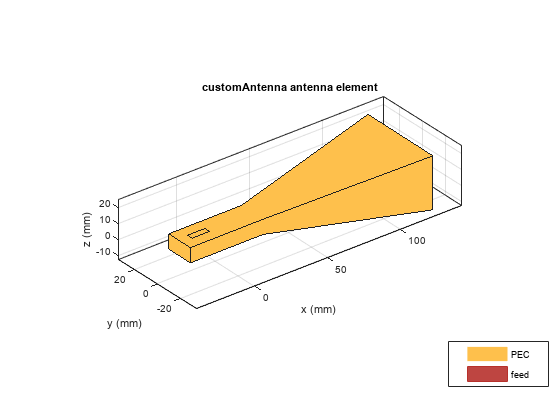
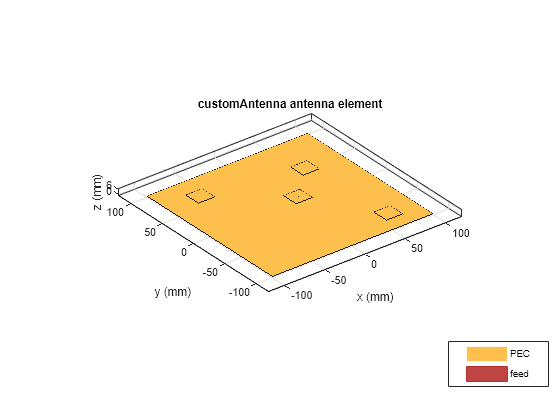
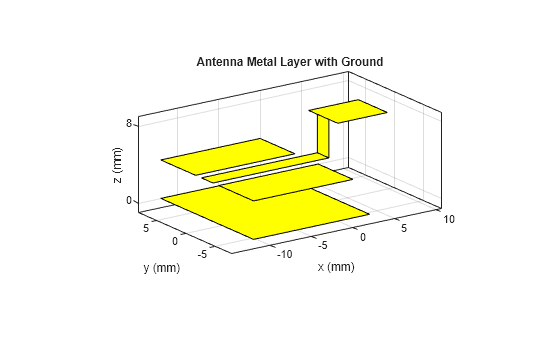
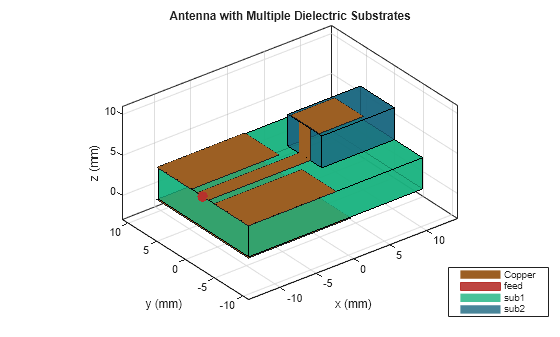
customAntenna
Description
The customAntenna object lets you create an antenna from a custom
shape. You can use the basic 2-D and 3-D shapes from the catalog and perform geometric
operations on them to create a custom shape. You can also use the triangulation or shape
vertices to create custom shapes. You assign a feed to a location on the shape to convert it
into an antenna. Perform port, surface, and field analysis on this antenna. You can use this
antenna as an exciter for the cavity and reflector type backing structures, element in the
arrays, element for the installed antenna analysis, or element in the plane wave excitation
environment.
Creation
Description
c = customAntenna
c = customAntenna(PropertyName=Value)PropertyName is the property
name and Value is the corresponding value. You can specify several
name-value arguments in any order as PropertyName1=Value1,
..., PropertyNameN=ValueN. Properties that you
do not specify retain their default values.
For example, c =
customAntenna(Shape=shape.Rectangle(Metal="Copper")) creates a rectangular
copper shape and default values for other properties.
Properties
Object Functions
axialRatio | Calculate and plot axial ratio of antenna or array |
bandwidth | Calculate and plot absolute bandwidth of antenna or array |
beamwidth | Beamwidth of antenna |
charge | Charge distribution on antenna or array surface |
createFeed | Create feed location for custom antenna |
current | Current distribution on antenna or array surface |
efficiency | Calculate and plot radiation efficiency of antenna or array |
EHfields | Electric and magnetic fields of antennas or embedded electric and magnetic fields of antenna element in arrays |
feedCurrent | Calculate current at feed for antenna or array |
impedance | Calculate and plot input impedance of antenna or scan impedance of array |
info | Display information about antenna, array, or platform |
memoryEstimate | Estimate memory required to solve antenna or array mesh |
mesh | Generate and view mesh for antennas, arrays, and custom shapes |
meshconfig | Change meshing mode of antenna, array, custom antenna, custom array, or custom geometry |
msiwrite | Write antenna or array analysis data to MSI planet file |
optimize | Optimize antenna and array catalog elements using SADEA or TR-SADEA algorithm |
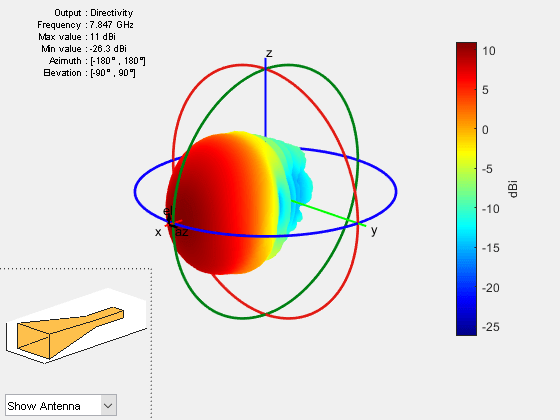
pattern | Plot radiation pattern of antenna, array, or embedded element of array |
patternAzimuth | Azimuth plane radiation pattern of antenna or array |
patternElevation | Elevation plane radiation pattern of antenna or array |
peakRadiation | Calculate and mark maximum radiation points of antenna or array on radiation pattern |
rcs | Calculate and plot monostatic and bistatic radar cross section (RCS) of platform, antenna, or array |
resonantFrequency | Calculate and plot resonant frequency of antenna |
returnLoss | Calculate and plot return loss of antenna or scan return loss of array |
show | Display antenna, array structures, shapes, or platform |
sparameters | Calculate S-parameters for antenna or array |
stlwrite | Write mesh information to STL file |
vswr | Calculate and plot voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) of antenna or array element |
Examples
Version History
Introduced in R2023b
See Also
Objects
Functions
Topics
- Design And Analyze Spherically Capped Biconical Antenna
- Analysis of Ultrawideband Trident Inset-Fed Monopole Antenna with Conical Ground
- Analysis of Edge-Wall Slotted Waveguide Array Antenna for High-Frequency Applications
- Analysis of Basic Delta Loop Antenna over Ground
- Rotate Antennas and Arrays
- Feed Model
- Port Analysis
- Surface Analysis
- Field Analysis
- Far-field Terminologies
- Meshing
- Electrical Length of Antenna