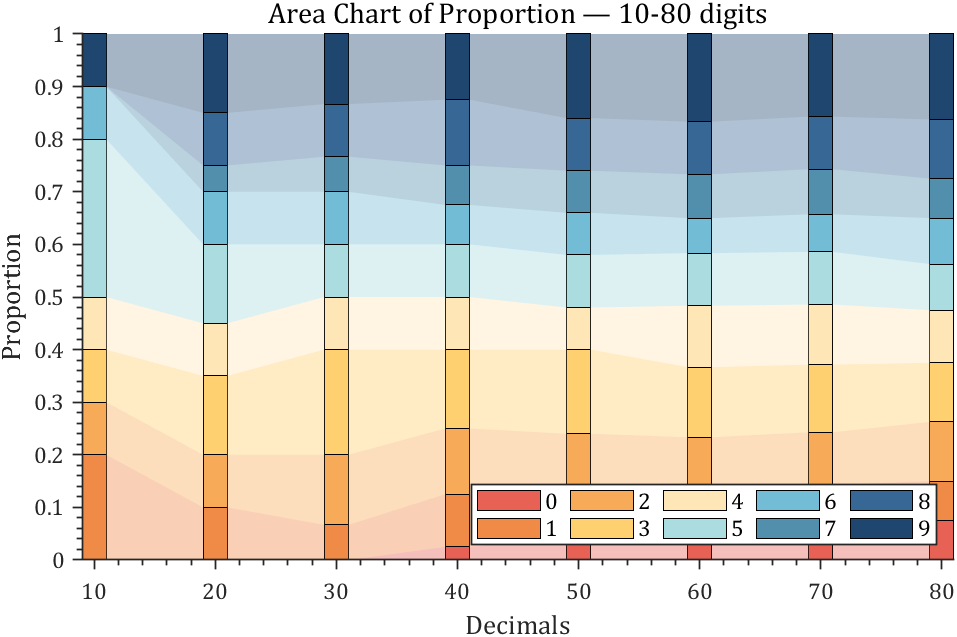
% 获取pi前100位小数
Pi=getPi(100);
% 计算比例变化
Ratio=cumsum(Pi==(0:9)',2);
Ratio=Ratio./sum(Ratio);
X=Ratio(:,10:10:80)';
barHdl=bar(X,'stacked','BarWidth',.2);
CM=[231,98,84;239,138,71;247,170,88;255,208,111;255,230,183;
170,220,224;114,188,213;82,143,173;55,103,149;30,70,110]./255;
for i=1:10
barHdl(i).FaceColor=CM(i,:);
end
% 以下是生成连接的部分
hold on;axis tight
yEndPoints=reshape([barHdl.YEndPoints]',length(barHdl(1).YData),[])';
zeros(1,length(barHdl(1).YData));
yEndPoints=[zeros(1,length(barHdl(1).YData));yEndPoints];
barWidth=barHdl(1).BarWidth;
for i=1:length(barHdl)
for j=1:length(barHdl(1).YData)-1
y1=min(yEndPoints(i,j),yEndPoints(i+1,j));
y2=max(yEndPoints(i,j),yEndPoints(i+1,j));
if y1*y2<0
ty=yEndPoints(find(yEndPoints(i+1,j)*yEndPoints(1:i,j)>=0,1,'last'),j);
y1=min(ty,yEndPoints(i+1,j));
y2=max(ty,yEndPoints(i+1,j));
end
y3=min(yEndPoints(i,j+1),yEndPoints(i+1,j+1));
y4=max(yEndPoints(i,j+1),yEndPoints(i+1,j+1));
if y3*y4<0
ty=yEndPoints(find(yEndPoints(i+1,j+1)*yEndPoints(1:i,j+1)>=0,1,'last'),j+1);
y3=min(ty,yEndPoints(i+1,j+1));
y4=max(ty,yEndPoints(i+1,j+1));
end
fill([j+.5.*barWidth,j+1-.5.*barWidth,j+1-.5.*barWidth,j+.5.*barWidth],...
[y1,y3,y4,y2],barHdl(i).FaceColor,'FaceAlpha',.4,'EdgeColor','none');
end
end
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,720,420]);
ax=gca;box off
ax.YLim=[0,1];
ax.XMinorTick='on';
ax.YMinorTick='on';
ax.LineWidth=.8;
ax.FontName='Cambria';
ax.FontSize=11;
ax.TickDir='out';
ax.XTickLabel={'10','20','30','40','50','60','70','80'};
ax.XLabel.String='Decimals';
ax.YLabel.String='Proportion';
ax.XLabel.FontSize=13;
ax.YLabel.FontSize=13;
ax.Title.String='Area Chart of Proportion — 10-80 digits';
ax.Title.FontSize=14;
% 绘制图例并修饰
lgdHdl=legend(barHdl,num2cell('0123456789'));
lgdHdl.NumColumns=5;
lgdHdl.FontSize=11;
lgdHdl.Location='southeast';
5 bichord chart
Need to use this tool:
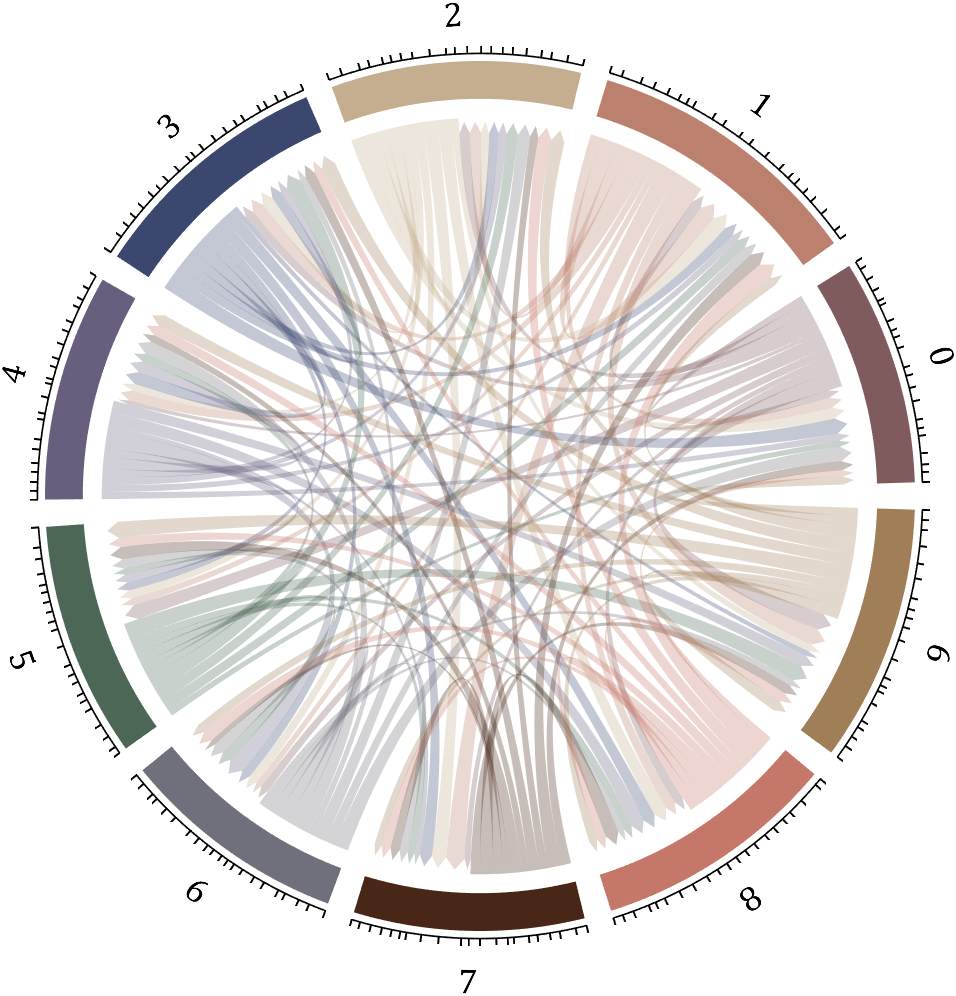
% 构建连接矩阵
dataMat=zeros(10,10);
Pi=getPi(1001);
for i=1:1000
dataMat(Pi(i)+1,Pi(i+1)+1)=dataMat(Pi(i)+1,Pi(i+1)+1)+1;
end
BCC=biChordChart(dataMat,'Arrow','on','Label',num2cell('0123456789'));
BCC=BCC.draw();
% 添加刻度
BCC.tickState('on')
% 修改字体,字号及颜色
BCC.setFont('FontName','Cambria','FontSize',17)
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,820,820]);
6 Gravity simulation diagram
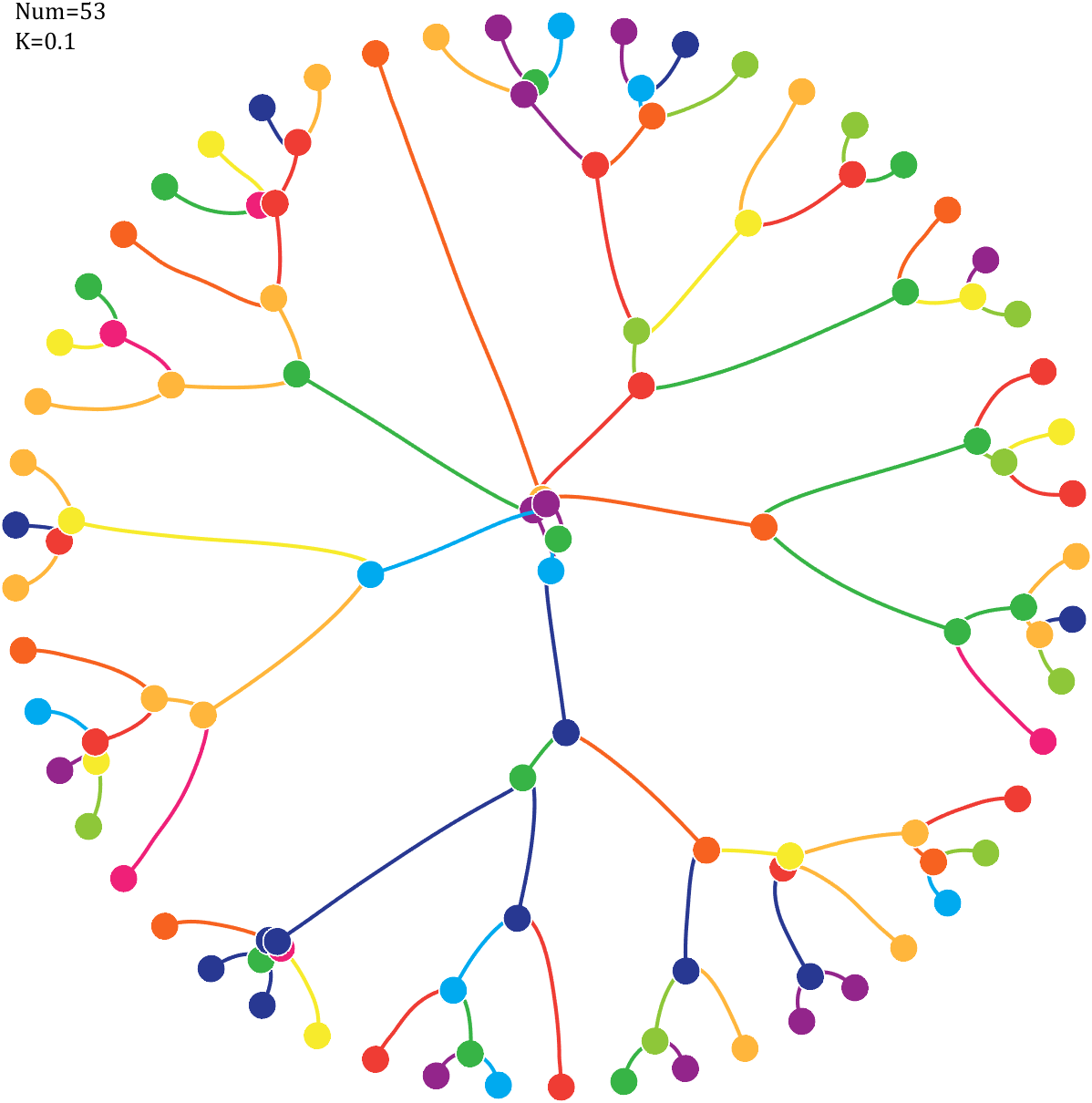
Imagine each decimal as a small ball with a mass of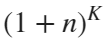
For example, if , the weight of ball 0 is 1, ball 9 is 1.2589, the initial velocity of the ball is 0, and it is attracted by other balls. Gravity follows the inverse square law, and if the balls are close enough, they will collide and their value will become
, the weight of ball 0 is 1, ball 9 is 1.2589, the initial velocity of the ball is 0, and it is attracted by other balls. Gravity follows the inverse square law, and if the balls are close enough, they will collide and their value will become 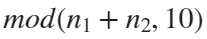
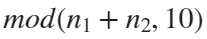
After adding, take the mod, add the velocity direction proportionally, and recalculate the weight.
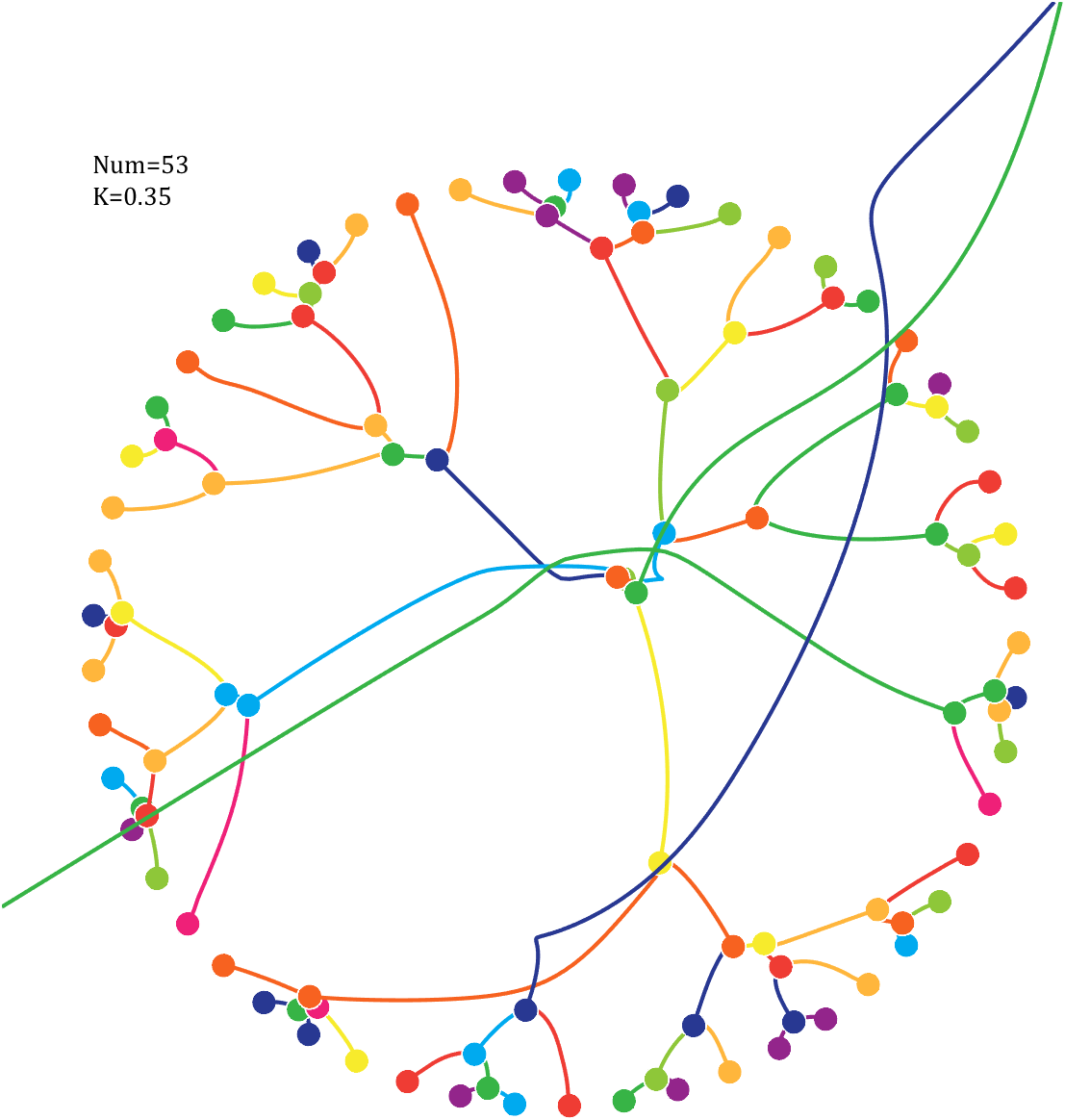
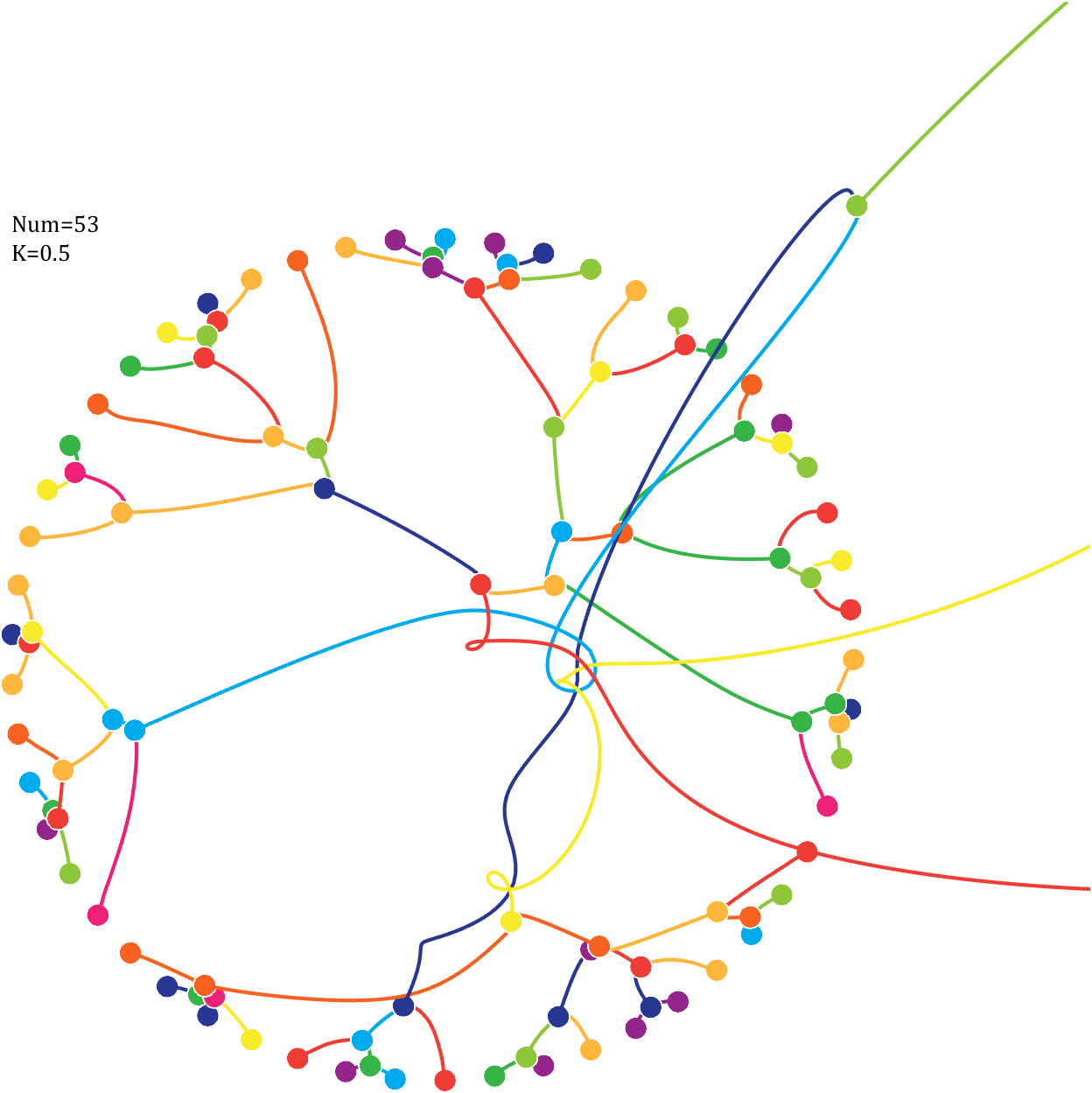
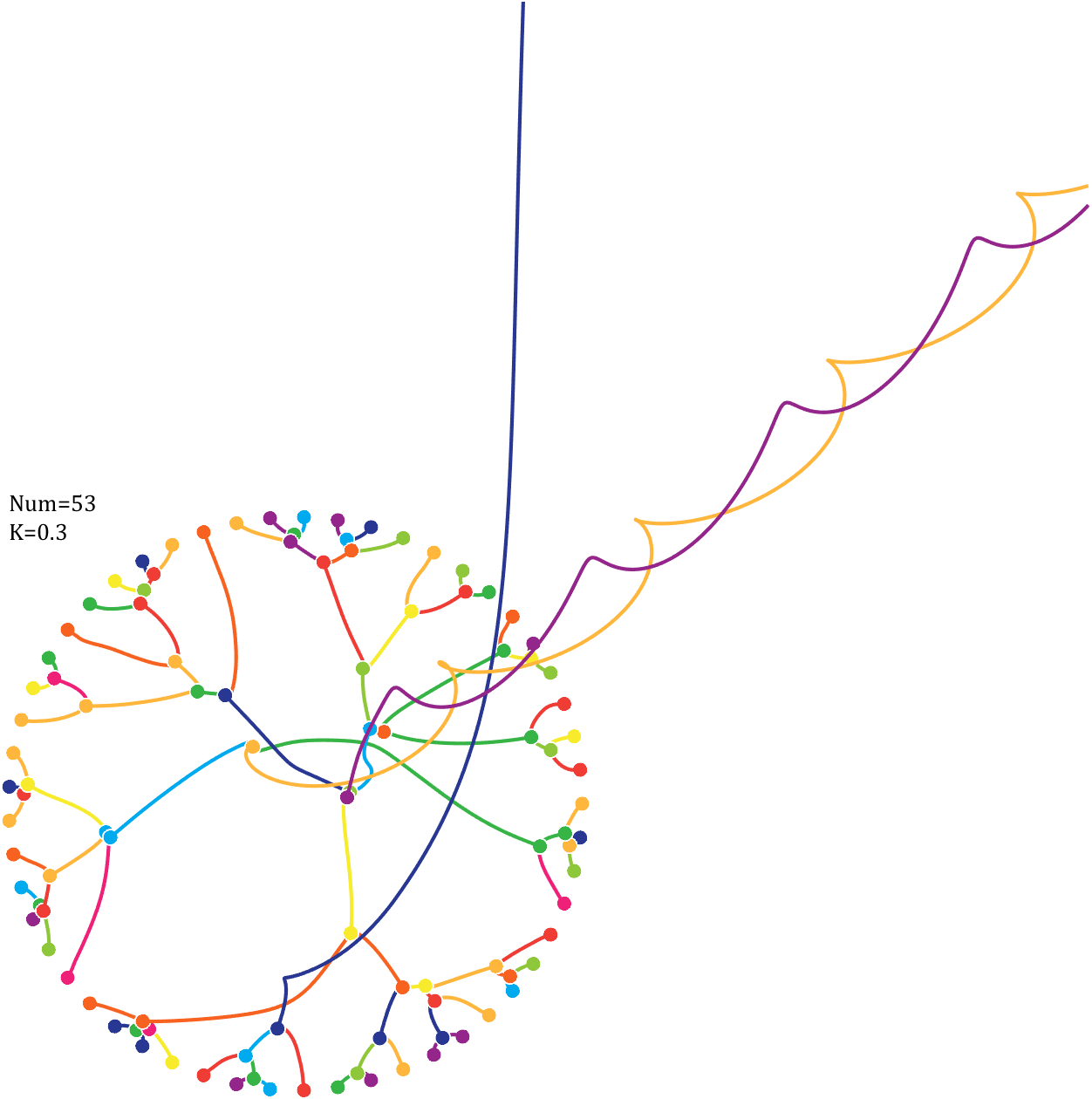
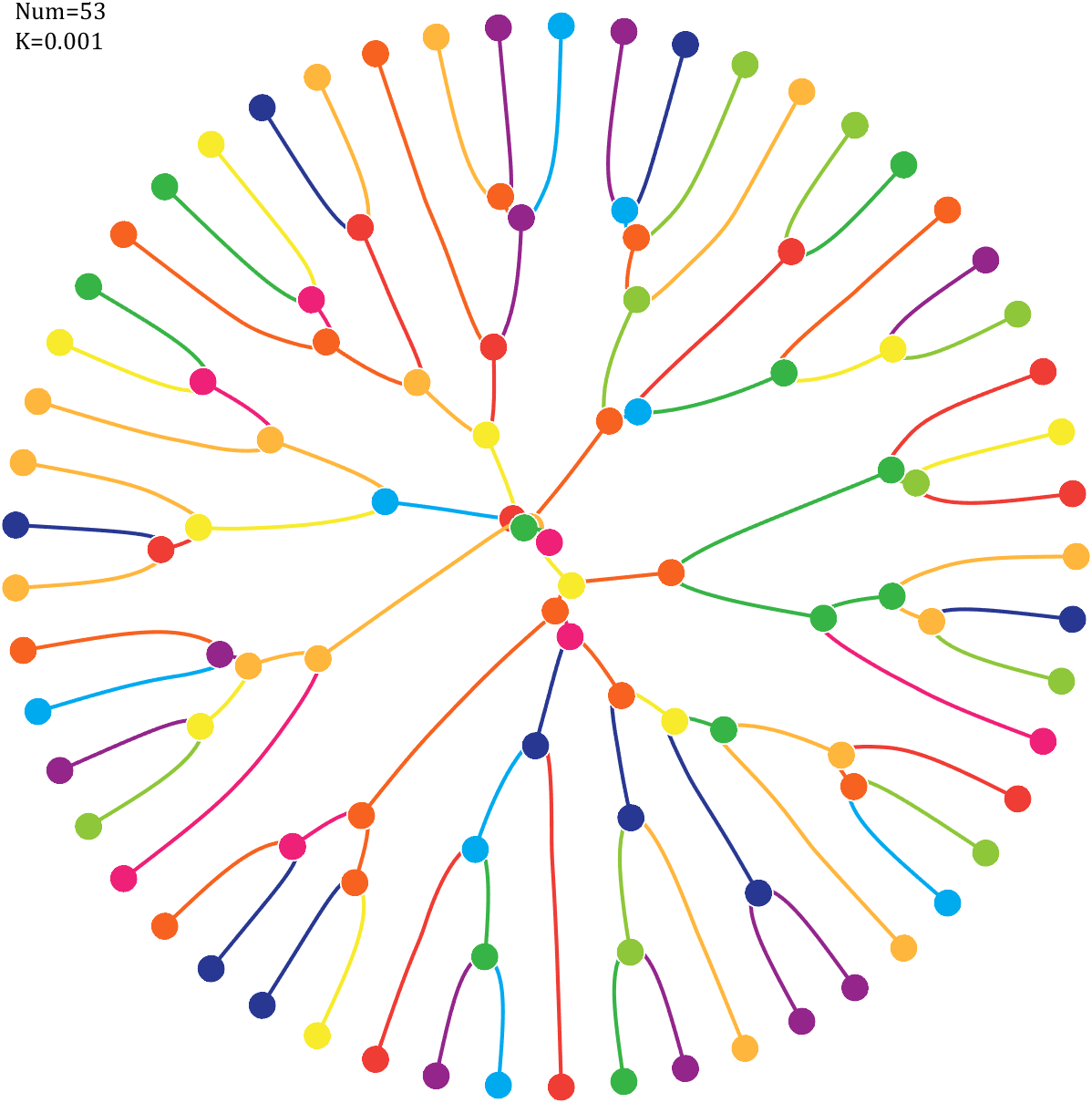
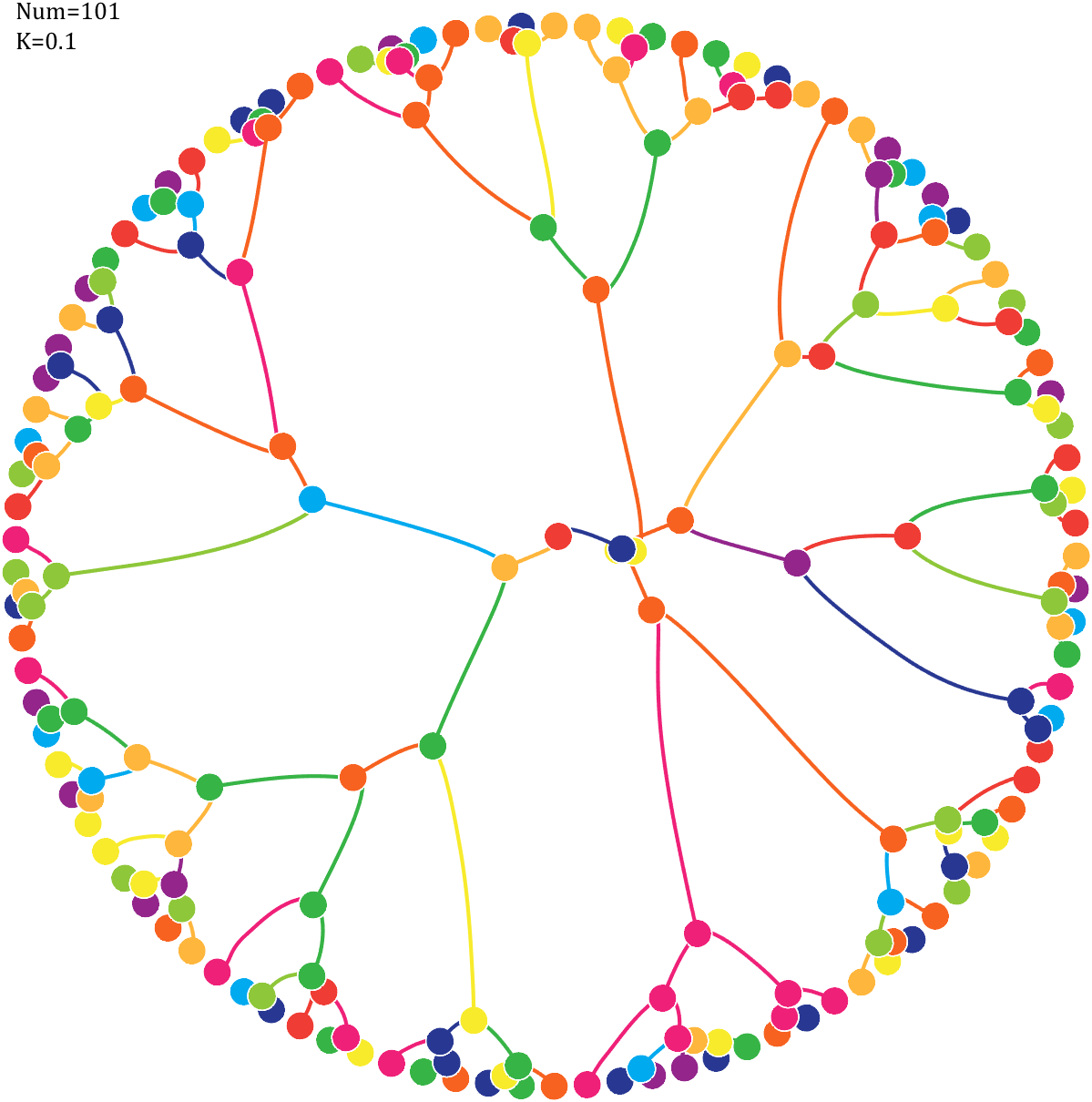
Pi=[3,getPi(71)];K=.18;
% 基础配置
CM=[239,32,120;239,60,52;247,98,32;255,182,60;247,235,44;
142,199,57;55,180,70;0,170,239;40,56,146;147,37,139]./255;
T=linspace(0,2*pi,length(Pi)+1)';
T=T(1:end-1);
ct=linspace(0,2*pi,100);
cx=cos(ct).*.027;
cy=sin(ct).*.027;
% 初始数据
Pi=Pi(:);
N=Pi;
X=cos(T);Y=sin(T);
VX=T.*0;VY=T.*0;
PX=X;PY=Y;
% 未碰撞时初始质量
getM=@(x)(x+1).^K;
M=getM(N);
% 绘制初始圆圈
hold on
for i=1:length(N)
fill(cx+X(i),cy+Y(i),CM(N(i)+1,:),'EdgeColor','w','LineWidth',1)
end
for k=1:800
% 计算加速度
Rn2=1./squareform(pdist([X,Y])).^2;
Rn2(eye(length(X))==1)=0;
MRn2=Rn2.*(M');
AX=X'-X;AY=Y'-Y;
normXY=sqrt(AX.^2+AY.^2);
AX=AX./normXY;AX(eye(length(X))==1)=0;
AY=AY./normXY;AY(eye(length(X))==1)=0;
AX=sum(AX.*MRn2,2)./150000;
AY=sum(AY.*MRn2,2)./150000;
% 计算速度及新位置
VX=VX+AX;X=X+VX;PX=[PX,X];
VY=VY+AY;Y=Y+VY;PY=[PY,Y];
% 检测是否有碰撞
R=squareform(pdist([X,Y]));
R(triu(ones(length(X)))==1)=inf;
[row,col]=find(R<=0.04);
if length(X)==1
break;
end
if ~isempty(row)
% 碰撞的点合为一体
XC=(X(row)+X(col))./2;YC=(Y(row)+Y(col))./2;
VXC=(VX(row).*M(row)+VX(col).*M(col))./(M(row)+M(col));
VYC=(VY(row).*M(row)+VY(col).*M(col))./(M(row)+M(col));
PC=nan(length(row),size(PX,2));
NC=mod(N(row)+N(col),10);
% 删除碰撞点并绘图
uniNum=unique([row;col]);
X(uniNum)=[];VX(uniNum)=[];
Y(uniNum)=[];VY(uniNum)=[];
for i=1:length(uniNum)
plot(PX(uniNum(i),:),PY(uniNum(i),:),'LineWidth',2,'Color',CM(N(uniNum(i))+1,:))
end
PX(uniNum,:)=[];PY(uniNum,:)=[];N(uniNum,:)=[];
% 绘制圆形
for i=1:length(XC)
fill(cx+XC(i),cy+YC(i),CM(NC(i)+1,:),'EdgeColor','w','LineWidth',1)
end
% 补充合体点
X=[X;XC];Y=[Y;YC];VX=[VX;VXC];VY=[VY;VYC];
PX=[PX;PC];PY=[PY;PC];N=[N;NC];M=getM(N);
end
end
for i=1:size(PX,1)
plot(PX(i,:),PY(i,:),'LineWidth',2,'Color',CM(N(i)+1,:))
end
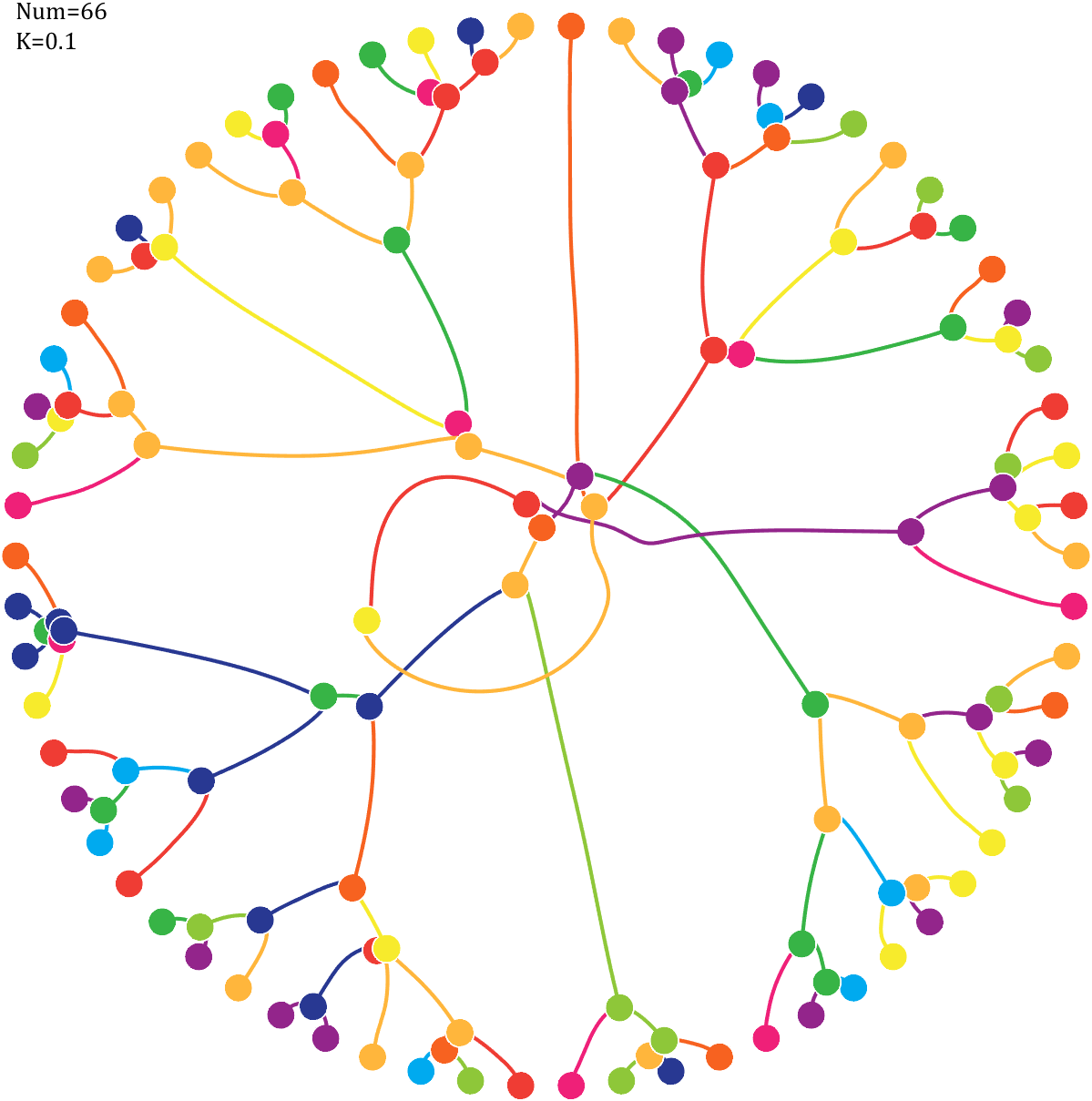
text(-1,1,{['Num=',num2str(length(Pi))];['K=',num2str(K)]},'FontSize',13,'FontName','Cambria')
% 图窗及坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,820,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.Position=[0,0,1,1];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
ax.XLim=[-1.1,1.1];
ax.YLim=[-1.1,1.1];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.XColor='none';
ax.YColor='none';
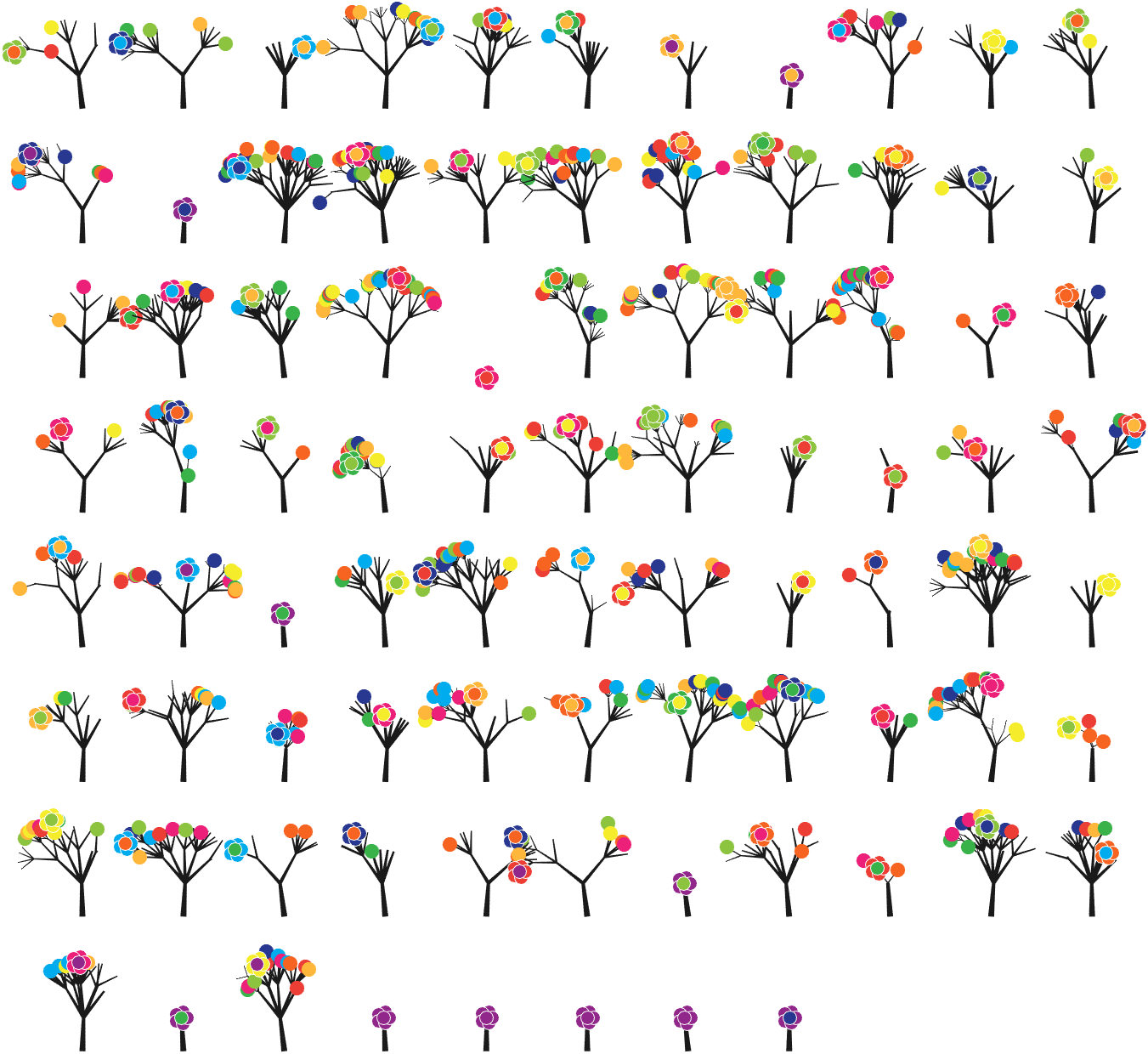
7 forest chart
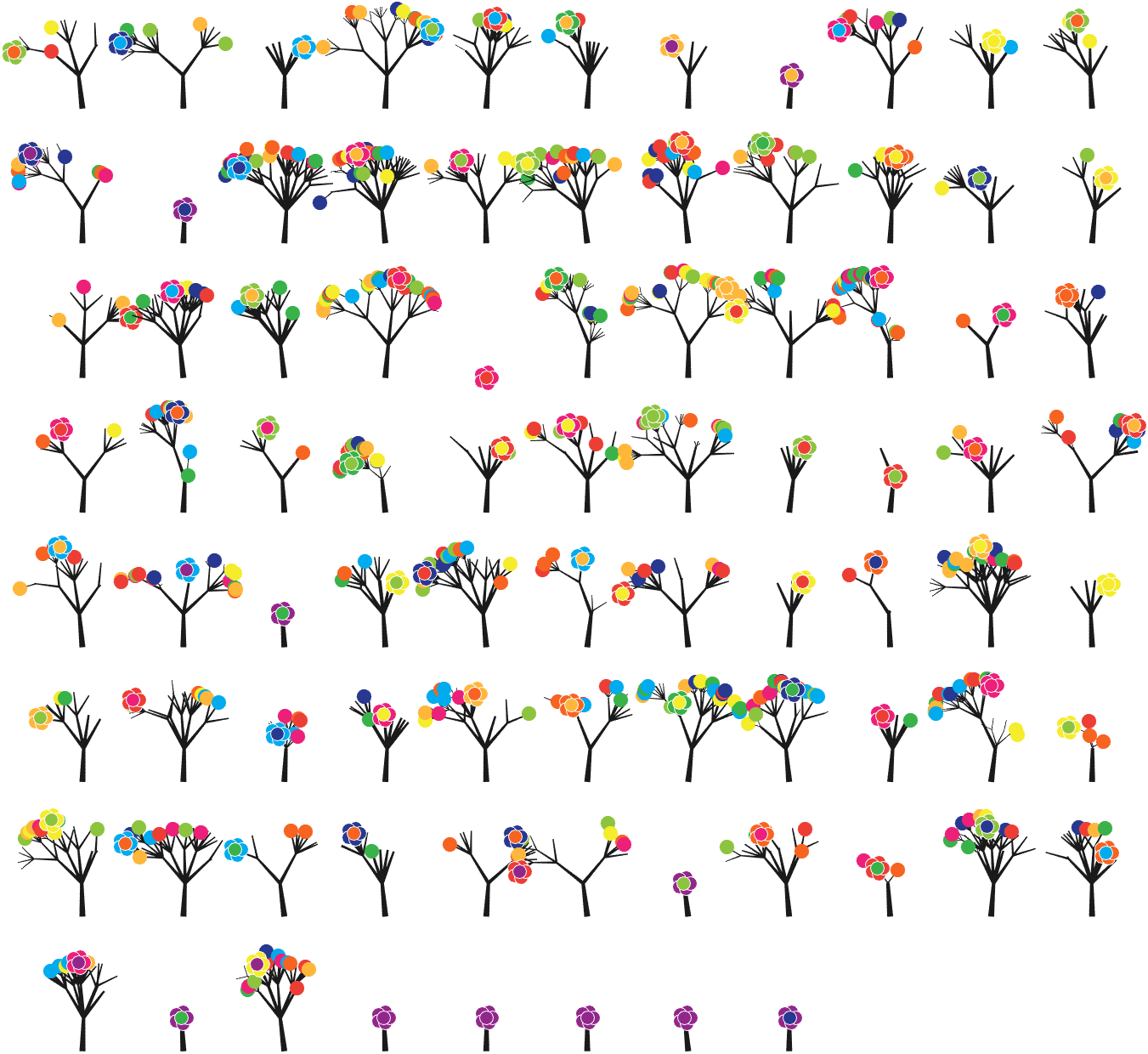
The method comes from
The digits of π are shown as a forest. Each tree in the forest represents the digits of π up to the next 9. The first 10 trees are "grown" from the digit sets 314159, 2653589, 79, 3238462643383279, 50288419, 7169, 39, 9, 3751058209, and 749.
BRANCHES
The first digit of a tree controls how many branches grow from the trunk of the tree. For example, the first tree's first digit is 3, so you see 3 branches growing from the trunk.
The next digit's branches grow from the end of a branch of the previous digit in left-to-right order. This process continues until all the tree's digits have been used up.
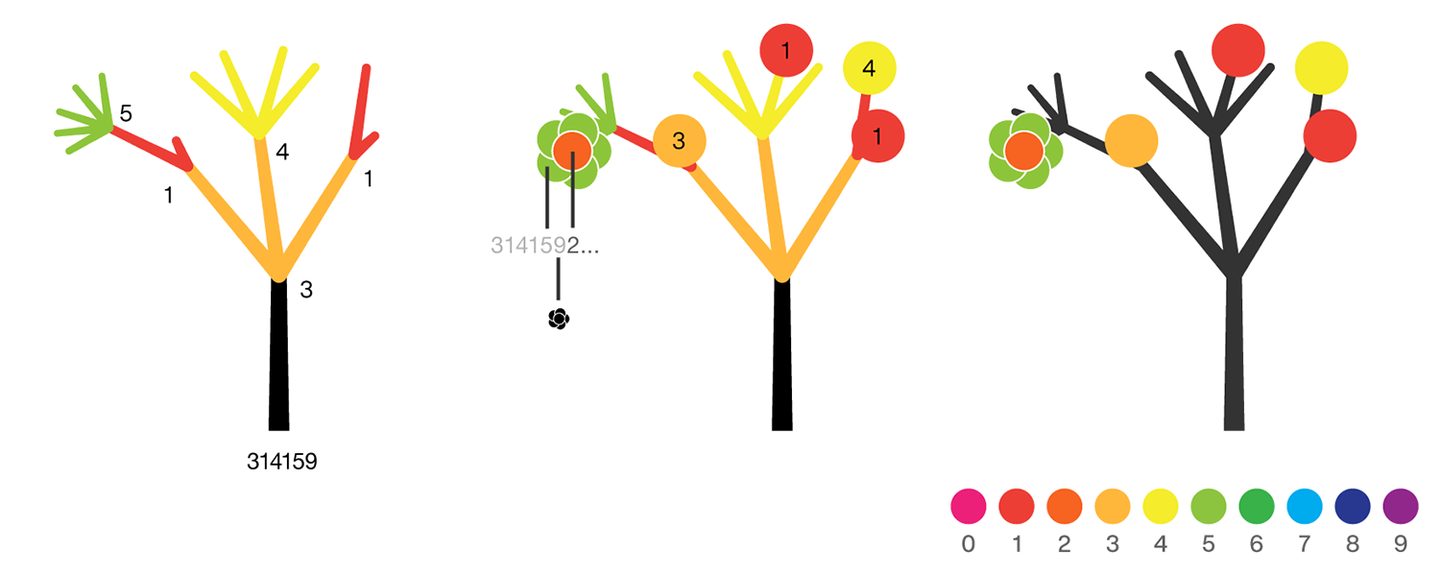
Each tree grows from a set of consecutive digits sampled from the digits of π up to the next 9. The first tree, shown here, grows from 314159. Each of the digits determine how many branches grow at each fork in the tree — the branches here are colored by their corresponding digit to illustrate this. Leaves encode the digits in a left-to-right order. The digit 9 spawns a flower on one of the branches of the previous digit. The branching exception is 0, which terminates the current branch — 0 branches grow!
LEAVES AND FLOWERS
The tree's digits themselves are drawn as circular leaves, color-coded by the digit.
The leaf exception is 9, which causes one of the branches of the previous digit to sprout a flower! The petals of the flower are colored by the digit before the 9 and the center is colored by the digit after the 9, which is on the next tree. This is how the forest propagates.
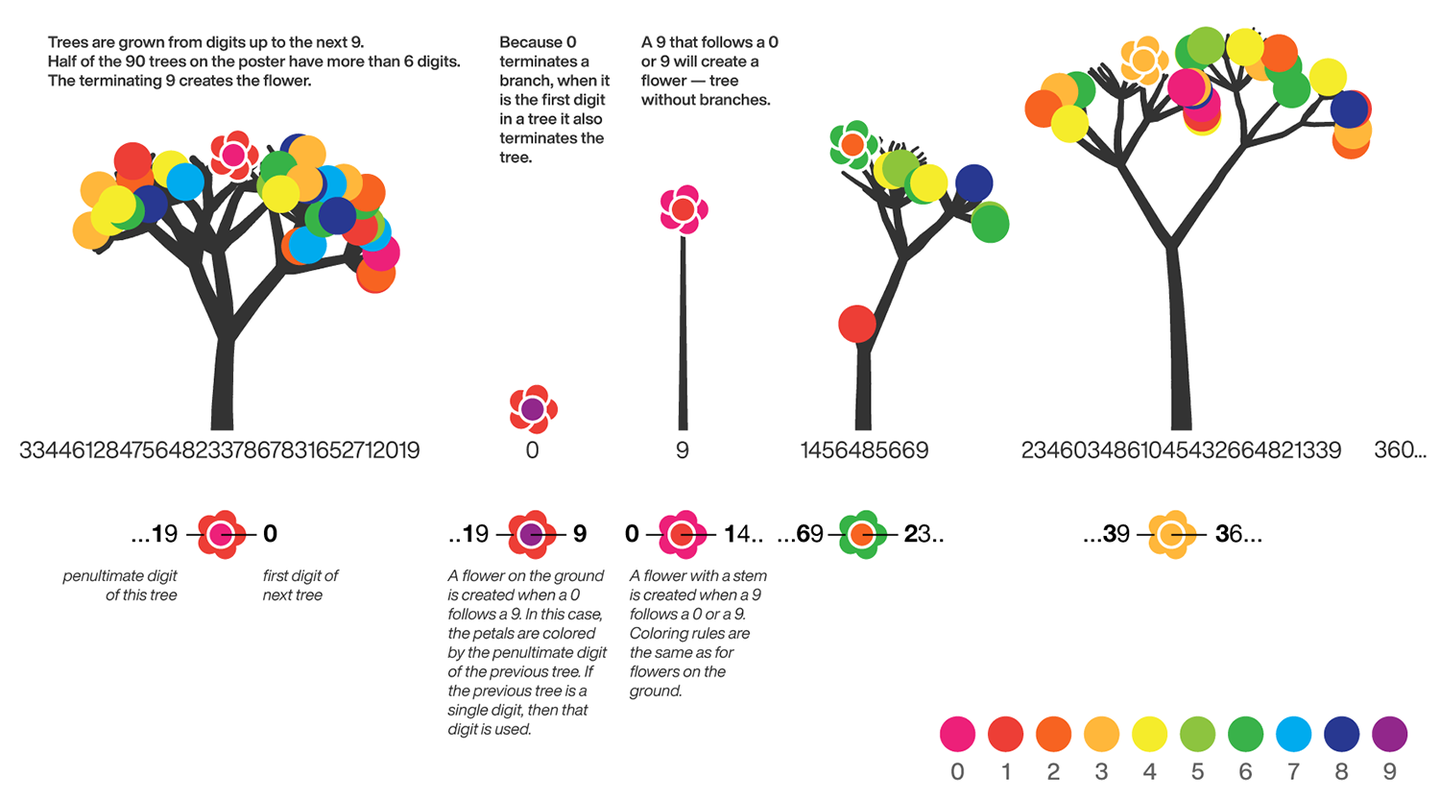
The colors of a flower are determined by the first digit of the next tree and the penultimate digit of the current tree. If the current tree only has one digit, then that digit is used. Leaves are placed at the tips of branches in a left-to-right order — you can "easily" read them off. Additionally, the leaves are distributed within the tree (without disturbing their left-to-right order) to spread them out as much as possible and avoid overlap. This order is deterministic.
The leaf placement exception are the branch set that sprouted the flower. These are not used to grow leaves — the flower needs space!
function PiTree(X,pos,D)
lw=2;
theta=pi/2+(rand(1)-.5).*pi./12;
% 树叶及花朵颜色
CM=[237,32,121;237,62,54;247,99,33;255,183,59;245,236,43;
141,196,63;57,178,74;0,171,238;40,56,145;146,39,139]./255;
hold on
if all(X(1:end-2)==0)
endSet=[pos,pos,theta];
else
kplot(pos(1)+[0,cos(theta)],pos(2)+[0,sin(theta)],lw./.6)
endSet=[pos,pos+[cos(theta),sin(theta)],theta];
% 计算层级
Layer=0;
for i=1:length(X)
Layer=[Layer,ones(1,X(i)).*i];
end
% 计算树枝
if D
for i=1:length(X)-2
if X(i)==0 % 若数值为0则不长树枝
newSet=endSet(1,:);
elseif X(i)==1 % 若数值为1则一长一短两个树枝
tTheta=endSet(1,5);
tTheta=linspace(tTheta+pi/8,tTheta-pi/8,2)'+(rand([2,1])-.5).*pi./8;
newSet=repmat(endSet(1,3:4),[X(i),1]);
newSet=[newSet.*[1;1],newSet+[cos(tTheta),sin(tTheta)].*.7^Layer(i).*[1;.1],tTheta];
else % 其他情况数值为几长几个树枝
tTheta=endSet(1,5);
tTheta=linspace(tTheta+pi/5,tTheta-pi/5,X(i))'+(rand([X(i),1])-.5).*pi./8;
newSet=repmat(endSet(1,3:4),[X(i),1]);
newSet=[newSet,newSet+[cos(tTheta),sin(tTheta)].*.7^Layer(i),tTheta];
end
% 绘制树枝
for j=1:size(newSet,1)
kplot(newSet(j,[1,3]),newSet(j,[2,4]),lw.*.6^Layer(i))
end
endSet=[endSet;newSet];
endSet(1,:)=[];
end
end
end
% 计算叶子和花朵位置
FLSet=endSet(:,3:4);
[~,FLInd]=sort(FLSet(:,1));
FLSet=FLSet(FLInd,:);
[~,tempInd]=sort(rand([1,size(FLSet,1)]));
tempInd=sort(tempInd(1:length(X)-2));
flowerInd=tempInd(randi([1,length(X)-2],[1,1]));
leafInd=tempInd(tempInd~=flowerInd);
% 绘制树叶
for i=1:length(leafInd)
scatter(FLSet(leafInd(i),1),FLSet(leafInd(i),2),70,'filled','CData',CM(X(i)+1,:))
end
% 绘制花朵
for i=1:5
% if ~D
% tC=CM(X(end)+1,:);
% else
% tC=CM(X(end-2)+1,:);
% end
scatter(FLSet(flowerInd,1)+cos(pi*2*i/5).*.18,FLSet(flowerInd,2)+sin(pi*2*i/5).*.18,60,...
'filled','CData',CM(X(end-2)+1,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',[1,1,1])
end
scatter(FLSet(flowerInd,1),FLSet(flowerInd,2),60,'filled','CData',CM(X(end)+1,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',[1,1,1])
drawnow;%axis tight
% =========================================================================
function kplot(XX,YY,LW,varargin)
LW=linspace(LW,LW*.6,10);%+rand(1,20).*LW./10;
XX=linspace(XX(1),XX(2),11)';
XX=[XX(1:end-1),XX(2:end)];
YY=linspace(YY(1),YY(2),11)';
YY=[YY(1:end-1),YY(2:end)];
for ii=1:10
plot(XX(ii,:),YY(ii,:),'LineWidth',LW(ii),'Color',[.1,.1,.1])
end
end
end
main part:
Pi=[3,getPi(800)];
pos9=[0,find(Pi==9)];
set(gcf,'Position',[200,50,900,900],'Color',[1,1,1]);
ax=gca;hold on
ax.Position=[0,0,1,1];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
ax.XLim=[.5,36];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.XColor='none';
ax.YColor='none';
for j=1:8
for i=1:11
n=i+(j-1)*11;
if n<=85
tPi=Pi((pos9(n)+1):pos9(n+1)+1);
if length(tPi)>2
PiTree(tPi,[0+i*3,0-j*4],true);
else
PiTree([Pi(pos9(n)),tPi],[0+i*3,0-j*4],false);
end
end
end
end
8 random walk

n=1200;
% 获取pi前n位小数
Pi=getPi(n);
CM=[239,65,75;230,115,48;229,158,57;232,136,85;239,199,97;
144,180,116;78,166,136;81,140,136;90,118,142;43,121,159]./255;
hold on
endPoint=[0,0];
t=linspace(0,2*pi,100);
T=linspace(0,2*pi,11)+pi/2;
fill(endPoint(1)+cos(t).*.5,endPoint(2)+sin(t).*.5,CM(Pi(1)+1,:),'EdgeColor','none')
for i=1:n
theta=T(Pi(i)+1);
plot(endPoint(1)+[0,cos(theta)],endPoint(2)+[0,sin(theta)],'Color',[CM(Pi(i)+1,:),.8],'LineWidth',1.2);
endPoint=endPoint+[cos(theta),sin(theta)];
end
fill(endPoint(1)+cos(t).*.5,endPoint(2)+sin(t).*.5,CM(Pi(n)+1,:),'EdgeColor','none')
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,820,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
ax.XLim=[-30,5];
ax.YLim=[-5,40];
% 绘制图例
endPoint=[1,35];
for i=1:10
theta=T(i);
plot(endPoint(1)+[0,cos(theta).*2],endPoint(2)+[0,sin(theta).*2],'Color',[CM(i,:),.8],'LineWidth',3);
text(endPoint(1)+cos(theta).*2.7,endPoint(2)+sin(theta).*2.7,num2str(i-1),'Color',[1,1,1].*.7,...
'FontSize',12,'FontWeight','bold','FontName','Cambria','HorizontalAlignment','center')
end
text(-15,35,'Random walk of \pi digits','Color',[1,1,1],'FontName','Cambria',...
'HorizontalAlignment','center','FontSize',25,'FontAngle','italic')
9 grid chart

Pi=[3,getPi(399)];
% 配色数据
CM=[248,65,69;246,152,36;249,198,81;67,170,139;87,118,146]./255;
% 绘制圆圈
hold on
t=linspace(0,2*pi,100);
x=cos(t).*.8.*.5;
y=sin(t).*.8.*.5;
for i=1:400
[col,row]=ind2sub([20,20],i);
if mod(Pi(i),2)==0
fill(x+col,y+row,CM(round((Pi(i)+1)/2),:),'LineWidth',1,'EdgeAlpha',.8)
else
fill(x+col,y+row,[0,0,0],'EdgeColor',CM(round((Pi(i)+1)/2),:),'LineWidth',1,'EdgeAlpha',.7)
end
end
text(10.5,-.4,'\pi on a grid — 400 digits','Color',[1,1,1],'FontName','Cambria',...
'HorizontalAlignment','center','FontSize',25,'FontAngle','italic')
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,820,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.YDir='reverse';
ax.XLim=[.5,20.5];
ax.YLim=[-1,20.5];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
10 scale grid diagram
Let's still put the numbers in the form of circles, but the difference is that six numbers are grouped together, and the pure purple circle at the end is the six 9s that we are familiar with decimal places 762-767
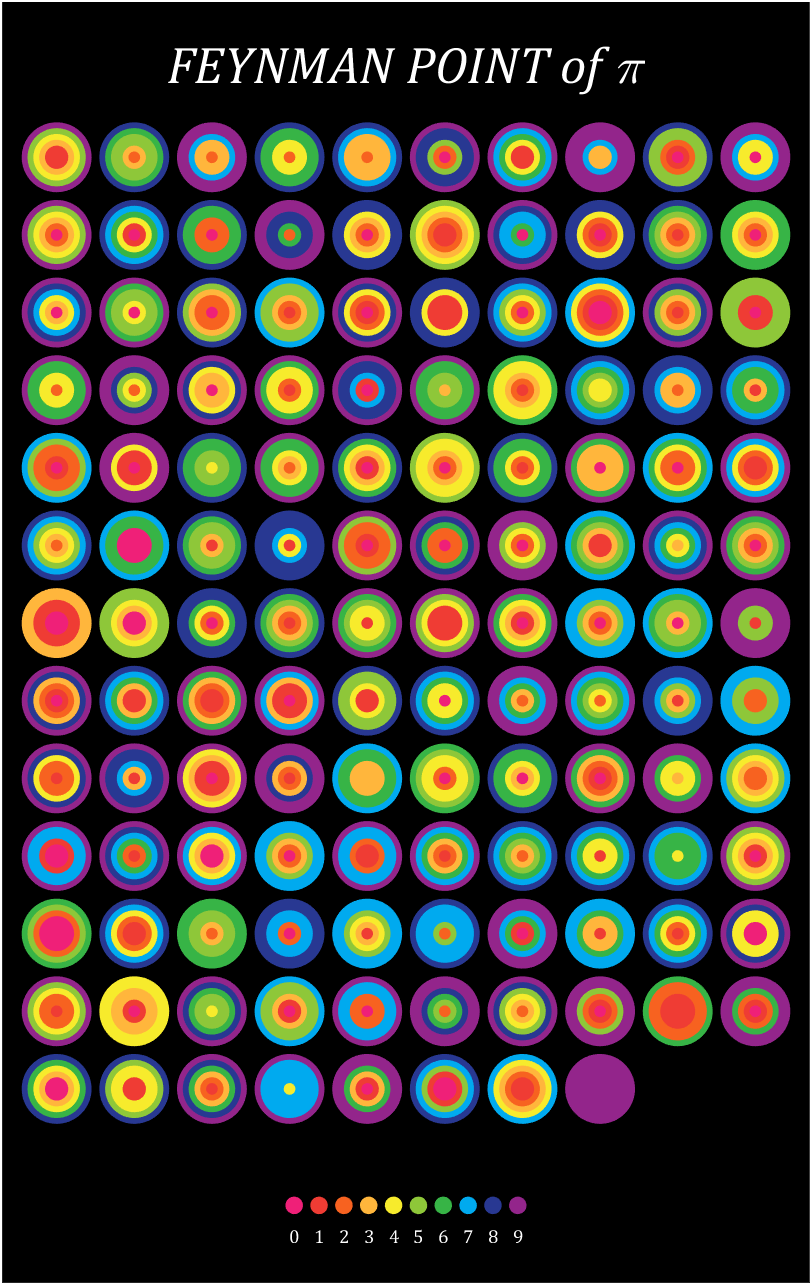
Pi=[3,getPi(767)];
% 762-767
% 配色数据
CM=[239,32,120;239,60,52;247,98,32;255,182,60;247,235,44;
142,199,57;55,180,70;0,170,239;40,56,146;147,37,139]./255;
% 绘制圆圈
hold on
t=linspace(0,2*pi,100);
x=cos(t).*.9.*.5;
y=sin(t).*.9.*.5;
for i=1:6:length(Pi)
n=round((i-1)/6+1);
[col,row]=ind2sub([10,13],n);
tNum=Pi(i:i+5);
numNum=find([diff(sort(tNum)),1]);
numNum=[numNum(1),diff(numNum)];
cumNum=cumsum(numNum);
uniNum=unique(tNum);
for j=length(cumNum):-1:1
fill(x./6.*cumNum(j)+col,y./6.*cumNum(j)+row,CM(uniNum(j)+1,:),'EdgeColor','none')
end
end
% 绘制图例
for i=1:10
fill(x./4+5.5+(i-5.5)*.32,y./4+14.5,CM(i,:),'EdgeColor','none')
text(5.5+(i-5.5)*.32,14.9,num2str(i-1),'Color',[1,1,1],'FontSize',...
9,'FontName','Cambria','HorizontalAlignment','center')
end
text(5.5,-.2,'FEYNMAN POINT of \pi','Color',[1,1,1],'FontName','Cambria',...
'HorizontalAlignment','center','FontSize',25,'FontAngle','italic')
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,600,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.YDir='reverse';
ax.Position=[0,0,1,1];
ax.XLim=[.3,10.7];
ax.YLim=[-1,15.5];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
11 text chart

First, write a code to generate an image of each letter:
function getLogo
if ~exist('image','dir')
mkdir('image\')
end
logoSet=['.',char(65:90)];
for i=1:27
figure();
ax=gca;
ax.XLim=[-1,1];
ax.YLim=[-1,1];
ax.XColor='none';
ax.YColor='none';
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
logo=logoSet(i);
hold on
text(0,0,logo,'HorizontalAlignment','center','FontSize',320,'FontName','Segoe UI Black')
exportgraphics(ax,['image\',logo,'.png'])
close
end
dotPic=imread('image\..png');
newDotPic=uint8(ones([400,size(dotPic,2),3]).*255);
newDotPic(end-size(dotPic,1)+1:end,:,1)=dotPic(:,:,1);
newDotPic(end-size(dotPic,1)+1:end,:,2)=dotPic(:,:,2);
newDotPic(end-size(dotPic,1)+1:end,:,3)=dotPic(:,:,3);
imwrite(newDotPic,'image\..png')
S=20;
for i=1:27
logo=logoSet(i);
tPic=imread(['image\',logo,'.png']);
sz=size(tPic,[1,2]);
sz=round(sz./sz(1).*400);
tPic=imresize(tPic,sz);
tBox=uint8(255.*ones(size(tPic,[1,2])+S));
tBox(S+1:S+size(tPic,1),S+1:S+size(tPic,2))=tPic(:,:,1);
imwrite(cat(3,tBox,tBox,tBox),['image\',logo,'.png'])
end
end

Pi=[3,-1,getPi(150)];
CM=[109,110,113;224,25,33;244,126,26;253,207,2;154,203,57;111,150,124;
121,192,235;6,109,183;190,168,209;151,118,181;233,93,163]./255;
ST={'.','ZERO','ONE','TWO','THREE','FOUR','FIVE','SIX','SEVEN','EIGHT','NINE'};
n=1;
hold on
% 循环绘制字母
for i=1:20%:10
STList='';
NMList=[];
PicListR=uint8(zeros(400,0));
PicListG=uint8(zeros(400,0));
PicListB=uint8(zeros(400,0));
% PicListA=uint8(zeros(400,0));
for j=1:6
STList=[STList,ST{Pi(n)+2}];
NMList=[NMList,ones(size(ST{Pi(n)+2})).*(Pi(n)+2)];
n=n+1;
if length(STList)>15&&length(STList)+length(ST{Pi(n)+2})>20
break;
end
end
for k=1:length(STList)
tPic=imread(['image\',STList(k),'.png']);
% PicListA=[PicListA,tPic(:,:,1)];
PicListR=[PicListR,(255-tPic(:,:,1)).*CM(NMList(k),1)];
PicListG=[PicListG,(255-tPic(:,:,2)).*CM(NMList(k),2)];
PicListB=[PicListB,(255-tPic(:,:,3)).*CM(NMList(k),3)];
end
PicList=cat(3,PicListR,PicListG,PicListB);
image([-1200,1200],[0,150]-(i-1)*150,flipud(PicList))
end
% 图窗及坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,600,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
ax.XLim=[-1300,1300];
ax.Position=[0,0,1,1];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
ax.YLim=[-19*150-80,230];
12 spiral chart

Pi=getPi(600);
% 配色列表
CM=[78,121,167;242,142,43;225,87,89;118,183,178;89,161,79;
237,201,72;176,122,161;255,157,167;156,117,95;186,176,172]./255;
% 绘制圆圈
hold on
t=linspace(0,2*pi,100);
x=cos(t).*.8;
y=sin(t).*.8;
for i=1:600
X=i.*cos(i./10)./10;
Y=i.*sin(i./10)./10;
fill(X+x,Y+y,CM(Pi(i)+1,:),'EdgeColor','none','FaceAlpha',.9)
end
text(0,65,'The Circle of \pi','Color',[1,1,1],'FontName','Cambria',...
'HorizontalAlignment','center','FontSize',25,'FontAngle','italic')
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,820,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.XLim=[-60,60];
ax.YLim=[-60,70];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
13 Archimedean spiral diagram

a=1;b=.227;
Pi=getPi(500);
% 配色列表
CM=[78,121,167;242,142,43;225,87,89;118,183,178;89,161,79;
237,201,72;176,122,161;255,157,167;156,117,95;186,176,172]./255;
% 绘制圆圈
hold on
T=0;R=1;
t=linspace(0,2*pi,100);
x=cos(t).*.7;
y=sin(t).*.7;
for i=1:500
X=R.*cos(T);Y=R.*sin(T);
fill(X+x,Y+y,CM(Pi(i)+1,:),'EdgeColor','none','FaceAlpha',.9)
T=T+1./R.*1.4;
R=a+b*T;
end
text(17.25,22,{'The Archimedes spiral of \pi';'—— 500 digits'},...
'Color',[1,1,1],'FontName','Cambria',...
'HorizontalAlignment','right','FontSize',25,'FontAngle','italic')
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,820,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.XLim=[-19,18.5];
ax.YLim=[-20,25];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
14 proportional Archimedean spiral diagram


Pi=[3,getPi(1199)];
% 配色数据
CM=[239,32,120;239,60,52;247,98,32;255,182,60;247,235,44;
142,199,57;55,180,70;0,170,239;40,56,146;147,37,139]./255;
% CM=slanCM(184,10);
% 绘制圆圈
hold on
T=0;R=1;
t=linspace(0,2*pi,100);
x=cos(t).*.7;
y=sin(t).*.7;
for i=1:4:length(Pi)
X=R.*cos(T);Y=R.*sin(T);
tNum=Pi(i:i+3);
numNum=find([diff(sort(tNum)),1]);
numNum=[numNum(1),diff(numNum)];
cumNum=cumsum(numNum);
uniNum=unique(tNum);
for j=length(cumNum):-1:1
fill(x./4.*cumNum(j)+X,y./4.*cumNum(j)+Y,CM(uniNum(j)+1,:),'EdgeColor','none')
end
T=T+1./R.*1.4;
R=a+b*T;
end
text(14,16.5,{'The ratio of four numbers from \pi';'—— 1200 digits'},...
'Color',[1,1,1],'FontName','Cambria',...
'HorizontalAlignment','right','FontSize',23,'FontAngle','italic')
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,820,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.XLim=[-15,15.5];
ax.YLim=[-15,19];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
15 graph
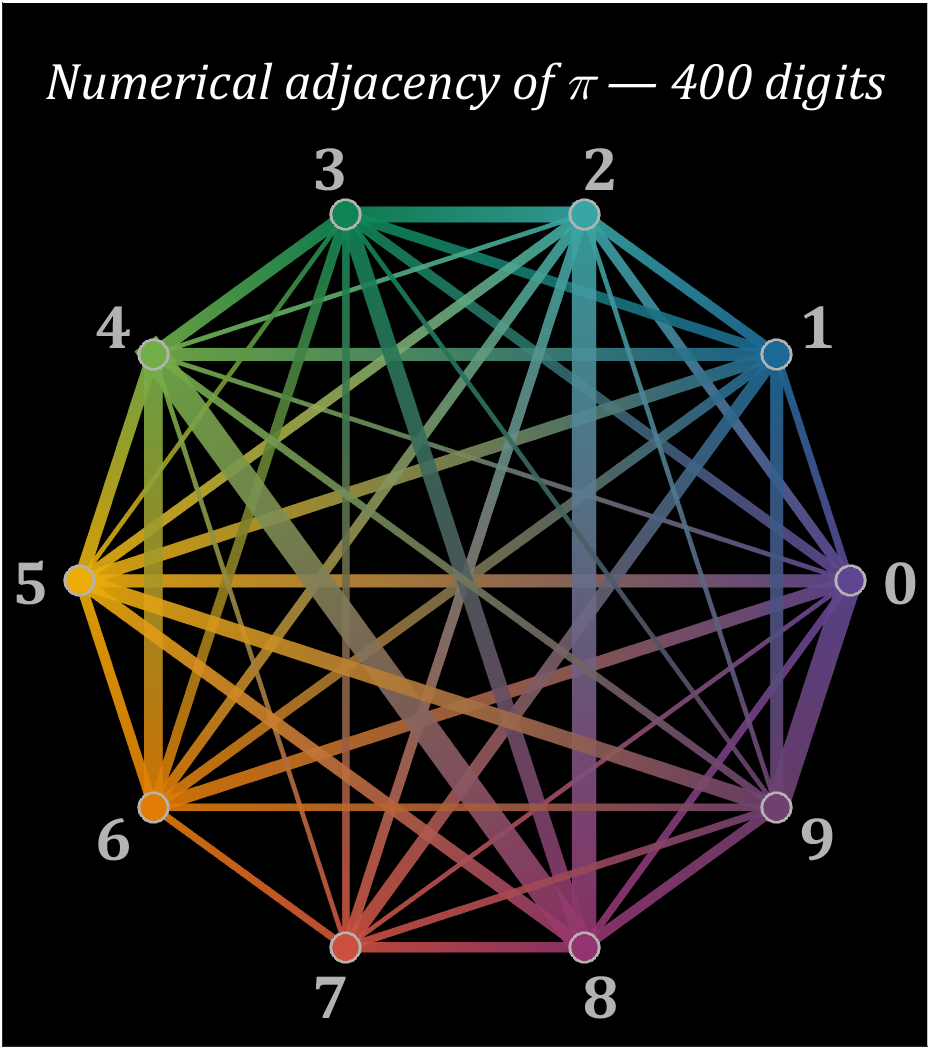
% 构建连接矩阵
corrMat=zeros(10,10);
Pi=getPi(401);
for i=1:400
corrMat(Pi(i)+1,Pi(i+1)+1)=corrMat(Pi(i)+1,Pi(i+1)+1)+1;
end
% 配色列表
colorList=[0.3725 0.2745 0.5647
0.1137 0.4118 0.5882
0.2196 0.6510 0.6471
0.0588 0.5216 0.3294
0.4510 0.6863 0.2824
0.9294 0.6784 0.0314
0.8824 0.4863 0.0196
0.8000 0.3137 0.2431
0.5804 0.2039 0.4314
0.4353 0.2510 0.4392];
t=linspace(0,2*pi,11);t=t(1:10)';
posXY=[cos(t),sin(t)];
maxWidth=max(corrMat(corrMat>0));
minWidth=min(corrMat(corrMat>0));
ttList=linspace(0,1,3)';
% 循环绘图
hold on
for i=1:size(corrMat,1)
for j=i+1:size(corrMat,2)
if corrMat(i,j)>0
tW=(corrMat(i,j)-minWidth)./(maxWidth-minWidth);
colorData=(1-ttList).*colorList(i,:)+ttList.*colorList(j,:);
CData(:,:,1)=colorData(:,1);
CData(:,:,2)=colorData(:,2);
CData(:,:,3)=colorData(:,3);
% 绘制连线
fill(linspace(posXY(i,1),posXY(j,1),3),...
linspace(posXY(i,2),posXY(j,2),3),[0,0,0],'LineWidth',tW.*12+1,...
'CData',CData,'EdgeColor','interp','EdgeAlpha',.7,'FaceAlpha',.7)
end
end
% 绘制圆点
scatter(posXY(i,1),posXY(i,2),200,'filled','LineWidth',1.2,...
'MarkerFaceColor',colorList(i,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',[.7,.7,.7]);
text(posXY(i,1).*1.13,posXY(i,2).*1.13,num2str(i-1),'Color',[1,1,1].*.7,...
'FontSize',30,'FontWeight','bold','FontName','Cambria','HorizontalAlignment','center')
end
text(0,1.3,'Numerical adjacency of \pi — 400 digits','Color',[1,1,1],'FontName','Cambria',...
'HorizontalAlignment','center','FontSize',25,'FontAngle','italic')
% 图窗和坐标区域修饰
set(gcf,'Position',[200,100,820,820]);
ax=gca;
ax.XLim=[-1.2,1.2];
ax.YLim=[-1.21,1.5];
ax.XTick=[];
ax.YTick=[];
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
ax.DataAspectRatio=[1,1,1];
16 circos chart
Need to use this tool:
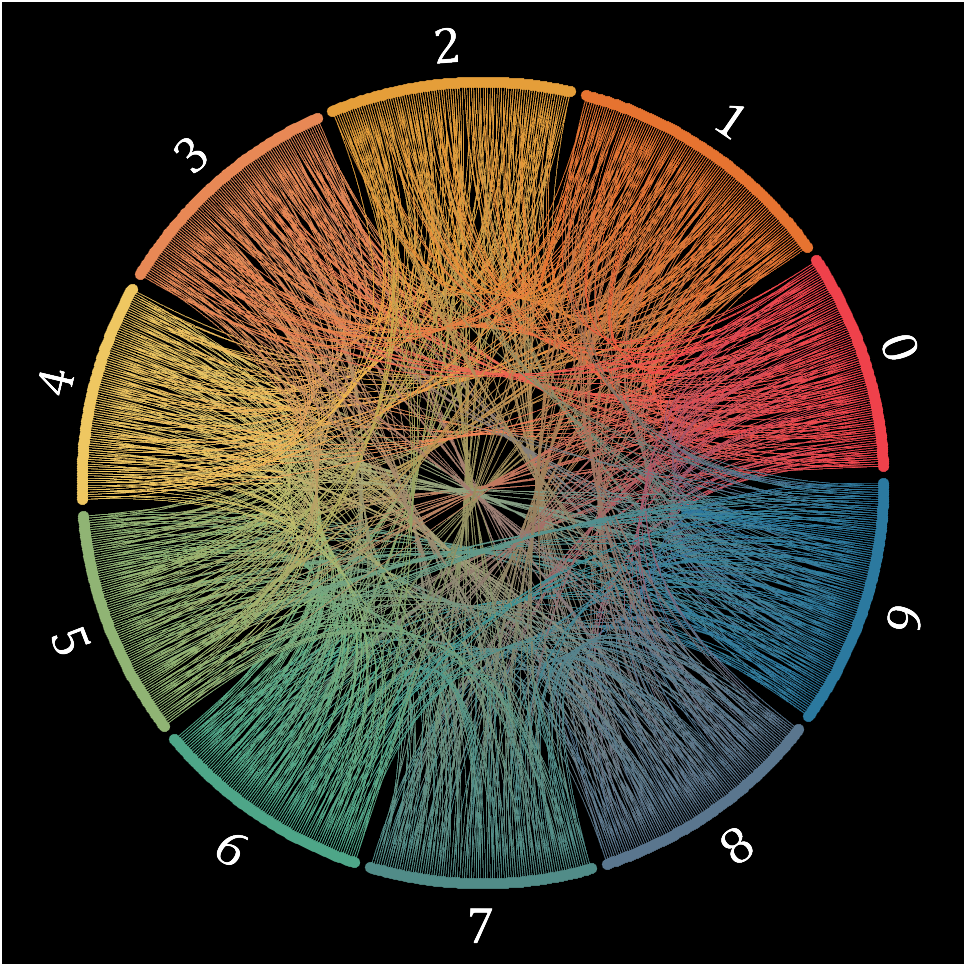

Class=getPi(1001)+1;
Data=diag(ones(1,1000),-1);
className={'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9'};
colorOrder=[239,65,75;230,115,48;229,158,57;232,136,85;239,199,97;
144,180,116;78,166,136;81,140,136;90,118,142;43,121,159]./255;
CC=circosChart(Data,Class,'ClassName',className,'ColorOrder',colorOrder);
CC=CC.draw();
ax=gca;
ax.Color=[0,0,0];
CC.setClassLabel('Color',[1,1,1],'FontSize',25,'FontName','Cambria')
CC.setLine('LineWidth',.7)
YOU CAN GET ALL CODE HERE:
Happy Pi Day
Happy Pi Day
Mathworks has always had quality documentation but in 2023, the documentation quality fell. Will this improve in 2024?
Hi
I have Matlab 2015b installed and if I try:
ones(2,3,4)+ones(2,3)
of course I get an error. But my student has R2023b installed and she gets a 2x3x4 matrix as a result, with all elements = 2.
How is it possible?
Thanks
A
This study explores the demographic patterns and disease outcomes during the cholera outbreak in London in 1849. Utilizing historical records and scholarly accounts, the research investigates the impact of the outbreak on the city' s population. While specific data for the 1849 cholera outbreak is limited, trends from similar 19th - century outbreaks suggest a high infection rate, potentially ranging from 30% to 50% of the population, owing to poor sanitation and overcrowded living conditions . Additionally, the birth rate in London during this period was estimated at 0.037 births per person per year . Although the exact reproduction number (R₀) for cholera in 1849 remains elusive, historical evidence implies a high R₀ due to the prevalent unsanitary conditions . This study sheds light on the challenges of estimating disease parameters from historical data, emphasizing the critical role of sanitation and public health measures in mitigating the impact of infectious diseases.
Introduction
The cholera outbreak of 1849 was a significant event in the history of cholera, a deadly waterborne disease caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholera. Cholera had several major outbreaks during the 19th century, and the one in 1849 was particularly devastating.
During this outbreak, cholera spread rapidly across Europe, including countries like England, France, and Germany . The disease also affected North America, with outbreaks reported in cities like New York and Montreal. The exact number of casualties from the 1849 cholera outbreak is difficult to determine due to limited record - keeping at that time. However, it is estimated that tens of thousands of people died as a result of the disease during this outbreak.
Cholera is highly contagious and spreads through contaminated water and food . The lack of proper sanitation and hygiene practices in the 19th century contributed to the rapid spread of the disease. It wasn't until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that advancements in public health, sanitation, and clean drinking water significantly reduced the incidence and impact of cholera outbreaks in many parts of the world.
Infection Rate
Based on general patterns observed in 19th - century cholera outbreaks and the conditions of that time, it' s reasonable to assume that the infection rate was quite high. During major cholera outbreaks in densely populated and unsanitary areas, infection rates could be as high as 30 - 50% or even more.
This means that in a densely populated city like London, with an estimated population of around 2.3 million in 1849, tens of thousands of people could have been infected during the outbreak. It' s important to emphasize that this is a rough estimation based on historical patterns and not specific to the 1849 outbreak. The actual infection rate could have varied widely based on the local conditions, public health measures in place, and the effectiveness of efforts to contain the disease.
For precise and localized estimations, detailed historical records specific to the 1849 cholera outbreak in a particular city or region would be required, and such data might not be readily available due to the limitations of historical documentation from that time period
Mortality Rate
It' s challenging to provide an exact death rate for the 1849 cholera outbreak because of the limited and often unreliable historical records from that time period. However, it is widely acknowledged that the death rate was significant, with tens of thousands of people dying as a result of the disease during this outbreak.
Cholera has historically been known for its high mortality rate, particularly in areas with poor sanitation and limited access to clean water. During cholera outbreaks in the 19th century, mortality rates could be extremely high, sometimes reaching 50% or more in affected communities. This high mortality rate was due to the rapid onset of severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance caused by the cholera toxin, leading to death if not promptly treated.
Studies and historical accounts from various cholera outbreaks suggest that the R₀ for cholera can range from 1.5 to 2.5 or even higher in conditions where sanitation is inadequate and clean water is scarce. This means that one person with cholera could potentially infect 1.5 to 2.5 or more other people in such settings.
Unfortunately, there are no specific and reliable data available regarding the recovery rates from the 1849 cholera outbreak, as detailed and accurate record - keeping during that time period was limited. Cholera outbreaks in the 19th century were often devastating due to the lack of effective medical treatments and poor sanitation conditions. Recovery from cholera largely depended on the individual's ability to rehydrate, which was difficult given the rapid loss of fluids through severe diarrhea and vomiting .
LONDON CASE OF STUDY
In 1849, the estimated population of London was around 2.3 million people. London experienced significant population growth during the 19th century due to urbanization and industrialization. It’s important to note that historical population figures are often estimates, as comprehensive and accurate record-keeping methods were not as advanced as they are today.
% Define parameters
R0 = 2.5;
beta = 0.5;
gamma = 0.2; % Recovery rate
N = 2300000; % Total population
I0 = 1; % Initial number of infected individuals
% Define the SIR model differential equations
sir_eqns = @(t, Y) [-beta * Y(1) * Y(2) / N; % dS/dt
beta * Y(1) * Y(2) / N - gamma * Y(2); % dI/dt
gamma * Y(2)]; % dR/dt
% Initial conditions
Y0 = [N - I0; I0; 0]; % Initial conditions for S, I, R
% Time span
tmax1 = 100; % Define the maximum time (adjust as needed)
tspan = [0 tmax1];
% Solve the SIR model differential equations
[t, Y] = ode45(sir_eqns, tspan, Y0);
% Plot the results
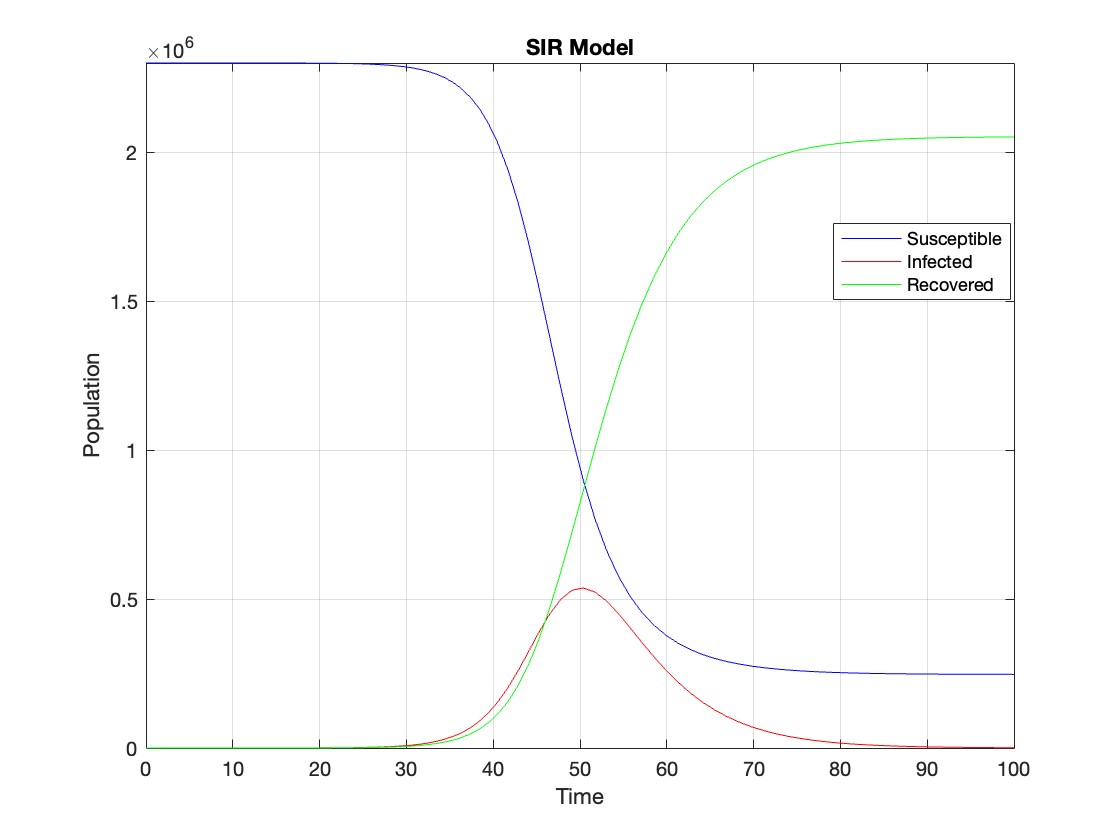
figure;
plot(t, Y(:,1), 'b', t, Y(:,2), 'r', t, Y(:,3), 'g');
legend('Susceptible', 'Infected', 'Recovered');
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('Population');
title('SIR Model');
axis tight;
grid on;
% Assuming t and Y are obtained from the ode45 solver for the SIR model
% Extract the infected population data (second column of Y)
infected = Y(:,2);
% Plot the infected population over time
figure;
plot(t, infected, 'r');
legend('Infected');
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('Population');
title('Infected Population over Time');
grid on;
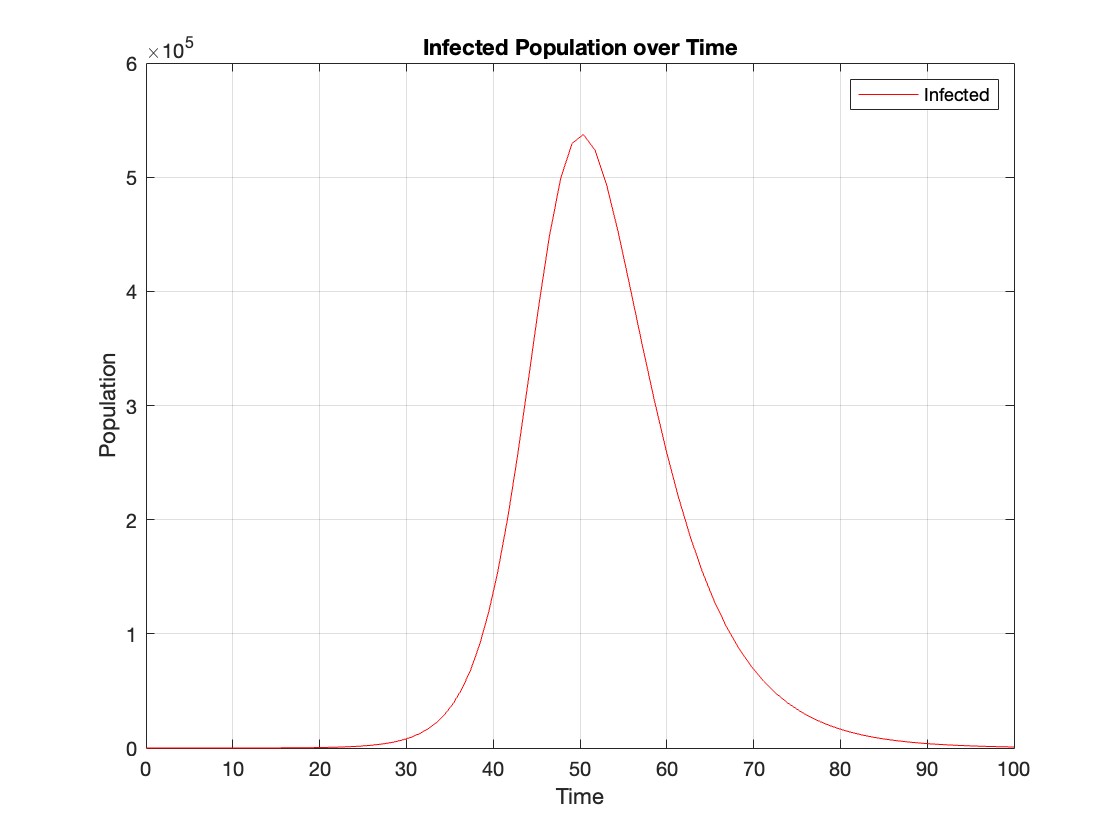
The code provides a visual representation of how the disease spreads and eventually diminishes within the population over the specified time interval . It can be used to understand the impact of different parameters (such as infection and recovery rates) on the progression of the outbreak .
The study of nonlinear dynamical systems in lattices is an area of research with continuously growing interest.The first systematic studies of these systems emerged in the late 1930 s,thanks to the work of Frenkel and Kontorova on crystal dislocations.These studies led to the formulation of the discrete Klein-Gordon equation (DKG).Specifically,in 1939,Frenkel and Kontorova proposed a model that describes the structure and dynamics of a crystal lattice in a dislocation core.The FK model has become one of the fundamental models in physics,as it has been proven to reliably describe significant phenomena observed in discrete media.The equation we will examine is a variation of the following form:
The process described involves approximating a nonlinear differential equation through the Taylor method and simplifying it into a linear model.Let's analyze step by step the process from the initial equation to its final form.For small angles, can be approximated through the Taylor series as:
can be approximated through the Taylor series as:
We substitute  in the original equation with the Taylor approximation:
in the original equation with the Taylor approximation:
To map this equation to a linear model,we consider the angles 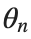 to correspond to displacements
to correspond to displacements 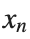 in a mass-spring system.Thus,the equation transforms into:
in a mass-spring system.Thus,the equation transforms into:
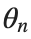 to correspond to displacements
to correspond to displacements We recognize that the term  expresses the nonlinearity of the system,while β is a coefficient corresponding to this nonlinearity,simplifying the expression.The final form of the equation is:
expresses the nonlinearity of the system,while β is a coefficient corresponding to this nonlinearity,simplifying the expression.The final form of the equation is:
The exact value of β depends on the mapping of coefficients in the Taylor approximation and its application to the specific physical problem.Our main goal is to derive results regarding stability and convergence in nonlinear lattices under nonlinear conditions.We will examine the basic characteristics of the discrete Klein-Gordon equation:
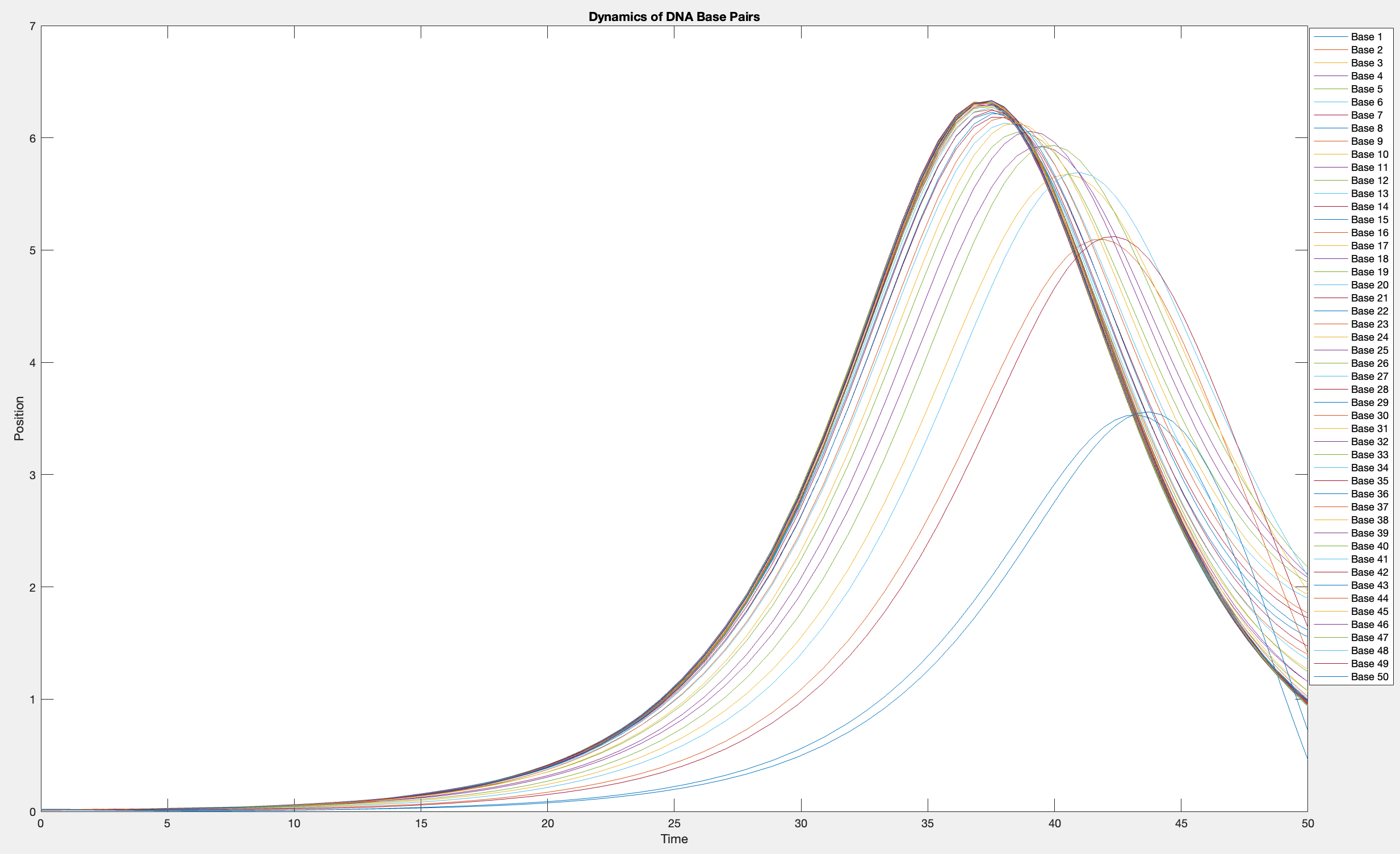
This model is often used to describe the opening of the DNA double helix during processes such as transcription.The model focuses on the transverse motion of the base pairs,which can be represented by a set of coupled nonlinear differential equations.
% Parameters
numBases = 50; % Number of base pairs
kappa = 0.1; % Elasticity constant
omegaD = 0.2; % Frequency term
beta = 0.05; % Nonlinearity coefficient
% Initial conditions
initialPositions = 0.01 + (0.02 - 0.01) * rand(numBases, 1);
initialVelocities = zeros(numBases, 1);
Time span
tSpan = [0 50];
>> % Differential equations
odeFunc = @(t, y) [y(numBases+1:end); ... % velocities
kappa * ([y(2); y(3:numBases); 0] - 2 * y(1:numBases) + [0; y(1:numBases-1)]) + ...
omegaD^2 * (y(1:numBases) - beta * y(1:numBases).^3)]; % accelerations
% Solve the system
[T, Y] = ode45(odeFunc, tSpan, [initialPositions; initialVelocities]);
% Visualization
plot(T, Y(:, 1:numBases))
legend(arrayfun(@(n) sprintf('Base %d', n), 1:numBases, 'UniformOutput', false))
xlabel('Time')
ylabel('Position')
title('Dynamics of DNA Base Pairs')
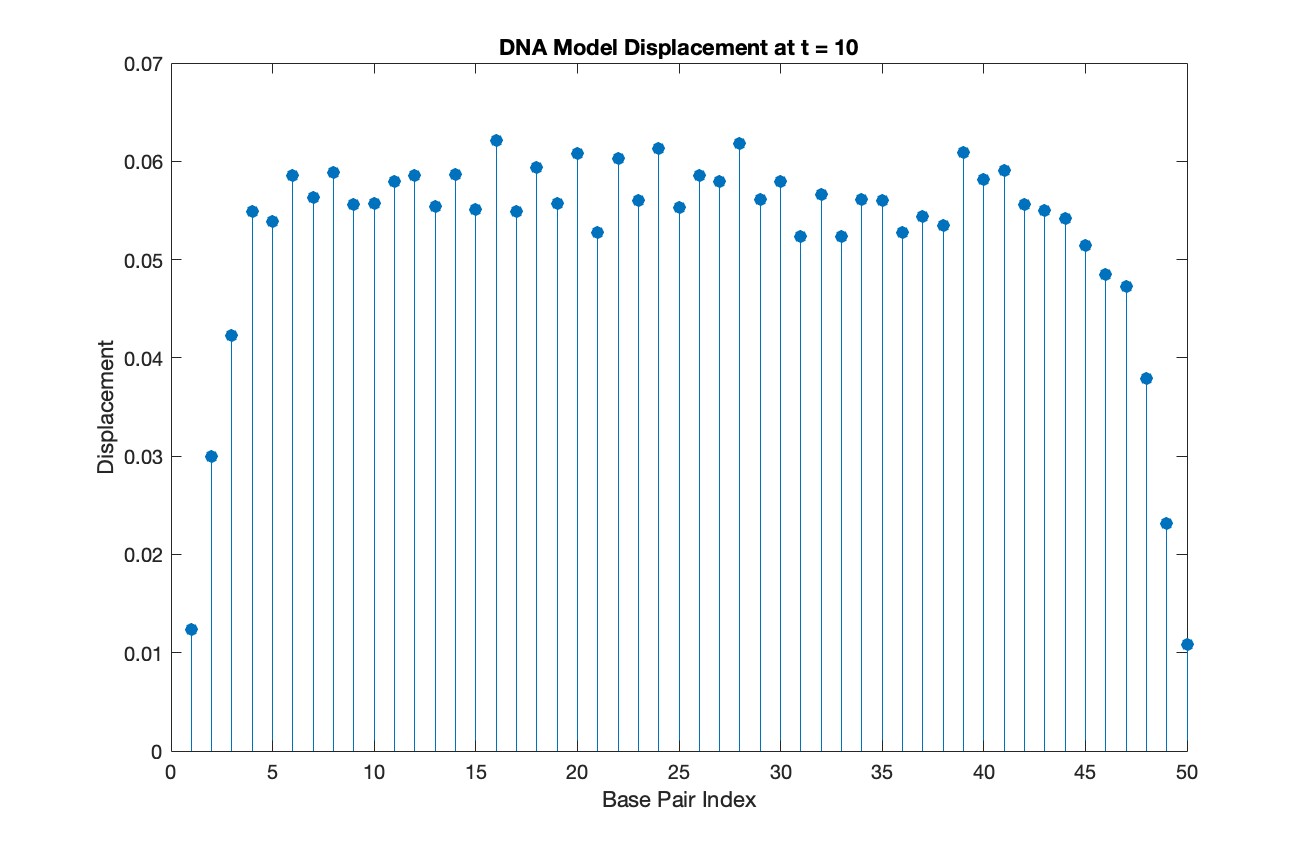
% Choose a specific time for the snapshot
snapshotTime = 10;
% Find the index in T that is closest to the snapshot time
[~, snapshotIndex] = min(abs(T - snapshotTime));
% Extract the solution at the snapshot time
snapshotSolution = Y(snapshotIndex, 1:numBases);
% Generate discrete plot for the DNA model at the snapshot time
figure;
stem(1:numBases, snapshotSolution, 'filled')
title(sprintf('DNA Model Displacement at t = %d', snapshotTime))
xlabel('Base Pair Index')
ylabel('Displacement')
% Time vector for detailed sampling
tDetailed = 0:0.5:50;
% Initialize an empty array to hold the data
data = [];
% Generate the data for 3D plotting
for i = 1:numBases
% Interpolate to get detailed solution data for each base pair
detailedSolution = interp1(T, Y(:, i), tDetailed);
% Concatenate the current base pair's data to the main data array
data = [data; repmat(i, length(tDetailed), 1), tDetailed', detailedSolution'];
end
% 3D Plot
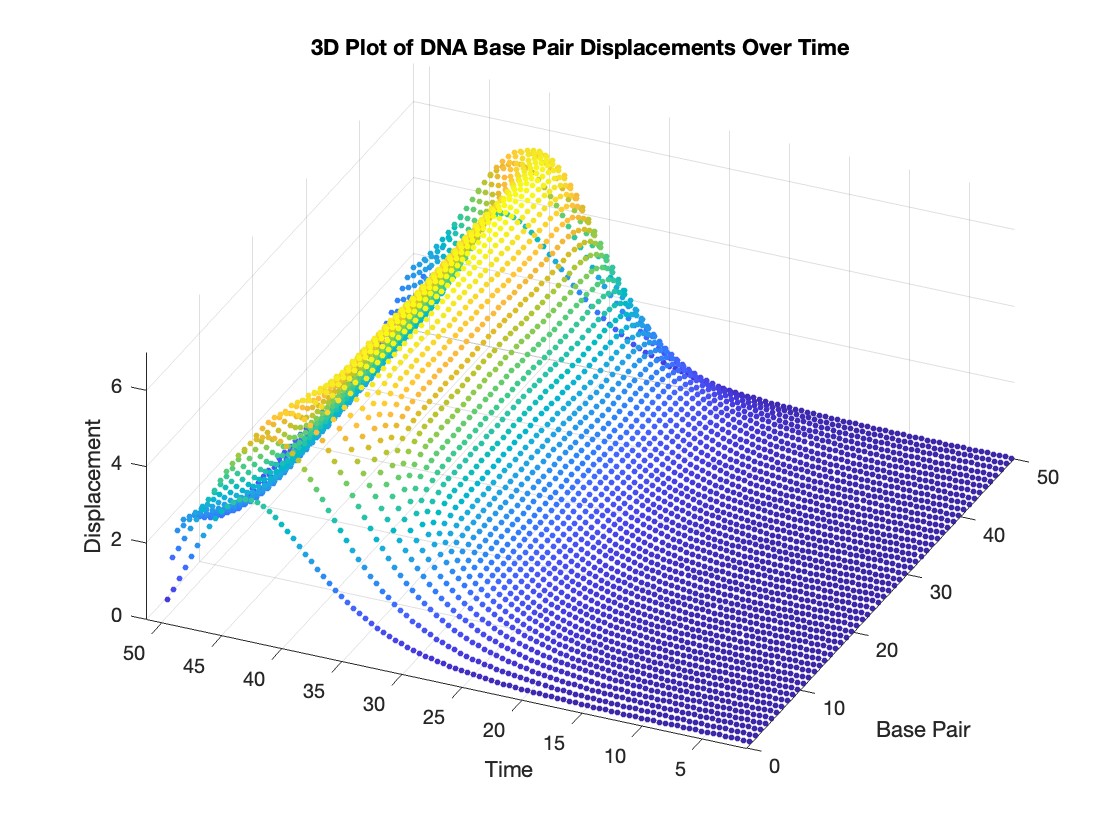
figure;
scatter3(data(:,1), data(:,2), data(:,3), 10, data(:,3), 'filled')
xlabel('Base Pair')
ylabel('Time')
zlabel('Displacement')
title('3D Plot of DNA Base Pair Displacements Over Time')
colormap('rainbow')
colorbar